Biomolecules I. Introduction. - biochemistry: study of chemical
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
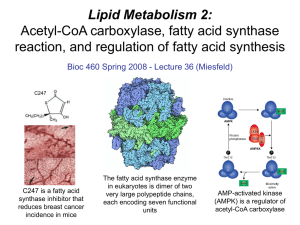
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... 3. What are the key enzymes in fatty acid synthesis? Acetyl CoA carboxylase - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid synthesis using a biotin-mediated reaction mechanism that carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form the C3 compound malonyl-CoA.. Fatty acid synthase - this large multi-functional enzyme i ...
... 3. What are the key enzymes in fatty acid synthesis? Acetyl CoA carboxylase - catalyzes the commitment step in fatty acid synthesis using a biotin-mediated reaction mechanism that carboxylates acetyl-CoA to form the C3 compound malonyl-CoA.. Fatty acid synthase - this large multi-functional enzyme i ...
Introduction to metabolism. Specific and general pathways of
... are oxidized to common metabolite (acetyl CoA) Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled dir ...
... are oxidized to common metabolite (acetyl CoA) Stage III. Acetyl CoA is oxidized in citric acid cycle to CO2 and water. As result reduced cofactor, NADH2 and FADH2, are formed which give up their electrons. Electrons are transported via the tissue respiration chain and released energy is coupled dir ...
Biology Chapter 2 - secondary
... Review Questions 6. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. How are the physical characteristics affected? – Saturated fatty acids have two hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms. – Unsaturated- have or more of the carbon atoms are double bonded – Saturated behave as solid ...
... Review Questions 6. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. How are the physical characteristics affected? – Saturated fatty acids have two hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms. – Unsaturated- have or more of the carbon atoms are double bonded – Saturated behave as solid ...
Macromolecules For Identification
... • A lot of lipids function as long-term energy storage. • One gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as one gram of carbohydrates. • Lipids are also an important component of the cell membrane. Lipids consist of glycerol and fatty acids "tails". The fatty acid "tails" are long chains of c ...
... • A lot of lipids function as long-term energy storage. • One gram of fat stores more than twice as much energy as one gram of carbohydrates. • Lipids are also an important component of the cell membrane. Lipids consist of glycerol and fatty acids "tails". The fatty acid "tails" are long chains of c ...
called “organic molecules”
... •Hydrolysis - Cells break bonds between monomers by adding water to them •Water (hydro) is used to break down( lysis ) a molecule ...
... •Hydrolysis - Cells break bonds between monomers by adding water to them •Water (hydro) is used to break down( lysis ) a molecule ...
Molecules of Life
... How enzymes work Substrate ( reactant) fits into the active site of the enzyme 2) The enzyme breaks/forms bonds and releases the products 3) The enzyme can then be used again with another substrate ...
... How enzymes work Substrate ( reactant) fits into the active site of the enzyme 2) The enzyme breaks/forms bonds and releases the products 3) The enzyme can then be used again with another substrate ...
Close Reading for Macromolecules
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
... 25. ____Peptide______ bonds form when water is removed to hold ____amino acids_____ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lip ...
Bio-Macromolecules Worksheet
... condensation as water is produced when the monomers are bonded together. To break the polymers down again the reaction is called hydrolysis. Notice how water is used or produced in these two reactions shown to the right There are four classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and n ...
... condensation as water is produced when the monomers are bonded together. To break the polymers down again the reaction is called hydrolysis. Notice how water is used or produced in these two reactions shown to the right There are four classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and n ...
bioc-2200-a-biol-2200-a-mock-final-exam
... d. proteins are asymmetrically distributed within the membrane 21. Which of the following is a sphingolipid? a. lecithin b. cholesterol c. phosphatidylinositol d. gangliosides 22. When Beta oxidation predominates in liver, mitochondrial pyruvate is likely to be: a. carboxylated to phosphoenolpuruvat ...
... d. proteins are asymmetrically distributed within the membrane 21. Which of the following is a sphingolipid? a. lecithin b. cholesterol c. phosphatidylinositol d. gangliosides 22. When Beta oxidation predominates in liver, mitochondrial pyruvate is likely to be: a. carboxylated to phosphoenolpuruvat ...
