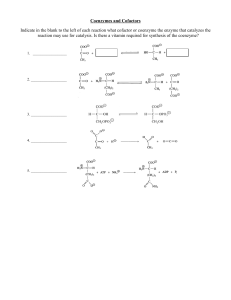
Chapter 2 Study Outline
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
File
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
... Lipids: Three kinds: What 3 elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ____________ ...
Is water a polar or nonpolar molecule
... 11. Solute transport across membranes The type of membrane transport that uses ion gradients as the energy source is: A) facilitated diffusion B) passive transport. C) primary active transport. D) secondary active transport. E) simple diffusion. 39. Fill in the blanks. The eicosanoid hormones, which ...
... 11. Solute transport across membranes The type of membrane transport that uses ion gradients as the energy source is: A) facilitated diffusion B) passive transport. C) primary active transport. D) secondary active transport. E) simple diffusion. 39. Fill in the blanks. The eicosanoid hormones, which ...
Biochemistry
... There are 20 amino acids that combine to make over millions of possibilities For example: a peptide (another name for protein) that ...
... There are 20 amino acids that combine to make over millions of possibilities For example: a peptide (another name for protein) that ...
Nucleic acids
... fats are made into solids by a process called hydrogenation. This process increases the shelf life of the fats, however this process places the hydrogen on opposite sides of the fatty acid making it inflexible. The more flexible the fatty acid the more healthy the fat. ...
... fats are made into solids by a process called hydrogenation. This process increases the shelf life of the fats, however this process places the hydrogen on opposite sides of the fatty acid making it inflexible. The more flexible the fatty acid the more healthy the fat. ...
Chapter 25
... • Breaks down glucose in cytosol into smaller molecules used by mitochondria • Does not require oxygen so it is anaerobic • 1 molecule of glucose yields only 2 ATP • Yields very little energy on its own, but it is enough to power your muscles for short periods • Some bacteria are entirely anaerobic ...
... • Breaks down glucose in cytosol into smaller molecules used by mitochondria • Does not require oxygen so it is anaerobic • 1 molecule of glucose yields only 2 ATP • Yields very little energy on its own, but it is enough to power your muscles for short periods • Some bacteria are entirely anaerobic ...
Chapter 24 Metabolism
... (in liver) of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors like – lactic acid – glycerol – amino acids ...
... (in liver) of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors like – lactic acid – glycerol – amino acids ...
Chapter Four The Lipids: Fats & Oils
... Also made & used in the body: – Structure of cell membranes – Used to make bile for digestion Bile: a mixture of compounds, made by the liver, stored in the gallbladder, & secreted into the small intestine Emulsifies lipids to prepare them for ...
... Also made & used in the body: – Structure of cell membranes – Used to make bile for digestion Bile: a mixture of compounds, made by the liver, stored in the gallbladder, & secreted into the small intestine Emulsifies lipids to prepare them for ...
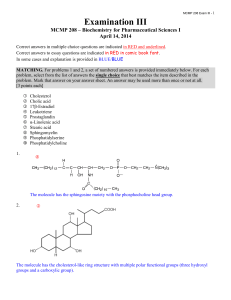
Final Examination
... as thioesters with coenzyme A Not a storage mechanism in a bilayer membrane Not a storage mechanism – membranes have an essential barrier function ...
... as thioesters with coenzyme A Not a storage mechanism in a bilayer membrane Not a storage mechanism – membranes have an essential barrier function ...
Monomers and Polymers
... Monomers called nucleotides – They will each have: 5 carbon sugar Phosphate Group Base (A,T,C, or G) ...
... Monomers called nucleotides – They will each have: 5 carbon sugar Phosphate Group Base (A,T,C, or G) ...
Monomers and Polymers
... Monomers called nucleotides – They will each have: 5 carbon sugar Phosphate Group Base (A,T,C, or G) ...
... Monomers called nucleotides – They will each have: 5 carbon sugar Phosphate Group Base (A,T,C, or G) ...
BIO 6.3 Carbon - Steinbach Science
... Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) or C—H bonds and less oxygen than carbohydrates (e.g., beef fat has the formula C57H110O6) Lipids are commonly call ...
... Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) or C—H bonds and less oxygen than carbohydrates (e.g., beef fat has the formula C57H110O6) Lipids are commonly call ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
... Ribonucleic acid (______) - plays many key roles in building of proteins and can act as enzymes. ...
... Ribonucleic acid (______) - plays many key roles in building of proteins and can act as enzymes. ...
Nutrition - Athens Academy
... A. The primary role of carbohydrates is to serve as an energy source. B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
... A. The primary role of carbohydrates is to serve as an energy source. B. Carbohydrates include sugars, starches, and amino acids. C. Maltose is a complex carbohydrate. D. Sucrose is the primary source of energy for most cells. E. Most carbohydrates come from animal products. ...
Metabolism 2010edit
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
MM Handouts
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
... form four bonds. Carbon can form single bonds with another atom and also bond to other carbon molecules forming double, triple, or quadruple bonds. Organic compounds also contain hydrogen. Since hydrogen has only one electron, it can form only single bonds. Each small organic molecule can be a unit ...
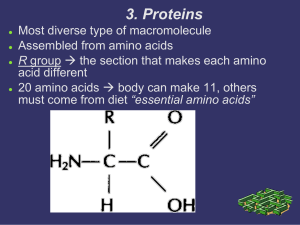
3. Proteins
... • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or genetic damage. ...
... • Occurs when the bonds of a protein are disrupted, causing an often permanent change in shape • ex. X-ray radiation or nuclear radioactivity can disrupt protein structure and can lead to cancer or genetic damage. ...
9.6 Respiration 4 (Control and other metabolites)
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
... – digestion • catabolism when organism needs energy or needs raw materials – synthesis • anabolism when organism has enough energy & a supply of raw materials – by regulating enzymes • feedback mechanisms • raw materials stimulate production • products inhibit further production ...
CHAPTER 6
... surrounded by water they cannot use. Ice and snow are too cold and seawater is too salty. They produce all the water they need from metabolism of fat: (CH2) + 1.5O2 → CO2 + H2O Interestingly, adult polar bears consume only fat (from seals they catch). By not consuming protein (and merely recycling t ...
... surrounded by water they cannot use. Ice and snow are too cold and seawater is too salty. They produce all the water they need from metabolism of fat: (CH2) + 1.5O2 → CO2 + H2O Interestingly, adult polar bears consume only fat (from seals they catch). By not consuming protein (and merely recycling t ...