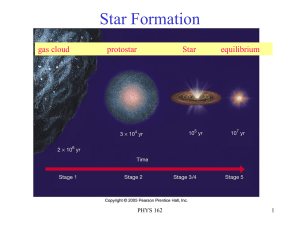
Lecture 15 Star Formation and Evolution 3/7
... Nature. Need to have Be+He reaction occur before the Be decays slows up reaction Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
... Nature. Need to have Be+He reaction occur before the Be decays slows up reaction Larger electric repulsion than p-p as larger electric charge (2 for He and 4 for Be). Therefore need about 100,000,000 degrees K for He burning Stars like our Sun remain main sequence longer due to this PHYS 162 ...
A Closer Earth and the Faint Young Sun Paradox
... paleoclimatology [7], the greenhouse effect [8], ancient cosmic ray flux [9], solar activity [10] and solar wind [11], it not only refuses to go away [2,12,13], but, rather, it becomes even more severe [14] in the view of some recent studies. This is not to claim that climatic solutions are nowadays ...
... paleoclimatology [7], the greenhouse effect [8], ancient cosmic ray flux [9], solar activity [10] and solar wind [11], it not only refuses to go away [2,12,13], but, rather, it becomes even more severe [14] in the view of some recent studies. This is not to claim that climatic solutions are nowadays ...
ppt - MIT Haystack Observatory
... flaring introduces variability in correlated Lx-Lr which increases the spread , but generally falls within the order of magnitude range of GB relation radio variability appears to be a larger factor than X-ray variability there are situations where even these well-understood (?!) systems belie our e ...
... flaring introduces variability in correlated Lx-Lr which increases the spread , but generally falls within the order of magnitude range of GB relation radio variability appears to be a larger factor than X-ray variability there are situations where even these well-understood (?!) systems belie our e ...
15_Uranus Litho.indd
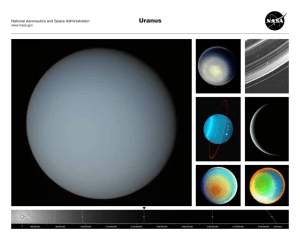
... Uranus was discovered in 1781 by astronomer William Herschel. The seventh planet from the Sun is so distant that it takes 84 years to complete one orbit. Uranus, with no solid surface, is one of the gas giant planets (the others are Jupiter, Saturn, and Neptune). ...
... Uranus was discovered in 1781 by astronomer William Herschel. The seventh planet from the Sun is so distant that it takes 84 years to complete one orbit. Uranus, with no solid surface, is one of the gas giant planets (the others are Jupiter, Saturn, and Neptune). ...
Exploring the Solar System Jeopardy!
... Most asteroids orbit along the “main asteroid belt.” Between what two planets does this main belt exist? ...
... Most asteroids orbit along the “main asteroid belt.” Between what two planets does this main belt exist? ...
uniview glossary - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... the size of Earth, it rotates in a day of 24.5 hours, and obits the sun in 687 Earth days (about 1.9 or 2 years). The daytime temperature starts at minus 21 degrees F. and rises to about 32 degrees F. Nights can get to minus 191 degrees F. The Valles Marineris Canyon, or Mars’ Grand Canyon, stretche ...
... the size of Earth, it rotates in a day of 24.5 hours, and obits the sun in 687 Earth days (about 1.9 or 2 years). The daytime temperature starts at minus 21 degrees F. and rises to about 32 degrees F. Nights can get to minus 191 degrees F. The Valles Marineris Canyon, or Mars’ Grand Canyon, stretche ...
1 Marsbugs: The Electronic Astrobiology Newsletter, Volume 12
... This artist's concept shows what a fiery hot star and its close-knit planetary companion might look close up if viewed in visible (left) and infrared light. In visible light, a star shines brilliantly, overwhelming the little light that is reflected by its planet. In infrared, a star is less blindin ...
... This artist's concept shows what a fiery hot star and its close-knit planetary companion might look close up if viewed in visible (left) and infrared light. In visible light, a star shines brilliantly, overwhelming the little light that is reflected by its planet. In infrared, a star is less blindin ...
Title: Abiotic Ozone and Oxygen in Atmospheres Similar to Prebiotic
... above missions might discriminate between any false positives and the true positives generated by life. We do not anticipate direct abiotic sources of these gases, such as from volcanoes or from reactions at the sea floors of extrasolar planets. Thus, the primary abiotic source of both of these gase ...
... above missions might discriminate between any false positives and the true positives generated by life. We do not anticipate direct abiotic sources of these gases, such as from volcanoes or from reactions at the sea floors of extrasolar planets. Thus, the primary abiotic source of both of these gase ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
... These large stars have diameters between 10X and 100X that of the Sun. If the star is a Super Giant, their diameters can be up to 1000X of the Sun. A late-life stage sub-species star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation that can be only seen when the beam of emission is pointing toward the ...
black holes activity
... The Sun in Bulk A.How does the text describe the structure of the Sun? -the Sun is __________ sized, temperature, mass, radius and composition, making it easy for life to flourish on ____________ B.What happens in each layer of the Sun? -_______________- where nuclear fusion takes place which powers ...
... The Sun in Bulk A.How does the text describe the structure of the Sun? -the Sun is __________ sized, temperature, mass, radius and composition, making it easy for life to flourish on ____________ B.What happens in each layer of the Sun? -_______________- where nuclear fusion takes place which powers ...
Science - State Goal 12: Understand the fundamental concepts
... STATE GOAL 12: Understand the fundamental concepts, principles and interconnections of the life, physical and earth/space sciences. Why This Goal Is Important: This goal is comprised of key concepts and principles in the life, physical and earth/space sciences that have considerable explanatory and ...
