Biology 301 Exam 3 Name Spring 2008 1. Which of the following is
... 64. During Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (Glycolysis) the phosporylation of ADP occurs between 1,3- bisphophoglycerate and 3-phosphoglycerate. What type of phosphorylation is this an example of? 65. If the methyl-accepting chemotoxis protein (MCP) is bounded to attractant molecules in which direction does ...
... 64. During Embden-Meyerhof Pathway (Glycolysis) the phosporylation of ADP occurs between 1,3- bisphophoglycerate and 3-phosphoglycerate. What type of phosphorylation is this an example of? 65. If the methyl-accepting chemotoxis protein (MCP) is bounded to attractant molecules in which direction does ...
Lipids
... • Lipids are diverse in form and are defined by solubility in non-polar solvents (and insolubility in water) • Lipids are used for efficient energy storage, as structural components of cell membranes, as chemical messengers and as fat-soluble vitamins with a variety of functions • We consume many li ...
... • Lipids are diverse in form and are defined by solubility in non-polar solvents (and insolubility in water) • Lipids are used for efficient energy storage, as structural components of cell membranes, as chemical messengers and as fat-soluble vitamins with a variety of functions • We consume many li ...
Document
... • Property o Amphiphathic: polar charged phosphate head and nonpolar uncharged fatty acid tails • Function: o Make up phospholipid bilayer found in all biological membranes ...
... • Property o Amphiphathic: polar charged phosphate head and nonpolar uncharged fatty acid tails • Function: o Make up phospholipid bilayer found in all biological membranes ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... Molecules interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... Molecules interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules that make up
... The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. The fatty acid tails of phospholipids face inside, away from water, whereas the phosphate heads face the outward aqueous side. Since the heads face outward, one layer is exposed to the interior of the cell and ...
... The cell membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids, which form a bilayer. The fatty acid tails of phospholipids face inside, away from water, whereas the phosphate heads face the outward aqueous side. Since the heads face outward, one layer is exposed to the interior of the cell and ...
Dear Notetaker:
... a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understand!! 7. How many moles of ATP are produced when one mole of glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dio ...
... a. The mitochondria when citrate builds up i. If Krebs cycle has enough energy, it slows down, citrate builds up, and acetyl CoA can leave then. Regulatory step that is important..need to understand!! 7. How many moles of ATP are produced when one mole of glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dio ...
Chapter 3 Chemistry of Life Modern Biology Textbook Holt
... Proteins are affected by environmental conditions such as heat and pH. Explain why the process of cooking an egg cannot be reversed. Answer: The heat that is added to the egg changes the bonds in the proteins and other molecules that make up the egg to such a large extent that the original protein s ...
... Proteins are affected by environmental conditions such as heat and pH. Explain why the process of cooking an egg cannot be reversed. Answer: The heat that is added to the egg changes the bonds in the proteins and other molecules that make up the egg to such a large extent that the original protein s ...
24.1 Structure and Classification of Lipids
... • Fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid; those in animal fats and vegetable oils often have 12–22 carbon atoms. • Waxes are carboxylic acid esters, RCOOR’ ,with long, straight hydrocarbon chains in both R groups; they are secreted by sebaceous glands in the skin of animals and perform mostly ...
... • Fatty acid: A long-chain carboxylic acid; those in animal fats and vegetable oils often have 12–22 carbon atoms. • Waxes are carboxylic acid esters, RCOOR’ ,with long, straight hydrocarbon chains in both R groups; they are secreted by sebaceous glands in the skin of animals and perform mostly ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Chapter 9 Outline: Energy Metabolism After studying this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the differences among metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. 2. Describe aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of glucose. 3. Illustrate how energy is extracted from glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and al ...
... Chapter 9 Outline: Energy Metabolism After studying this chapter, you will be able to: 1. Explain the differences among metabolism, catabolism, and anabolism. 2. Describe aerobic and anaerobic metabolism of glucose. 3. Illustrate how energy is extracted from glucose, fatty acids, amino acids, and al ...
Biochemistry, Digestion, and Energy Transfer
... hydrogenated products because the process of hydrogenation converts the natural cis fatty acids to trans fatty acids. The trans fatty acids stack like saturated fatty acids and are stored and not metabolized by the body as the natural cis fatty acids are. Cis fatty acids react with cholesterol and t ...
... hydrogenated products because the process of hydrogenation converts the natural cis fatty acids to trans fatty acids. The trans fatty acids stack like saturated fatty acids and are stored and not metabolized by the body as the natural cis fatty acids are. Cis fatty acids react with cholesterol and t ...
MOLECULES of LIFE Matter is anything that has mass and takes up
... Whenever the carbon chain has a double bond in it, we say that the fat is unsaturated. Some lipids have a phosphate group replacing one of the fatty acids. Such molecules are important molecules for the storage of energy. They are also found protecting nerve cells and can be remodeled into seteroids ...
... Whenever the carbon chain has a double bond in it, we say that the fat is unsaturated. Some lipids have a phosphate group replacing one of the fatty acids. Such molecules are important molecules for the storage of energy. They are also found protecting nerve cells and can be remodeled into seteroids ...
