pkt 14 Astrophysics
... Constellations - A group of stars in a recognizable pattern that appear to be near each other in space. Nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas and plasma. It is the first stage of a star's cycle but it can also refer to the remains of a dying star (planetary nebula). Originally nebula ...
... Constellations - A group of stars in a recognizable pattern that appear to be near each other in space. Nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas and plasma. It is the first stage of a star's cycle but it can also refer to the remains of a dying star (planetary nebula). Originally nebula ...
4. The Solar System
... 4.4 Planets Beyond the Solar System • This plot shows the masses of many extrasolar planets discovered so far. Most have masses closer to the mass of Jupiter or Neptune than that of Earth. ...
... 4.4 Planets Beyond the Solar System • This plot shows the masses of many extrasolar planets discovered so far. Most have masses closer to the mass of Jupiter or Neptune than that of Earth. ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
... mass. Stars with greater mass have a greater gravitational attraction – causing the core temperature to be greater, which in turn increases the rate of nuclear fusion and decreases the star’s time on the main sequence. Likewise, lower mass stars have lesser rates of fusion and greater amounts of tim ...
Front Matter - Assets - Cambridge University Press
... The second edition of The Cambridge Guide to the Solar System brings this comprehensive description of the planets and moons up to date, by extending it to include fascinating new discoveries made during the previous decade. As with the first edition, it is written at an introductory level appropriat ...
... The second edition of The Cambridge Guide to the Solar System brings this comprehensive description of the planets and moons up to date, by extending it to include fascinating new discoveries made during the previous decade. As with the first edition, it is written at an introductory level appropriat ...
FutureEnvironments
... who attempts to hold his breath must make a Constitution check (DC 15) every round; the DC increases by 1 each round, and on a successful check the character takes 1 point of Constitution damage (from the pressure on the linings of his lungs). If the check fails, or when the character simply stops h ...
... who attempts to hold his breath must make a Constitution check (DC 15) every round; the DC increases by 1 each round, and on a successful check the character takes 1 point of Constitution damage (from the pressure on the linings of his lungs). If the check fails, or when the character simply stops h ...
A sound nebula: the origin of the Solar System in the field of a
... processes is beyond the scope of this article; we note here only that the power of the explosion would have been large enough for the shock wave to spread all over the pre-solar nebula2 . A long time observed active processes, such as jets and outflows associated with star formation, e.g. [10]-[18], ...
... processes is beyond the scope of this article; we note here only that the power of the explosion would have been large enough for the shock wave to spread all over the pre-solar nebula2 . A long time observed active processes, such as jets and outflows associated with star formation, e.g. [10]-[18], ...
BASIC PROPERTIES of STARS - 2
... 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant position? (A 850; B 1700; C 2550; D 3400 seconds) If (1) is 300 seconds and (2) is 1700 seconds, what is 1 AU in km? ...
... 105 km/s (A 150; B 200; C 300; D 400 seconds) (2) What is the approximate time to get a return signal from Venus when Venus is at its most distant position? (A 850; B 1700; C 2550; D 3400 seconds) If (1) is 300 seconds and (2) is 1700 seconds, what is 1 AU in km? ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
... Composition unknown. Probably mostly exotic particles that don't interact with ordinary matter at all (except gravity). Some may be brown dwarfs, dead white dwarfs … Most likely it's a dark halo surrounding the Milky Way. ...
Lecture 15, PPT version
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
... In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase of stellar evolution. When the core helium supply is exhausted, the additional mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would ...
... In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase of stellar evolution. When the core helium supply is exhausted, the additional mass allows stellar collapse to take place and the outer layers to reignite. A cross section through the star at this point would ...
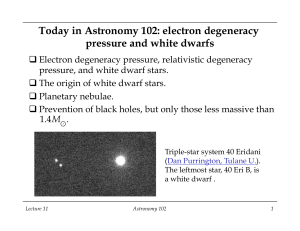
Today in Astronomy 102: electron degeneracy pressure and white
... he invented it (1926), to white dwarf stars. His result: q Stars supported by degeneracy pressure instead of gas pressure would have sizes close to that determined from astronomical observations of Sirius B. Soon thereafter, Edmund Stoner (1929) noticed that this result implies a peculiar relation b ...
... he invented it (1926), to white dwarf stars. His result: q Stars supported by degeneracy pressure instead of gas pressure would have sizes close to that determined from astronomical observations of Sirius B. Soon thereafter, Edmund Stoner (1929) noticed that this result implies a peculiar relation b ...
KS1 Education Guide - Immersive Theatres
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
... (From the Merriam-Webster Dictionary) Average – (adjective) being about midway between extremes, not out of the ordinary: Common Planet – any of the large bodies that revolve around the sun in the solar system Star – a: a natural luminous body visible in the sky especially at night b: a self-luminou ...
featured in the Arizona Daily Star
... they can’t visit a star to extract a sample of it. But there are ways to get a piece of a star and study it in the laboratory. That’s what I do — I study pieces of ancient stardust. But instead of using a telescope, I use a microscope to look for stardust inside meteorites. Over their lifetimes, sta ...
