* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomy Club
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
International Year of Astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
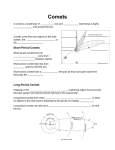
Astronomy Club Science and Technology Council Students’ Gymkhana Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Presents CYGNUS The Wall Magazine 2002-2003 I Club Coordinators 1. Amar V. Chandra 2. Ashutosh K. Gupta 3. Jaya Jha Other Contributors 1. Anshuman Sinha 2. Vinay Mishra 3. Saujanya Golwalker (Alumnus!) Special Thanks To 1. Abhinav Sharma Quiz Corner Try finding out the answers to the following questions. Look out the next issue of Cygnus for the answers. If you get the answers, do post those on iitk.gymkhana. 1. Recently a new Couiper Belt Object has been seen in sky, which is largest ever seen minor planet. Can you tell the name of second largest Minor Planet (KBO)? 2. What is a Great Year? 3. Which Star is the brightest star in sky? 4. What are Meteor showers? Can you explain why these happen? 5. What is special about the relation between revolution and rotation of Pluto? 6. What is “Butterfly of Tunguska”? 7. What is the name of Constellation Orion in Hindu Mythology? 8. Which is the galaxy, closest to us? 9. In which Zodiac sign brightest object is in Messier Catalogue? 10. What is the diameter of Celestial sphere? On the lighter side Laws Of Observational Astronomy The most popular part of the activities of Astronomy Club at IIT Kanpur is Observational Astronomy. With the years of experience the club has been able to formulate the following laws. Additions from experienced people are invited. 1st Law: The skies are never clear within 3 days of new moon. Explanation: There is not enough solar energy reflected off the moon to dissipate the clouds those days. 2nd Law: Rare astronomical events usually occur within 3 days of full moon and/or within 30 apparent degrees from the sun. Explanation: Gravitational interpretation of Murphy's Law. * 3rd Law: When observing, the object you want to see will always be below the horizon or less than 10 degrees from the horizon with the most light pollution Explanation: Since frustration is related to Entropy, it must always increase. 4th Law: Supernovae, comets, and asteroids are always discovered by someone else Explanation: No matter where you are, the sun will always set earlier somewhere else, and therefore someone else will find it first. 5th Law: 90 percent of meteors occur behind you when everyone else is facing you (so they can all say, "ooh! You missed a good one!”) Explanation?? Invited! *Murphy's Law: If it can go wrong, it will. Mythology cannot go unnoticed Aquarius- In Greek Mythology 1. Abduction of a Child: Ganymede was the son of King Tros, after whom the city of Troy was named. The story of Ganymede is rather horrifying if you bother to think about it. What it concerns is the abduction of a child from his parents. Ganymede was abducted one day while he was keeping watch over a herd of his father's sheep. In one story it was Eos, the Goddess of the Dawn, who abducted the boy. She had a passion for young men. Then Zeus noted the beauty of the boy and stole him away from Eos. 2. The Eagle Steals the Boy: In the more common version of the story it was Zeus himself that was taken with the beauty of the shepherd boy and sent his eagle down to steal away the boy in its claws. Some say that the eagle was Zeus himself, who had transformed into the shape of the royal bird. The boy was carried off to the top of Mount Olympus to become the serving boy to the gods, pouring out from his jar the mixture of water and nectar quaffed by the gods in their revels. Learn about the Celestial Objects Comets: Their origin Couiper Belt: The birthplace of comets Comets have an important place in human history. Astronomers and scientists are crazy about the origin and motion of comets. There is general belief in scientific community that the answer to the key question of the origin of solar system lies in the comets. Comets are basically spatial objects of ice and cold gases. Their central part extends upto10-12 Kilometers. As they approach the sun, the central part acquires a large amount of heat .Due to heat gases and dusts vaporize and create an atmosphere around them. This atmosphere is called "Coma" and it can extend up to 1 million Kilometers The rays coming out of the sun push the upper part of coma and the dust and gases makes a tail, which increases in the direction opposite to that of the sun. This tail can extend up to a range of 10-100 million Kilometers. Big comets have tails of maximum length of an order of 30 crore Kilometers. Our solar system has an age of 450 crore years approximately .If all comets were of the same age, then all of them would not have been there today. But as we know, they are swirling around proudly. It means that the age of comets is less than that of the solar system. Now the question arises that if comets were born some few million years ago, then where they were before that. This question was first answered by Dutch astronomer Jane Ourt in 1950.He proposed that there is an icy spherical object at a distance of 75 trillion Kilometers from the sun. This region, called 'Ourt Cloud', was assumed to be the birthplace of comets. If any star passing closely affects this spatial object, then some comets leave the cloud and enter into the solar system. The large planets like Jupiter, Saturn etc. destroy some of the comets. Some change their paths and come out of the solar system and rest move towards the Sun with continuous increase in tail length and start revolving around the Sun. Our earth and other planets revolve around the sun in fixed parallel orbits, except Mercury and Pluto. These orbits have an angle of 7 &17 degrees with respect to the earth's orbit respectively. But comets emerging out of the ‘Ourt Cloud’ have disordered orbit. Comets are mainly of two types. Those of the first type take more than 200 years for revolution around the sun and others takes less than 20 years. 