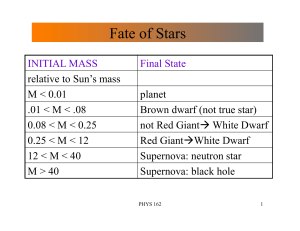
Fate of Stars
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
... Stars with larger sizes are brighter then a smaller star with the same surface temperature ...
Word doc - GDN - University of Gloucestershire
... The more distant a galaxy, the greater the redshift. Until recently the greatest redshift was 5.64. However, new data reported in the journal Science in 1999 reports galaxies with a redshift of 10. These formed when the Universe was only 9% of its current size and probably just a few hundred million ...
... The more distant a galaxy, the greater the redshift. Until recently the greatest redshift was 5.64. However, new data reported in the journal Science in 1999 reports galaxies with a redshift of 10. These formed when the Universe was only 9% of its current size and probably just a few hundred million ...
How far away are the Stars?
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
... The Distance to the Stars! • Angular Separation is not enough! • We want to know the answer to the ‘age old question’: How far away are the stars? ...
The Formation of Systems with Tightly
... forces will be eliminated. However, this may not be able to explain the wide range of planetary systems known, including the Solar System. If rapid inward drift occurs early in the disk’s evolution, when the inner edge of the disk may only be a few stellar radii (Eisner et al. 2005), the solids will ...
... forces will be eliminated. However, this may not be able to explain the wide range of planetary systems known, including the Solar System. If rapid inward drift occurs early in the disk’s evolution, when the inner edge of the disk may only be a few stellar radii (Eisner et al. 2005), the solids will ...
PHYS101 Sec 001 Hour Exam No. 3 Preview 2 Page: 1 1 It
... 1 EModule 016.102 Earth’s Living Surface An Active Crust 2 Module 013.203 Comets and the Outer Solar System Meteor Showers 3 Module 014.302 Formation of the Solar System Condensation of the Planets 4 Module 018.305 Requirements for Life The Requirements for a Carbon Cycle 5 ***Module 013.206-g01 Com ...
... 1 EModule 016.102 Earth’s Living Surface An Active Crust 2 Module 013.203 Comets and the Outer Solar System Meteor Showers 3 Module 014.302 Formation of the Solar System Condensation of the Planets 4 Module 018.305 Requirements for Life The Requirements for a Carbon Cycle 5 ***Module 013.206-g01 Com ...
Star Types - College of Engineering and Computer Science
... (American) had the idea of plotting the luminosity of a star against its spectral type. For a star cluster, all the stars are at the same distance. So, apparent brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars appeared only in certain parts of the ...
... (American) had the idea of plotting the luminosity of a star against its spectral type. For a star cluster, all the stars are at the same distance. So, apparent brightness vs spectral type is basically the same as luminosity vs temperature. They found that stars appeared only in certain parts of the ...
What is a Hertzsprung
... Cepheid Variable Stars • Cepheid variable’s magnitude will vary between 0.5-2 magnitudes over a period from days to months. • They have been show to have a period of variability that depends on luminosity. • This allows Cepheid variables to be used as a standard candle to measure distance. ...
... Cepheid Variable Stars • Cepheid variable’s magnitude will vary between 0.5-2 magnitudes over a period from days to months. • They have been show to have a period of variability that depends on luminosity. • This allows Cepheid variables to be used as a standard candle to measure distance. ...
Stars
... • After billions of years, these stars eventually use up most of their nuclear fuel used for fusion and collapse to form a ____________ ...
... • After billions of years, these stars eventually use up most of their nuclear fuel used for fusion and collapse to form a ____________ ...
Untitled - Notion Press
... mass is more than 20 times of solar mass then it will continue collapsing. None of the forces in the universe would be able to stop the core collapsing. This collapsing gets to a point. The gravity at this point becomes such intense that not even light can escape from its gravitational force. This i ...
... mass is more than 20 times of solar mass then it will continue collapsing. None of the forces in the universe would be able to stop the core collapsing. This collapsing gets to a point. The gravity at this point becomes such intense that not even light can escape from its gravitational force. This i ...
Project Medley Topics
... Choose 1 or 2 of the planets within our Solar System and discuss them in detail (ex. properties, structure, formation, etc.) Include any space missions or probes sent to the planet(s) and their discoveries. Be sure to also discuss any large moons or other notable features/properties of the planet(s) ...
