The main characteristics of atmospheric circulation associated with
... and ii) daily (00:00 UTC) 2.5×2.5 grid point values of mean sea-level pressure, 500 hPa geopotential height, 850 hPa and 500 hPa air temperatures and 1000–500 hPa thickness over Europe for the period 1957–2002. 1055 fog events are extracted from the 3-hourly meteorological observations. A specific m ...
... and ii) daily (00:00 UTC) 2.5×2.5 grid point values of mean sea-level pressure, 500 hPa geopotential height, 850 hPa and 500 hPa air temperatures and 1000–500 hPa thickness over Europe for the period 1957–2002. 1055 fog events are extracted from the 3-hourly meteorological observations. A specific m ...
Meteorology Practice Exam
... ____ 33. In July, at middle latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, the day is ____ long and is ____ with each passing day. a. less than 12 hours; getting longer b. less than 12 hours; getting shorter c. more than 12 hours; getting longer d. more than 12 hours; getting shorter ____ 34. Assuming that t ...
... ____ 33. In July, at middle latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, the day is ____ long and is ____ with each passing day. a. less than 12 hours; getting longer b. less than 12 hours; getting shorter c. more than 12 hours; getting longer d. more than 12 hours; getting shorter ____ 34. Assuming that t ...
01 - the role of national meteorological services in the p…
... “The stress of service has hampered the progress of the science. Apart from the opportunity which it gives to what may be called rash speculation or imposture, it places the science in an awkward position. It is the habit of scientific folk who work in the seclusion of a laboratory to draw inference ...
... “The stress of service has hampered the progress of the science. Apart from the opportunity which it gives to what may be called rash speculation or imposture, it places the science in an awkward position. It is the habit of scientific folk who work in the seclusion of a laboratory to draw inference ...
5(2)_Stringer
... more recently the MTSAT. During the 1980’s the standard frequency of provision of satellite images was 3hourly. However an arrangement was in place allowing provision of hourly images during emergencies, for limited durations. The situation most likely to trigger this provision was a tropical cycl ...
... more recently the MTSAT. During the 1980’s the standard frequency of provision of satellite images was 3hourly. However an arrangement was in place allowing provision of hourly images during emergencies, for limited durations. The situation most likely to trigger this provision was a tropical cycl ...
Lay Observers, Telegraph Lines, and Kansas Weather: The Field
... observing networks, probably more than any other kind, have been continuously dependent on a regular geographical distribution of collaborators (Locher 2008). The large geographical scale of weather phenomena, while consistent with presentday notions in meteorology, was not always assumed by local w ...
... observing networks, probably more than any other kind, have been continuously dependent on a regular geographical distribution of collaborators (Locher 2008). The large geographical scale of weather phenomena, while consistent with presentday notions in meteorology, was not always assumed by local w ...
department of defense weather programs
... mission-sensor data to DOD landbased and shipborne terminals located worldwide. The present DMSP satellite series (Block 5D-2) uses an operational linescan system. The visible detectors were selected to optimize distinction among clouds, ground, snow, and water. It uses both stellar and inertial ref ...
... mission-sensor data to DOD landbased and shipborne terminals located worldwide. The present DMSP satellite series (Block 5D-2) uses an operational linescan system. The visible detectors were selected to optimize distinction among clouds, ground, snow, and water. It uses both stellar and inertial ref ...
© 2008 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted.... reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for...
... Program (AWRP) has led to very successful development of forecasts of both convective and winter storms, using heuristic and numerical models, for aviation applications. We have reached a point where there are several overlapping capabilities, and the smorgasbord of choices has become confusing (Fig ...
... Program (AWRP) has led to very successful development of forecasts of both convective and winter storms, using heuristic and numerical models, for aviation applications. We have reached a point where there are several overlapping capabilities, and the smorgasbord of choices has become confusing (Fig ...
18. Atmospheric Boundary Layer
... Because winds in high-pressure regions are relatively light, ABL air lingers over the surface for sufficient time to take on characteristics of that surface. These characteristics include temperature, humidity, pollution, odor, and others. Such ABL air is called an airmass, and was discussed in th ...
... Because winds in high-pressure regions are relatively light, ABL air lingers over the surface for sufficient time to take on characteristics of that surface. These characteristics include temperature, humidity, pollution, odor, and others. Such ABL air is called an airmass, and was discussed in th ...