'Ourt Cloud’ hypothesis gives a correct explanation about the orbit's inclination and number of comets with large period. But for almost all the comets with small period, orbit is not too much inclined with respect to the earth's orbit. To explain this difference in inclinations, it was suggested that initially all comets with large period had a large inclination but the gravitational attraction of big planets, especially Jupiter, reduced this angle. All astronomers were not too much satisfied with this explanation. In 1951 Gerard Couiper gave a suggestion that there must be a flat belt in the outer portion of solar system beyond Neptune and Pluto. This belt should be very less dense and hence the particles there did not combine to form the planets. Due to large distance from the Sun it should be very cold and like central part of the comets it should be consisting of dust and gases. This flat belt is called 'Couiper Belt'. Couiper assumed that all small period comets emerge from this belt. It is worth mentioning that most of comets have maximum distance from the sun, which is nearly same as that of Neptune's orbit. So if couiper belt is present than these solid objects should be visible. But at that time, telescopes were not so powerful so as to look beyond Pluto’s orbit. So no objects could be identified and people forgot about Couiper Belt. But at last Martin Duncan of Toronto University, with some of his colleagues, identified some comets. In 1988, a study showed that number of comets with small period is very large. Then again the question arose that if these objects were not from the Ourt cloud, from where had they come? In 1992, astronomers David Jewitt and Jen Lugot found a planet sized object with their 2.2 m long telescope. Slowly moving this comet was beyond Pluto's orbit. It got the name '1992 QB1'. In 1993 another object was identified in a direction opposite to this one. Then people started finding more and more such spatial objects. Till now 43 of such objects have been identified. All these objects have orbits inclined with respect to the earth's orbit. This inclination is same as that of the comets with small period. The number of these objects is not very high, however existence of Couiper belt can't be neglected. All these objects are situated outside the Neptune’s orbits. According to an approximation, Couiper Belt consists of around 35000 such objects with a size of approx 100 kilometers. Now many astronomers believe that the comets with large period have come from Ourt Cloud and the comets with small period have come from the Couiper Belt. After the discovery of Couiper Belt many astronomers believe that Pluto is not a free planet but a large object emerged from Couiper Belt. If new discoveries prove this fact than we will loose one planet from our solar system and number will reduce from 9 to 8!! Enough Scopes for Art Astroart It is not just about the “same old stars” (though even this, I do not believe is true!), images of galaxy and supernovae in IR Region etc. Here is something very comprehensible to Human eyes. We are presenting before you the mounting of the telescope through Astroart. To learn more about it, wait for the coming issues of Cygnus, or post your queries on iitk.gymkhana or search Google! 1. The Telescope . ' . " ' . . . "` . . 3. Adding Counter weight 3. ' ' Attempt to add equatorial (``', mounting w/ counterweight. / `''/ / / o\/ / \, / _ ( / ,',`, /x`''7/_________r_ ,=, (x //---, (------',=, / `''7' \ \ ' ,=, / / \ \ '-' ( / )\ `''' /(o)\ `|~~~|` |===| | | |===| | | |___| /`___`\ ,-----'`~~~~~~~`'-----, `~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~` ' ' . ' _______________ ==c(___(o(______(_() \=\ )=\ //|\\ //|| \\ // || \\ // || \\ // \\ 2. Plain Mounting (``', First try on plain mounting. / `''/ / / O\/ / \, / ( / /x`''7/ (x //`\ / `''7'`\_\ / / /__\ ( / `|~~|` `''' |==| | | |==| | | |__| /`____`\ ,-------'`~~~~~~~~`'-------, `~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~` David Riley What do the coordinators say Tradition is to be continued and enriched 1. We are grateful to our earlier coordinators of terms 2000-2001 and 2001-2002 (i.e. since we are here) for leaving an enriched tradition of activities, learning and fun at Astronomy Club and we assure that we will try our best to add new colours to the flower they have grown. 2. We expect more and enthusiastic participation from Junta in the activities of the club. A list of planned activities is being given here. We expect more suggestions from you. 3. We expect guidance from faculty and seniors and enthusiasm and support from our friends. Planned Activities Come, Enjoy, Learn and Gain 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Regular Observation Sessions A Freshers’ Astronomy Quiz after Freshers’ Nite in August-2002 An Astronomy Debate after first mid-sems (2002-2003 1st Semester) An astronomy festival open to all students and faculty members after 2 nd mid-sems (2002-2003 1st Semester) 1st Discussion of our discussion series will be during the Astronomy festival. Two more discussions in the 2nd Semester of academic year 2002-2003 Three more issues of Cygnus Persuasion of the plan of the observatory Before We End Quotes Not to Be Quoted ;-) 1. Black holes are the places where Mother Nature is dividing by zero. 2. Living on Earth in expensive, but it does include a free trip round the sun. 3. If you can read this you are not looking through Hubble Scope Telescope! But you can quote this one: That's one small step for a man; one giant leap for mankind. A thin man ran... made a large stride... left planet... pined flag on moon... on to Mars!