... Choose 1 or 2 of the planets within our Solar System and discuss them in detail (ex. properties, structure, formation, etc.) Include any space missions or probes sent to the planet(s) and their discoveries. Be sure to also discuss any large moons or other notable features/properties of the planet(s) ...
Diapozitivul 1
... The sun, like Earth, is magnetic The sun was born about 4.6 billion years ago The inside of the sun and most of its atmosphere consist of plasma National College Iasi ...
... The sun, like Earth, is magnetic The sun was born about 4.6 billion years ago The inside of the sun and most of its atmosphere consist of plasma National College Iasi ...
newsletter - Thanet Astronomy Group
... direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed in the night sky all at the same time. This is exactly what is happening now. The planets that have aligned are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the five planets that are visible ...
... direction visible from the side of the Earth that faces away from the Sun, the planets can be observed in the night sky all at the same time. This is exactly what is happening now. The planets that have aligned are Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. These are the five planets that are visible ...
Advanced AMG EOC Review 2014-2015
... What causes wind (both the ultimate source and in terms of higher and lower pressure)? What three factors combine to control wind? How does the spacing of isobars on a weather map indicate wind speed? How does the Coriolis effect deflect wind in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres? How and where d ...
... What causes wind (both the ultimate source and in terms of higher and lower pressure)? What three factors combine to control wind? How does the spacing of isobars on a weather map indicate wind speed? How does the Coriolis effect deflect wind in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres? How and where d ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
... 2. Students have a misconception that nighttime visible stars are located within our solar system. Such a notion has been considered since the times of the ancient Greeks. Aristotle proposed a geocentric model of the solar system with Earth at the center. Crystalline spheres surrounded Earth. Each o ...
... 2. Students have a misconception that nighttime visible stars are located within our solar system. Such a notion has been considered since the times of the ancient Greeks. Aristotle proposed a geocentric model of the solar system with Earth at the center. Crystalline spheres surrounded Earth. Each o ...
Celebrating the centennial of a celestial yardstick
... had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercury’s composition from orbit, bu ...
... had abundant volcanic activity (and may have some ongoing activity today), which is involved in concentrating such elements. Yet the amounts of these elements, their distribution, and many other factors are completely unknown. The MESSENGER spacecraft is studying Mercury’s composition from orbit, bu ...
1. INTRODUCTION
... within 3 AU is commonly accompanied by additional giant planets farther out, as demanded by dynamical evolution scenarios that involve mutual perturbations. Further Doppler measurements of existing and future planets can help ascertain the occurrence and character of multipleplanet systems. The broa ...
... within 3 AU is commonly accompanied by additional giant planets farther out, as demanded by dynamical evolution scenarios that involve mutual perturbations. Further Doppler measurements of existing and future planets can help ascertain the occurrence and character of multipleplanet systems. The broa ...
EX PLANET E - Institute of Physics
... The practical activity Students use thermometers to measure the temperature at different distances from a radiant heater. They should start at a good distance (around 70 cm) from the heater and move towards it. Warn them not allow their thermometers to get hotter than 100°C. Students will probably r ...
... The practical activity Students use thermometers to measure the temperature at different distances from a radiant heater. They should start at a good distance (around 70 cm) from the heater and move towards it. Warn them not allow their thermometers to get hotter than 100°C. Students will probably r ...
Assessment Schedule
... Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation). Eg: The core of the star then collapses, combining pro ...
... Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation). Eg: The core of the star then collapses, combining pro ...
Level 2 Science (90764) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation). Eg: The core of the star then collapses, combining pro ...
... Supernova gives out clouds of gases and plasma exploding off its surface. AND These gas clouds are the birth places for new stars. AND After this process ceases, a black hole or a dense neutron star remains (detail provided about the formation). Eg: The core of the star then collapses, combining pro ...
1-structure-of-the-universe-and-the-big-bang
... 63. Fourteen billion years represents the approximate age of A) Earth B) Earth's Moon C) our solar system D) the universe 64. A major piece of evidence supporting the Big Bang theory is the observation that wavelengths of light from stars in distant galaxies show a A) B) C) D) ...
... 63. Fourteen billion years represents the approximate age of A) Earth B) Earth's Moon C) our solar system D) the universe 64. A major piece of evidence supporting the Big Bang theory is the observation that wavelengths of light from stars in distant galaxies show a A) B) C) D) ...
Extreme Optics and the Search for Earth-Like Planets
... In order to have a large enough sample of stars to survey, we need to consider stars out to say 40 light years. That gives a sample of about 1000 stars. Consider for a moment how our own Solar System would look if we could step away and look back at it from a distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 33 light y ...
