Galactic Evolution:
... times in the Milky Way with the same metallicity as the Sun will not necessarily form habitable Earth like planets. As a result of the radial Galactic metafficity gradient, the outer limit of the GHZ is set primarily by the minimum required metallicity to build large terrestrial planets. Regions of ...
... times in the Milky Way with the same metallicity as the Sun will not necessarily form habitable Earth like planets. As a result of the radial Galactic metafficity gradient, the outer limit of the GHZ is set primarily by the minimum required metallicity to build large terrestrial planets. Regions of ...
The Astrobiology Primer
... A blob of gas several times the size of our Solar System, called a pre-stellar core, contracts under its own gravity to form a protostar. Half of the system’s initial gravitational energy disperses through radiation while the other half is converted into heat. The temperature of the core begins to r ...
... A blob of gas several times the size of our Solar System, called a pre-stellar core, contracts under its own gravity to form a protostar. Half of the system’s initial gravitational energy disperses through radiation while the other half is converted into heat. The temperature of the core begins to r ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Lab - Introduction to Astronomy
... learner can specify the differences and similarities among the meteoroids, asteroids, comets and small bodies within our solar system ...
... learner can specify the differences and similarities among the meteoroids, asteroids, comets and small bodies within our solar system ...
Evolution of Warm Debris Around Sun-like Stars: Clues to Terrestrial
... for our solar system, and that this fraction does not strongly depend on environment. INTRODUCTION: Are solar systems like our own common or rare in the Milky Way galaxy? The answer to this question depends on what aspect of our solar system one is comparing against. Gas and dust rich circumstellar ...
... for our solar system, and that this fraction does not strongly depend on environment. INTRODUCTION: Are solar systems like our own common or rare in the Milky Way galaxy? The answer to this question depends on what aspect of our solar system one is comparing against. Gas and dust rich circumstellar ...
Astronomy Club
... Our earth and other planets revolve around the sun in fixed parallel orbits, except Mercury and Pluto. These orbits have an angle of 7 &17 degrees with respect to the earth's orbit respectively. But comets emerging out of the ‘Ourt Cloud’ have disordered orbit. Comets are mainly of two types. Those ...
... Our earth and other planets revolve around the sun in fixed parallel orbits, except Mercury and Pluto. These orbits have an angle of 7 &17 degrees with respect to the earth's orbit respectively. But comets emerging out of the ‘Ourt Cloud’ have disordered orbit. Comets are mainly of two types. Those ...
Binaries
... Gravitational Force = Centripetal Force Me = v2Rm/G Similarly we can calculate the Sun’s mass using Earth’s orbit. We need at least two object rotating around each other to calculate the mass of them. ...
... Gravitational Force = Centripetal Force Me = v2Rm/G Similarly we can calculate the Sun’s mass using Earth’s orbit. We need at least two object rotating around each other to calculate the mass of them. ...
Shining Light on the Stars: The Hertzsprung-Russell
... Remember, the HR Diagram shows the temperatures of stars versus their luminosities. Our Sun is located here on the diagram, and as before, the 122 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are to ...
... Remember, the HR Diagram shows the temperatures of stars versus their luminosities. Our Sun is located here on the diagram, and as before, the 122 brightest stars visible in the night sky from Earth are located here. But what about all the stars in the nearby solar neighborhood, most of which are to ...
File
... *The collapse of a white dwarf is different from the collapse of a massive star because the core of the white dwarf contains usable fuel. ...
... *The collapse of a white dwarf is different from the collapse of a massive star because the core of the white dwarf contains usable fuel. ...
The Search for Exoplanets - Worcester Polytechnic Institute
... being large gas giants like Jupiter or Saturn, while others are small and rocky, like Earth and Mars. Exoplanets are almost always found to be gravitationally bound to a stellar system, however, there is at least some evidence to suggest that there may be a small minority of “rogue exoplanets” that ...
... being large gas giants like Jupiter or Saturn, while others are small and rocky, like Earth and Mars. Exoplanets are almost always found to be gravitationally bound to a stellar system, however, there is at least some evidence to suggest that there may be a small minority of “rogue exoplanets” that ...
Constraints on the exosphere of CoRoT-7b*
... To some extent, the local environment of CoRoT-7b is an extreme version of Mercury, as its distance to the host star is 23 times smaller than that of Mercury. Hence the planet receives about 250–370 times more radiation than Mercury. In addition, the stellar wind is more intensive than at Mercury, b ...
... To some extent, the local environment of CoRoT-7b is an extreme version of Mercury, as its distance to the host star is 23 times smaller than that of Mercury. Hence the planet receives about 250–370 times more radiation than Mercury. In addition, the stellar wind is more intensive than at Mercury, b ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... expanding and contracting periodically. Astronomers can use the period of the star (or the time it takes to vary) and its luminosity to measure the distance to the star. The nuclear fusion reactions continue until all the helium in the core has been converted to carbon and oxygen. The nuclear reacti ...
... expanding and contracting periodically. Astronomers can use the period of the star (or the time it takes to vary) and its luminosity to measure the distance to the star. The nuclear fusion reactions continue until all the helium in the core has been converted to carbon and oxygen. The nuclear reacti ...
doc Brandon`s (Precise Final Rev.)
... Gravity was not great enough on the moon or Mars to hold the water onto its surface ...
... Gravity was not great enough on the moon or Mars to hold the water onto its surface ...
assessing the massive young sun hypothesis to solve the warm
... above the freezing point of water. However, laboratory studies of CO2 cloud formation under Martian conditions seem to suggest that the types of clouds that could form on Mars, even with a CO2 atmosphere with pressures as high as 5 bars, would not warm the planet above the freezing point of water (G ...
