23. ______ layers of ______ make up the cell
... 17. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ________ in a process called ____________. 18. Chains of amino acids make _______________ which can join together to make a __________. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up ...
... 17. Amino acids are linked together to make proteins by removing a molecule of ________ in a process called ____________. 18. Chains of amino acids make _______________ which can join together to make a __________. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up ...
Macromolecules biologyjunction
... outer electrons and can form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic ...
... outer electrons and can form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic ...
Matching review Connect with lines
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
... Matching review Connect with lines Water Carbon dioxide Oxygen PGAL NADP NAD+ FAD Glucose ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 2. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
... 2. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... 2. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
... 2. Show the three reactions in the citric acid cycle in which NADH is produced, including the structures. None of these reactions involves molecular oxygen (O2), but all three reactions are strongly inhibited by anaerobic conditions; explain why. ...
Slide 1
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
... Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from glucogenic precursors which are not of carbohydrate origin (gluconeogenic precursors) It occurs during prolonged fasting to synthesize glucose for tissues requiring continuous supply of glucose as a source of energy: Brain, RBCs, Kidney medulla, Lens, ...
Carbon Compounds
... 6. Protein function varies greatly • Control rate of chemical reactions • Regulate cell processes • Structural components (muscle, bone) • Transport substances • Fight disease ...
... 6. Protein function varies greatly • Control rate of chemical reactions • Regulate cell processes • Structural components (muscle, bone) • Transport substances • Fight disease ...
ReviewExamIII
... How does pH and temperature affect enzymatic rate (velocity)? How does a graph of enzymatic rate look versus pH and temperature? How do catabolic and anabolic reactions differ with respect to energy requirements or use, and which is a "build-up" and which a "break-down" group of reactions? What are ...
... How does pH and temperature affect enzymatic rate (velocity)? How does a graph of enzymatic rate look versus pH and temperature? How do catabolic and anabolic reactions differ with respect to energy requirements or use, and which is a "build-up" and which a "break-down" group of reactions? What are ...
Lipids
... Kingdom, Belgium, Norway, the Netherlands, and Iceland. • Recent decreases in the trans content of the diet have been observed, presumably due to modifications of commercially available fats or changes in consumer choices. • Today, most margarines in the European market have a lower content of trans ...
... Kingdom, Belgium, Norway, the Netherlands, and Iceland. • Recent decreases in the trans content of the diet have been observed, presumably due to modifications of commercially available fats or changes in consumer choices. • Today, most margarines in the European market have a lower content of trans ...
Biological (organic) Molecules
... Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes Test for proteins: use biuret’s reagent, turns from blue to violet in the presence of proteins ...
... Relay messages – hormones Speed up reactions – enzymes Test for proteins: use biuret’s reagent, turns from blue to violet in the presence of proteins ...
Biochemistry
... Biomolecules •Biomolecules are molecules that are made and used by living things. •A polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. ...
... Biomolecules •Biomolecules are molecules that are made and used by living things. •A polymer is a large molecule that is made up of smaller molecules called monomers. ...
syllabus - option b(human biochemistry)
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules foundin the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stud ...
... The aim of this option is to give students an understanding of the chemistry of important molecules foundin the human body, and the need for a balanced and healthy diet. Although the role that these molecules play in the body should be appreciated, the emphasis is placed on their chemistry, and stud ...
You may have heard the terms saturated and unsaturated in rela
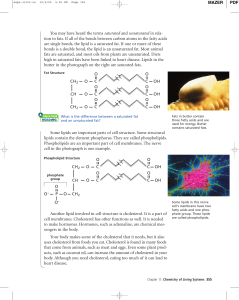
... Phospholipids are an important part of cell membranes. The nerve cell in the photograph is one example. ...
... Phospholipids are an important part of cell membranes. The nerve cell in the photograph is one example. ...
6) Metabolism
... into pyruvate or intermediate of the TCA cycle; gluconeogenesis • Ketogenic amino acids—an a.a.a broken down into acetyl CoA which can be converted into ketone bodies ...
... into pyruvate or intermediate of the TCA cycle; gluconeogenesis • Ketogenic amino acids—an a.a.a broken down into acetyl CoA which can be converted into ketone bodies ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
... catabolized, releasing amino acids into circulation (including glutamine, alanine, and the branched chain amino acids [BCAAs]), while hepatic amino acid uptake is enhanced. This allows for reprioritization of protein synthesis to acute phase reactants and the production of glucose via gluconeogenesi ...
practice exam
... 2. ______ Ketone body formation A. produces a water-insoluble fuel for brain cells. B. occurs only under starvation conditions. C. takes place in the cytosol. D. allows acetyl CoA to be made into net glucose. E. is favored when the citric acid cycle is inhibited. 3. ______ Which statement concerning ...
... 2. ______ Ketone body formation A. produces a water-insoluble fuel for brain cells. B. occurs only under starvation conditions. C. takes place in the cytosol. D. allows acetyl CoA to be made into net glucose. E. is favored when the citric acid cycle is inhibited. 3. ______ Which statement concerning ...
BIOL103 Review Questions for Midterm 2 SP16
... 11. How does their bond type (e.g. alpha vs. beta) affect the carbohydrates digestion in the human body? 12. Who has lactose intolerance? 13. Explain how carbohydrates digest in the human body from mouth ...
... 11. How does their bond type (e.g. alpha vs. beta) affect the carbohydrates digestion in the human body? 12. Who has lactose intolerance? 13. Explain how carbohydrates digest in the human body from mouth ...
Chapter 24 – Lipids_Summary
... of the membrane and released. -Among other substances, glucose passes into many cells by facilitated diffusion. In active transport, substances can pass against a concentration gradient. -Active transport requires a supply of energy (often ATP) to overcome the concentration gradient. • The relativel ...
... of the membrane and released. -Among other substances, glucose passes into many cells by facilitated diffusion. In active transport, substances can pass against a concentration gradient. -Active transport requires a supply of energy (often ATP) to overcome the concentration gradient. • The relativel ...
Lipids - University of Winnipeg
... • Waxes: Waxes are part of the lipid family. Waxes are esters of long-chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (having 14-36 carbon atoms) with long-chain alcohol(having 16-30 carbon atoms). • Waxes are low- melting, stable solids which appear in nature in both plants and animals. A wax coat prot ...
... • Waxes: Waxes are part of the lipid family. Waxes are esters of long-chain saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (having 14-36 carbon atoms) with long-chain alcohol(having 16-30 carbon atoms). • Waxes are low- melting, stable solids which appear in nature in both plants and animals. A wax coat prot ...
Lipogenesis (2014)
... 1- Transport of acetyl CoA to cytoplasm: Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate) and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cyto ...
... 1- Transport of acetyl CoA to cytoplasm: Acetyl CoA is the precursor of fatty acid synthesis. It is produced from oxidation of glucose (by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate) and metabolism of ketogenic and mixed amino acids. Acetyl CoA is produced in mitochondria, and FA synthesis occurs in cyto ...