... data needs to be made operational as soon as possible.) Automated data quality editing of the radar data is critical for removing nonmeteorological returns without changing the real weather signals, and Smalley et al. (2008) have made recent significant improvements. The mosaic process provides moti ...
AOSC 200 Weather and Climate
... Recognizes that weather causing patterns move but assumes the following remain unchanged: • speed • intensity • size • direction Forecast fails if any of our assumptions are no longer valid For example, the system dies out, slows down, etc. ...
... Recognizes that weather causing patterns move but assumes the following remain unchanged: • speed • intensity • size • direction Forecast fails if any of our assumptions are no longer valid For example, the system dies out, slows down, etc. ...
Weather Influences on Carlisle`s Air Quality
... the differences, dashed lines indicate negative differences. Solid lines indicate positive differences. The thick solid line indicates zero difference. Figure 4 shows similar maps for SLP. Patterns in SLP correspond to the upper air patterns. For high PM 2.5 concentration days during winter, spring, ...
... the differences, dashed lines indicate negative differences. Solid lines indicate positive differences. The thick solid line indicates zero difference. Figure 4 shows similar maps for SLP. Patterns in SLP correspond to the upper air patterns. For high PM 2.5 concentration days during winter, spring, ...
synoptic and local weather conditions associated with pm2
... the differences, dashed lines indicate negative differences. Solid lines indicate positive differences. The thick solid line indicates zero difference. Figure 4 shows similar maps for SLP. Patterns in SLP correspond to the upper air patterns. For high PM 2.5 concentration days during winter, spring, ...
... the differences, dashed lines indicate negative differences. Solid lines indicate positive differences. The thick solid line indicates zero difference. Figure 4 shows similar maps for SLP. Patterns in SLP correspond to the upper air patterns. For high PM 2.5 concentration days during winter, spring, ...
MESONET WEATHER CAMP
... the Mesonet for any month. The latest U.S. Drought Monitor map released on June 30 indicates 33 percent of Oklahoma – virtually the entire western third of the state – is experiencing exceptional drought, the highest designation on the drought intensity scale. Severe-to-exceptional drought covers ne ...
... the Mesonet for any month. The latest U.S. Drought Monitor map released on June 30 indicates 33 percent of Oklahoma – virtually the entire western third of the state – is experiencing exceptional drought, the highest designation on the drought intensity scale. Severe-to-exceptional drought covers ne ...
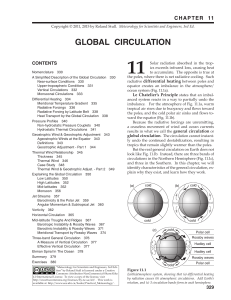
11. Global Circulation
... high pressure along the tops of the ITCZ thunderstorms. Air in this belt blows from the east, due to easterly inertia from the trade winds being carried upward in the thunderstorm convection. Diverging from this belt are winds that blow toward the north in the N. Hemisphere, and toward the south in ...
... high pressure along the tops of the ITCZ thunderstorms. Air in this belt blows from the east, due to easterly inertia from the trade winds being carried upward in the thunderstorm convection. Diverging from this belt are winds that blow toward the north in the N. Hemisphere, and toward the south in ...
En Route Weather Depiction Benefits of the NEXRAD Vertically
... to detect the initial development of storm cells at heights generally between 15-20 kft. Conversely, limited basescan sampling of BREF data precludes any detection of new cell growth within 90 miles of the radar. The relative impact of hazardous convective weather represented by each weather depicti ...
... to detect the initial development of storm cells at heights generally between 15-20 kft. Conversely, limited basescan sampling of BREF data precludes any detection of new cell growth within 90 miles of the radar. The relative impact of hazardous convective weather represented by each weather depicti ...
5.2 EN ROUTE WEATHER DEPICTION BENEFITS OF THE NEXRAD VERTICALLY
... to detect the initial development of storm cells at heights generally between 15-20 kft. Conversely, limited basescan sampling of BREF data precludes any detection of new cell growth within 90 miles of the radar. The relative impact of hazardous convective weather represented by each weather depicti ...
... to detect the initial development of storm cells at heights generally between 15-20 kft. Conversely, limited basescan sampling of BREF data precludes any detection of new cell growth within 90 miles of the radar. The relative impact of hazardous convective weather represented by each weather depicti ...
Met 61 - San Jose State University
... – Isotherms (lines of constant temperature) are parallel with isobars. If flow is geostrophic (parallel to isobars), no temperature advection can occur. ...