... they can’t visit a star to extract a sample of it. But there are ways to get a piece of a star and study it in the laboratory. That’s what I do — I study pieces of ancient stardust. But instead of using a telescope, I use a microscope to look for stardust inside meteorites. Over their lifetimes, sta ...
EEn.1.1 Explain the Earth`s role as a body in space. EEn
... • Explain planetary orbits, especially that of the Earth, using Kepler’s laws. • Explain barycenterthe point between two objects where they balance each other (For example, it is the center of mass where two or more celestial bodies orbit each other. When a moon orbits a planet, or a planet orbi ...
... • Explain planetary orbits, especially that of the Earth, using Kepler’s laws. • Explain barycenterthe point between two objects where they balance each other (For example, it is the center of mass where two or more celestial bodies orbit each other. When a moon orbits a planet, or a planet orbi ...
Directions: your answers to the questions below. Check your answers... and then go ...
... 16. During a total lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks all of the Sun's light that would usually reflect off the Moon. 17. The phase that results when the Moon is on the same side of the Earth as the Sun is New Moon. During New Moon, the entire lighted surface of the Moon is facing away from the Earth. ...
... 16. During a total lunar eclipse, the Earth blocks all of the Sun's light that would usually reflect off the Moon. 17. The phase that results when the Moon is on the same side of the Earth as the Sun is New Moon. During New Moon, the entire lighted surface of the Moon is facing away from the Earth. ...
Publisher: Emily Barrosse Acquisitions Editor: Kelley Tyner
... (Types Ib and Ic are variations of explosions of heavyweight stars, and we won’t discuss them further here.) If too much matter is added to the white dwarf by its companion, causing the white dwarf to reach the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses, it can no longer support itself. The white dwarf ...
... (Types Ib and Ic are variations of explosions of heavyweight stars, and we won’t discuss them further here.) If too much matter is added to the white dwarf by its companion, causing the white dwarf to reach the Chandrasekhar limit of 1.4 solar masses, it can no longer support itself. The white dwarf ...
Extreme Optics and the Search for Earth-Like Planets
... • Are there Earth-like planets? • Are they common? • Is there life on some of them? ...
... • Are there Earth-like planets? • Are they common? • Is there life on some of them? ...
Folie 1
... pressure, temperature etc. with distance to the core • Similar to equations of stellar structure. They include the possibility of convection. • Assumption of nebula of hydrogen and helium • Radiative and pressure equilibrium at layer between protoplanet and nebula • Infall of planetesimals onto the ...
... pressure, temperature etc. with distance to the core • Similar to equations of stellar structure. They include the possibility of convection. • Assumption of nebula of hydrogen and helium • Radiative and pressure equilibrium at layer between protoplanet and nebula • Infall of planetesimals onto the ...
Cataclysmic Variable Stars
... accretion disk. When the mass-accretion rate is high (Mdot ~ 10^-8 Msun/yr; e.g., novalike variables and dwarf novae in outburst), the boundary layer is optically thick and its temperature ~ 10^5 K (10 eV), so it radiates primarily in the extreme ultraviolet and soft X-ray bandpasses. When the mass- ...
... accretion disk. When the mass-accretion rate is high (Mdot ~ 10^-8 Msun/yr; e.g., novalike variables and dwarf novae in outburst), the boundary layer is optically thick and its temperature ~ 10^5 K (10 eV), so it radiates primarily in the extreme ultraviolet and soft X-ray bandpasses. When the mass- ...
02. Earth in space
... Earth in Space Although we were able to explain Earth's position in space, the unique nature of our planet was not driven home until we were able to look at our home from the outside. The astronauts aboard the Apollo 8 spacecraft were the first to glimpse our home planet from space (Fig. 2). While ...
... Earth in Space Although we were able to explain Earth's position in space, the unique nature of our planet was not driven home until we were able to look at our home from the outside. The astronauts aboard the Apollo 8 spacecraft were the first to glimpse our home planet from space (Fig. 2). While ...
Formation, Habitability, and Detection of Extrasolar Moons
... hibernate in the ice or migrate into the ocean or to another active site. Exposure of water at the surface would allow some oxygen to enter the ocean directly. The gradual buildup of frozen ocean water over the surface exposes fresh ice to the production of oxidants and also buries ever deeper the p ...
... hibernate in the ice or migrate into the ocean or to another active site. Exposure of water at the surface would allow some oxygen to enter the ocean directly. The gradual buildup of frozen ocean water over the surface exposes fresh ice to the production of oxidants and also buries ever deeper the p ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... A cloud with a larger radius than the Jeans length R > RJ will undergo gravitational collapse. The Jeans criterion for the collapse of a cloud is a good approximation in the absence of rotation, turbulence and magnetic fields. In reality however, all these factors do contribute and far more complica ...
... A cloud with a larger radius than the Jeans length R > RJ will undergo gravitational collapse. The Jeans criterion for the collapse of a cloud is a good approximation in the absence of rotation, turbulence and magnetic fields. In reality however, all these factors do contribute and far more complica ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.