Macromolecules
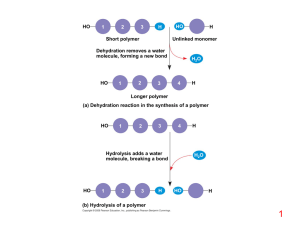
... • A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, which can also bind forming large polymers called macromolecules (macro = LARGE) • Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called dehydration synthesis. During the formation of polymers, water is released or is a by-product. ...
... • A polymer consists of repeated, linked units, which can also bind forming large polymers called macromolecules (macro = LARGE) • Monomers link to form polymers through a chemical reaction called dehydration synthesis. During the formation of polymers, water is released or is a by-product. ...
Chapter 21 - Evangel University
... • Acetyl-CoA is transported to the cytosol and converted to malonyl-CoA • The biosynthesis of FA proceeds by the addition of 2-carbon units to the hydrocarbon chain. • The process is catalyzed by the fatty-acid synthase complex Comparison of FA Degradation and Biosynthesis ...
... • Acetyl-CoA is transported to the cytosol and converted to malonyl-CoA • The biosynthesis of FA proceeds by the addition of 2-carbon units to the hydrocarbon chain. • The process is catalyzed by the fatty-acid synthase complex Comparison of FA Degradation and Biosynthesis ...
Chapter 2 - SCHOOLinSITES
... – Substrate binds to enzyme at active site – Enzymes act on substrates to reduce energy needed to make product – Substrate is changed – Enzyme separates from products and can form an association with another substrate – Enzyme, as a catalyst is not used up in the reaction – Increases reaction rate ...
... – Substrate binds to enzyme at active site – Enzymes act on substrates to reduce energy needed to make product – Substrate is changed – Enzyme separates from products and can form an association with another substrate – Enzyme, as a catalyst is not used up in the reaction – Increases reaction rate ...
Topic: B2b Lesson: 2 Title: Enzymes and digestion
... 2. What are the following broken down into by digestive enzymes? a) Carbohydrates simple sugars b) Proteins amino acids c) Fats fatty acids + glycerol 3. Where are most enzymes produced? Pancreas ...
... 2. What are the following broken down into by digestive enzymes? a) Carbohydrates simple sugars b) Proteins amino acids c) Fats fatty acids + glycerol 3. Where are most enzymes produced? Pancreas ...
Handout 5 - Fatty Acid Synthesis
... 3. The AcCoA is utilized for fatty acid synthesis (palmitate). 4. The OAA is reduced to malate, when then is oxidatively decarboxylated back to pyruvate generating NADPH. This cycle can produce about 1/2 the NADPH required for fatty acid biosynthesis. B. Acetate. Acetate is converted to AcCoA in the ...
... 3. The AcCoA is utilized for fatty acid synthesis (palmitate). 4. The OAA is reduced to malate, when then is oxidatively decarboxylated back to pyruvate generating NADPH. This cycle can produce about 1/2 the NADPH required for fatty acid biosynthesis. B. Acetate. Acetate is converted to AcCoA in the ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... on or off. Please note: once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click in the white background before you advance the next slide. ...
... on or off. Please note: once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click in the white background before you advance the next slide. ...
control of intermediary metabolism
... AEROBIC METABOLISM PYRUVIC ACID (3 C FRAGMENT) ENTERS MITOCHONDRIA COMBINES WITH COENZYME A LOOSING A CO2 AND BECOMING ACETYL COENZYME A (2 C FRAGMENT) THIS FRAGMENT ENTERS A CYCLIC REACTION SCHEME, THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE, ATP IS PRODUCED PRODUCTS OF THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE ENTER THE ELECTRON ...
... AEROBIC METABOLISM PYRUVIC ACID (3 C FRAGMENT) ENTERS MITOCHONDRIA COMBINES WITH COENZYME A LOOSING A CO2 AND BECOMING ACETYL COENZYME A (2 C FRAGMENT) THIS FRAGMENT ENTERS A CYCLIC REACTION SCHEME, THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE, ATP IS PRODUCED PRODUCTS OF THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE ENTER THE ELECTRON ...
Poikilothermic and Homoeothermic Organisms
... body temperatures constant regardless of the temperatures around them. They often have the ability to generate heat and lose heat as well. 2. Poikilothermic organisms have more variant cell membrane composition, while homoeothermic organisms have a similar type of cell membrane for all their cells. ...
... body temperatures constant regardless of the temperatures around them. They often have the ability to generate heat and lose heat as well. 2. Poikilothermic organisms have more variant cell membrane composition, while homoeothermic organisms have a similar type of cell membrane for all their cells. ...
CHAPTER 26: Lipid Metabolism
... -- You eat plenty of proteins and carbs -- You eat Linoleic and linolenic fatty acids (essential fatty acids) - Avg. Man is 16% fat and Avg. Woman is 25% fat 26.1 Storage and Mobilization of fats - Your fat now is enough for you to starve for 30 – 40 days, if you have water - Contrast to the amount ...
... -- You eat plenty of proteins and carbs -- You eat Linoleic and linolenic fatty acids (essential fatty acids) - Avg. Man is 16% fat and Avg. Woman is 25% fat 26.1 Storage and Mobilization of fats - Your fat now is enough for you to starve for 30 – 40 days, if you have water - Contrast to the amount ...
AS and A2 Biology resource
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...