1. Which of the following is not a feature of scientific hypotheses? A
... E) repairing damage to the stomach wall and aiding in blood clotting. ...
... E) repairing damage to the stomach wall and aiding in blood clotting. ...
PASS MOCK EXAM
... 55. Phosphorylation does NOT play a regulatory role in the reaction catalyzed by: a. glycogen phosphorylase b. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase c. pyruvate dehydrogenase d. pyruvate kinase e. none of the above 56. When the liver converts excess glucose to fatty acids all of the following are ...
... 55. Phosphorylation does NOT play a regulatory role in the reaction catalyzed by: a. glycogen phosphorylase b. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase c. pyruvate dehydrogenase d. pyruvate kinase e. none of the above 56. When the liver converts excess glucose to fatty acids all of the following are ...
$doc.title
... Aka. polymers b/c they are made from same units linked together (draw train cars linked) ...
... Aka. polymers b/c they are made from same units linked together (draw train cars linked) ...
The Organic Molecules of Life
... The organelle in cells that acts like a power plant, producing energy for the cell; cellular respiration occurs here. common storage form of glucose in plants; composed of long chains made of hundreds of glucose molecules carboncontaining compounds synthesized by cells (2 words) (2 words) covalent ...
... The organelle in cells that acts like a power plant, producing energy for the cell; cellular respiration occurs here. common storage form of glucose in plants; composed of long chains made of hundreds of glucose molecules carboncontaining compounds synthesized by cells (2 words) (2 words) covalent ...
Macromolecules and Reactions
... Catabolic reactions involve the breakdown of macromolecules into subunits (ex/ nutrient breakdown during digestion) Many reactions involve either hydrolysis or condensation, where a linkage is created or destroyed Condensation or dehydration synthesis: two molecules combine through covalent bo ...
... Catabolic reactions involve the breakdown of macromolecules into subunits (ex/ nutrient breakdown during digestion) Many reactions involve either hydrolysis or condensation, where a linkage is created or destroyed Condensation or dehydration synthesis: two molecules combine through covalent bo ...
Biology Unit 2
... Protein Examples Structural Proteins Hair, fingernails, feathers, muscle fibers, spider webs Functional Proteins - have a specific role to carry out in a cell Hemoglobin – transports oxygen in your blood Insulin – transports glucose to the cells for energy Antibodies – fight off disease ...
... Protein Examples Structural Proteins Hair, fingernails, feathers, muscle fibers, spider webs Functional Proteins - have a specific role to carry out in a cell Hemoglobin – transports oxygen in your blood Insulin – transports glucose to the cells for energy Antibodies – fight off disease ...
Chemical Basis for Life
... ◦ Saturated triglycerides —the 3 fatty acids are saturated: hard at room temp: found in butter and red meat: “bad fats” ◦ Unsaturated triglycerides —the 3 fatty acids are unsaturated: soft at room temp: found in plant seeds: “good fats” ...
... ◦ Saturated triglycerides —the 3 fatty acids are saturated: hard at room temp: found in butter and red meat: “bad fats” ◦ Unsaturated triglycerides —the 3 fatty acids are unsaturated: soft at room temp: found in plant seeds: “good fats” ...
Chapter 2 Chemical Basis of Life
... Lipids: Three kinds: What three elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ________ ...
... Lipids: Three kinds: What three elements do they all contain? _________________ supply energy, are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. Fatty acids with hydrogen at every position along the carbon chain are saturated; those with one or more double bonds are called ______________ fats. ________ ...
Molecules of life 2.4 - Madison County Schools
... c. Cellulose -Structural component of plant cell walls. a. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. d. Chitin= This is the exoskeleton of some animals and also Fungi cell walls. C. The chemical composition is: Carbon = Oxygen; 2x as many hydrogen atoms also present. 1. Generic carbo ...
... c. Cellulose -Structural component of plant cell walls. a. Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound on Earth. d. Chitin= This is the exoskeleton of some animals and also Fungi cell walls. C. The chemical composition is: Carbon = Oxygen; 2x as many hydrogen atoms also present. 1. Generic carbo ...