... above the freezing point of water. However, laboratory studies of CO2 cloud formation under Martian conditions seem to suggest that the types of clouds that could form on Mars, even with a CO2 atmosphere with pressures as high as 5 bars, would not warm the planet above the freezing point of water (G ...
Scale in the Solar System
... times. You could fly from Los Angeles to New York and back every day and it would still take you 20 years to travel that far. Jupiter is ten times farther away. Students have a hard time dealing with such huge numbers. We need a simpler way to think about the solar system. It involves reducing the s ...
... times. You could fly from Los Angeles to New York and back every day and it would still take you 20 years to travel that far. Jupiter is ten times farther away. Students have a hard time dealing with such huge numbers. We need a simpler way to think about the solar system. It involves reducing the s ...
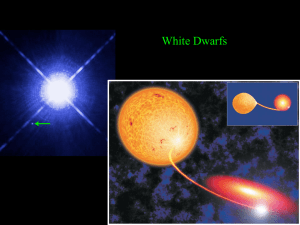
white dwarf supernova
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
The Resounding Universe
... disciplines. Sight and hearing are complementary senses: eyes are made for looking at celestial bodies and ears to follow their harmonious motions. Aristotle (c. 384 BC – c. 322 BC) explains why mortals cannot hear these sounds. In fact, a sound or a noise can be perceived only when in contrast with ...
... disciplines. Sight and hearing are complementary senses: eyes are made for looking at celestial bodies and ears to follow their harmonious motions. Aristotle (c. 384 BC – c. 322 BC) explains why mortals cannot hear these sounds. In fact, a sound or a noise can be perceived only when in contrast with ...
Mankind`s Purple Dawn
... red-light spectrum rather than the harsh and bright ultraviolet light of the Sun. So it is not inconceivable that life on Earth as we know it could have existed, and even flourished, in a predominantly nocturnal world, provided there was some form of radiated red-spectrum light or energy. In fact, m ...
... red-light spectrum rather than the harsh and bright ultraviolet light of the Sun. So it is not inconceivable that life on Earth as we know it could have existed, and even flourished, in a predominantly nocturnal world, provided there was some form of radiated red-spectrum light or energy. In fact, m ...
Earth Science Standards-with explanations
... understanding of accepted scientific evidence. To promote scientific literacy, school libraries should try to keep their collections up to date. Students can benefit from the significant amount of new data gained from space exploration during the past 20 years. Earth' s Place in the Universe (Stars, ...
... understanding of accepted scientific evidence. To promote scientific literacy, school libraries should try to keep their collections up to date. Students can benefit from the significant amount of new data gained from space exploration during the past 20 years. Earth' s Place in the Universe (Stars, ...
astronomy - Jiri Brezina Teaching
... formed and attitudes. The scientific method has evolved over many centuries and has now come to be described in terms of a well-organized and well-defined series of steps (3). But what about the attitudes (5-7)? Does science produce truth? The scientist strives to arrive at truth but the way to it m ...
... formed and attitudes. The scientific method has evolved over many centuries and has now come to be described in terms of a well-organized and well-defined series of steps (3). But what about the attitudes (5-7)? Does science produce truth? The scientist strives to arrive at truth but the way to it m ...
sc engl 3 mini The Sun test
... (1) The sun is a bright star made of hot gases that burn all the time. The main gas that makes up the sun is called hydrogen. ...
... (1) The sun is a bright star made of hot gases that burn all the time. The main gas that makes up the sun is called hydrogen. ...
The extreme physical properties of the CoRoT-7b super
... silicate rocks and the formation of a lava ocean. These possible features of CoRoT-7b could be common to many small and hot planets, including the recently discovered Kepler-10b. They define a new class of objects that we propose to name ’’Lava-ocean planets’’. ...
... silicate rocks and the formation of a lava ocean. These possible features of CoRoT-7b could be common to many small and hot planets, including the recently discovered Kepler-10b. They define a new class of objects that we propose to name ’’Lava-ocean planets’’. ...
Earth Science Teaching Curriculum
... side is super-heated by the Sun, but at night, temperatures drop hundreds of degrees below freezing. Ice may even exist in the craters. Mercury's egg-shaped orbit takes it around the Sun every 88 days. There is no water on Mercury. But there might be a little ice in deep craters. Mercury has cliffs ...
... side is super-heated by the Sun, but at night, temperatures drop hundreds of degrees below freezing. Ice may even exist in the craters. Mercury's egg-shaped orbit takes it around the Sun every 88 days. There is no water on Mercury. But there might be a little ice in deep craters. Mercury has cliffs ...
Finish up Sun and begin Stars of the Sun Test 1 Study
... within same “solar system” •Alpha Centauri and Procyon are close binary systems. Proxima Centauri is a red dwarf which probably orbits Alpha Centauri every 500,000 years PHYS 162 ...
... within same “solar system” •Alpha Centauri and Procyon are close binary systems. Proxima Centauri is a red dwarf which probably orbits Alpha Centauri every 500,000 years PHYS 162 ...
“And God Said, Let There Be Lights in the Firmament of Heaven”
... although we do not understand the specifics of the processes by which stars produce hot coronas and accelerate energetic particles we have identified the essential ingredients of these processes those ingredients are ions rotation and internal motion all stars possess the first two and most possess ...
... although we do not understand the specifics of the processes by which stars produce hot coronas and accelerate energetic particles we have identified the essential ingredients of these processes those ingredients are ions rotation and internal motion all stars possess the first two and most possess ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.