... – Isotherms (lines of constant temperature) are parallel with isobars. If flow is geostrophic (parallel to isobars), no temperature advection can occur. ...
answer list - Big Sioux Water Festival
... The ultimate source of energy for earth’s weather system is _____ ...
... The ultimate source of energy for earth’s weather system is _____ ...
A Study of the Nocturnal Boundary Layer Inversion in the Yampa
... to tell if these are typical values of inversion strength or not. The conditions may not have been favorable to form strong inversions. Winds were also not as calm as they could have been which may have helped disrupt formation. Also, as mentioned above, a residential population living in the Yampa ...
... to tell if these are typical values of inversion strength or not. The conditions may not have been favorable to form strong inversions. Winds were also not as calm as they could have been which may have helped disrupt formation. Also, as mentioned above, a residential population living in the Yampa ...
Tim Canty - University of Maryland
... Line of storms (squall line) forms along cold front Updraft brings in warm, humid air Downdraft spreads cool air along the surface http://earthsky.org/earth/what-you-need-to-know-about-derechos Copyright © 2016 University of Maryland This material may not be reproduced or redistributed, in whole or ...
... Line of storms (squall line) forms along cold front Updraft brings in warm, humid air Downdraft spreads cool air along the surface http://earthsky.org/earth/what-you-need-to-know-about-derechos Copyright © 2016 University of Maryland This material may not be reproduced or redistributed, in whole or ...
ITU/WMO Seminar “Use of Radio Spectrum for Meteorology
... Report ITU-R M.2136, Theoretical Analysis and Testing Results Pertaining to the Determination of Relevant Interference Protection Criteria of Ground-Based Meteorological radars, ITU 2008 Report ITU-R M.2112, Compatibility/Sharing if Airport Surveillance and Meteorological Radar wit IMT Systems withi ...
... Report ITU-R M.2136, Theoretical Analysis and Testing Results Pertaining to the Determination of Relevant Interference Protection Criteria of Ground-Based Meteorological radars, ITU 2008 Report ITU-R M.2112, Compatibility/Sharing if Airport Surveillance and Meteorological Radar wit IMT Systems withi ...
Severe and Unusual Weather ESAS 1115
... The addition of vertical wind shear allows for new updrafts to reach maturity in some organized fashion Even though each cell moves with the mean wind of the cloud-bearing layer, new updrafts form where low-level convergence is strongest and is enhanced by the vertical wind shear When updrafts initi ...
... The addition of vertical wind shear allows for new updrafts to reach maturity in some organized fashion Even though each cell moves with the mean wind of the cloud-bearing layer, new updrafts form where low-level convergence is strongest and is enhanced by the vertical wind shear When updrafts initi ...
Weather Stations for Meteorological Applications
... The Mean-Time-Between-Failure (MTBF) values of Vaisala Automatic Weather Stations are high – more than 20,000 hours. When weather-station field checking is necessary, Vaisala’s hand-held instruments make it quick and easy. The meteorological data from weather stations can be integrated with data fro ...
... The Mean-Time-Between-Failure (MTBF) values of Vaisala Automatic Weather Stations are high – more than 20,000 hours. When weather-station field checking is necessary, Vaisala’s hand-held instruments make it quick and easy. The meteorological data from weather stations can be integrated with data fro ...
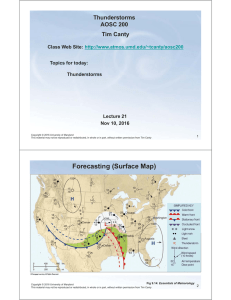
Surface weather analysis

Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea level pressure, temperature, and cloud cover onto a geographical map to help find synoptic scale features such as weather fronts.The first weather maps in the 19th century were drawn well after the fact to help devise a theory on storm systems. After the advent of the telegraph, simultaneous surface weather observations became possible for the first time, and beginning in the late 1840s, the Smithsonian Institution became the first organization to draw real-time surface analyses. Use of surface analyses began first in the United States, spreading worldwide during the 1870s. Use of the Norwegian cyclone model for frontal analysis began in the late 1910s across Europe, with its use finally spreading to the United States during World War II.Surface weather analyses have special symbols that show frontal systems, cloud cover, precipitation, or other important information. For example, an H may represent high pressure, implying good and fair weather. An L on the other hand may represent low pressure, which frequently accompanies precipitation. Various symbols are used not just for frontal zones and other surface boundaries on weather maps, but also to depict the present weather at various locations on the weather map. Areas of precipitation help determine the frontal type and location.