... STATE GOAL 12: Understand the fundamental concepts, principles and interconnections of the life, physical and earth/space sciences. Why This Goal Is Important: This goal is comprised of key concepts and principles in the life, physical and earth/space sciences that have considerable explanatory and ...
ON THE FORMATION OF MASSIVE STELLAR CLUSTERS
... Richtler 2000 and Larsen 1999). This star-forming activity in which masses similar to the total gas content found in galactic giant molecular clouds (massive elongated structures that extend over 100 pc in length) are turned into stars, all in a very small volume (∼ few pc) much smaller than the typ ...
... Richtler 2000 and Larsen 1999). This star-forming activity in which masses similar to the total gas content found in galactic giant molecular clouds (massive elongated structures that extend over 100 pc in length) are turned into stars, all in a very small volume (∼ few pc) much smaller than the typ ...
ASTR 1010 Homework Solutions
... AU. (b) The distance between perihelion and aphelion equals the major-axis, i.e., two times the semi-major axis or 2a. So, if the comet is 31.5 AU from the Sun at aphelion, then it must be (2 × 16 AU) – 31.5 AU = 0.5 AU from the Sun at perihelion. 43. Newton's law of universal gravitation states tha ...
... AU. (b) The distance between perihelion and aphelion equals the major-axis, i.e., two times the semi-major axis or 2a. So, if the comet is 31.5 AU from the Sun at aphelion, then it must be (2 × 16 AU) – 31.5 AU = 0.5 AU from the Sun at perihelion. 43. Newton's law of universal gravitation states tha ...
Sample pages 1 PDF
... meteorite that resemble products of life. Nagy and his team performed their analysis on a sample obtained from the Museum of Natural History in New York. They took incredible care to avoid the possibility of contamination. Using a mass spectrometer, they identified various hydrocarbons including par ...
... meteorite that resemble products of life. Nagy and his team performed their analysis on a sample obtained from the Museum of Natural History in New York. They took incredible care to avoid the possibility of contamination. Using a mass spectrometer, they identified various hydrocarbons including par ...
Image Credit: NASA,ESA, HEIC, Hubble
... Where do we expect to find stars on this plot? Anywhere? In some places and not others? ...
... Where do we expect to find stars on this plot? Anywhere? In some places and not others? ...
Pluto
... Research your astronomical object on the internet or in the library. Your poster must be at least 12” x 18”. I can provide you with a 12” x 18” poster board or you may supply your own. Your poster will be worth 50 points as follows: ...
... Research your astronomical object on the internet or in the library. Your poster must be at least 12” x 18”. I can provide you with a 12” x 18” poster board or you may supply your own. Your poster will be worth 50 points as follows: ...
p35-KIDS_Layout 1
... is close enough to Neptune to be locked into asynchronous rotation, and it is slowly spiralling inward because of tidal acceleration. It will eventually be torn apart, in about 3.6 billion years, when it reaches the Roche limit. In 1989, Triton was the coldest object that had yet been measured in th ...
... is close enough to Neptune to be locked into asynchronous rotation, and it is slowly spiralling inward because of tidal acceleration. It will eventually be torn apart, in about 3.6 billion years, when it reaches the Roche limit. In 1989, Triton was the coldest object that had yet been measured in th ...
Open Houses at the Campus Observatory Astronomical Horizons Lecture
... • Baseballs hit walls faster & more often • Pressure is higher ...
... • Baseballs hit walls faster & more often • Pressure is higher ...
Convocatory Topics 7th Grade TOPICS
... Define hydrosphere and explain where it is found. Define cryosphere, name the form solid water takes. Explain atmosphere and its size and composition. Define and explain biosphere. Describe how Earth’s spheres interact. Give examples of interactions among Earth’s spheres. Identify the main source of ...
... Define hydrosphere and explain where it is found. Define cryosphere, name the form solid water takes. Explain atmosphere and its size and composition. Define and explain biosphere. Describe how Earth’s spheres interact. Give examples of interactions among Earth’s spheres. Identify the main source of ...
Earth Science Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... A) cylindrical B) polar C) conic D) polyconic 48. Compared to other stars in the Hertzsprung-Russell main sequence, the sun in size and color is A) small and red B) medium and red C) medium and yellow D) large and yellow 49. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that the Earth A) has a magnetic fiel ...
... A) cylindrical B) polar C) conic D) polyconic 48. Compared to other stars in the Hertzsprung-Russell main sequence, the sun in size and color is A) small and red B) medium and red C) medium and yellow D) large and yellow 49. The Coriolis effect provides evidence that the Earth A) has a magnetic fiel ...
Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli) Chapter 33
... 5) In terms of the mass M of our sun, what is the Chandrasekhar limit of stellar mass, below which a star will eventually collapse into a white dwarf? A) 0.8 M B) 1.2 M C) 1.4 M D) 1.9 M Answer: C Var: 1 ...
... 5) In terms of the mass M of our sun, what is the Chandrasekhar limit of stellar mass, below which a star will eventually collapse into a white dwarf? A) 0.8 M B) 1.2 M C) 1.4 M D) 1.9 M Answer: C Var: 1 ...
The Little Star That Could - Challenger Learning Center
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
The Parallax Activity: Measuring the Distances to
... 1. The distance of Earth to the sun (one AU) is very small compared to interstellar distances, so parallax angles are smaller than one arcsecond, which is 1/3600 of a degree. 2. An alternative distance measurement for stars used by most astronomers is the ...
... 1. The distance of Earth to the sun (one AU) is very small compared to interstellar distances, so parallax angles are smaller than one arcsecond, which is 1/3600 of a degree. 2. An alternative distance measurement for stars used by most astronomers is the ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.