... In order to have a large enough sample of stars to survey, we need to consider stars out to say 40 light years. That gives a sample of about 1000 stars. Consider for a moment how our own Solar System would look if we could step away and look back at it from a distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 33 light y ...
Pluto, the Kuiper Belt, and Trans- Neptunian Objects
... Whenever you have a large number of objects with various masses, useful to describe the number as a function of mass, N(M), or size, N(R). Constrains theories of their origin. Useful for Kuiper Belt, asteroids, impact craters, Saturn’s ring particles, stars, gas clouds, galaxies. Often have many sma ...
... Whenever you have a large number of objects with various masses, useful to describe the number as a function of mass, N(M), or size, N(R). Constrains theories of their origin. Useful for Kuiper Belt, asteroids, impact craters, Saturn’s ring particles, stars, gas clouds, galaxies. Often have many sma ...
Jupiter - Midland ISD
... Hydrogen and helium make up 92% of Jupiter When Jupiter formed 4.6 billion years ago, it did not have enough mass to allow nuclear fusion to begin so it never became a star. The alternating light and dark burst of its surface makes Jupiter unique in our solar system. ...
... Hydrogen and helium make up 92% of Jupiter When Jupiter formed 4.6 billion years ago, it did not have enough mass to allow nuclear fusion to begin so it never became a star. The alternating light and dark burst of its surface makes Jupiter unique in our solar system. ...
Vulcan Chasers
... tions were later criticized by Peters, who suggested he had made a simple mistake and incorrectly marked the two stars Theta and Zeta Cancri, "haste and excitement doing the rest." Watson refused to give up and spent the rest of his life pursuing his Vulcan obsession. After leaving Ann Arbor to supe ...
... tions were later criticized by Peters, who suggested he had made a simple mistake and incorrectly marked the two stars Theta and Zeta Cancri, "haste and excitement doing the rest." Watson refused to give up and spent the rest of his life pursuing his Vulcan obsession. After leaving Ann Arbor to supe ...
Planetary habitability

Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to develop and sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia. As the existence of life beyond Earth is unknown, planetary habitability is largely an extrapolation of conditions on Earth and the characteristics of the Sun and Solar System which appear favourable to life's flourishing—in particular those factors that have sustained complex, multicellular organisms and not just simpler, unicellular creatures. Research and theory in this regard is a component of planetary science and the emerging discipline of astrobiology.An absolute requirement for life is an energy source, and the notion of planetary habitability implies that many other geophysical, geochemical, and astrophysical criteria must be met before an astronomical body can support life. In its astrobiology roadmap, NASA has defined the principal habitability criteria as ""extended regions of liquid water, conditions favourable for the assembly of complex organic molecules, and energy sources to sustain metabolism.""In determining the habitability potential of a body, studies focus on its bulk composition, orbital properties, atmosphere, and potential chemical interactions. Stellar characteristics of importance include mass and luminosity, stable variability, and high metallicity. Rocky, terrestrial-type planets and moons with the potential for Earth-like chemistry are a primary focus of astrobiological research, although more speculative habitability theories occasionally examine alternative biochemistries and other types of astronomical bodies.The idea that planets beyond Earth might host life is an ancient one, though historically it was framed by philosophy as much as physical science. The late 20th century saw two breakthroughs in the field. The observation and robotic spacecraft exploration of other planets and moons within the Solar System has provided critical information on defining habitability criteria and allowed for substantial geophysical comparisons between the Earth and other bodies. The discovery of extrasolar planets, beginning in the early 1990s and accelerating thereafter, has provided further information for the study of possible extraterrestrial life. These findings confirm that the Sun is not unique among stars in hosting planets and expands the habitability research horizon beyond the Solar System.The chemistry of life may have begun shortly after the Big Bang, 13.8 billion years ago, during a habitable epoch when the Universe was only 10–17 million years old. According to the panspermia hypothesis, microscopic life—distributed by meteoroids, asteroids and other small Solar System bodies—may exist throughout the universe. Nonetheless, Earth is the only place in the universe known to harbor life. Estimates of habitable zones around other stars, along with the discovery of hundreds of extrasolar planets and new insights into the extreme habitats here on Earth, suggest that there may be many more habitable places in the universe than considered possible until very recently. On 4 November 2013, astronomers reported, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of Sun-like stars and red dwarfs within the Milky Way. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting Sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.