Biomolecule Discussion Guide KEY
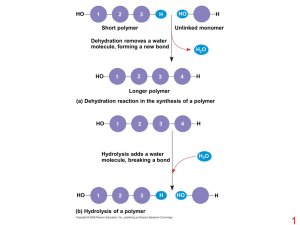
... a. How are polymers formed? Polymers are formed through a process called dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagra ...
... a. How are polymers formed? Polymers are formed through a process called dehydration synthesis or condensation. During this process, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom are removed from the monomers to form water, and then, the two monomers are joined together. (Students may wish to draw a diagra ...
Macromolecules
... steel rod of the same diameter, yet it is much more elastic, so scientists hope to use it for products as diverse as bulletproof vests and artificial joints. ...
... steel rod of the same diameter, yet it is much more elastic, so scientists hope to use it for products as diverse as bulletproof vests and artificial joints. ...
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
... and cardiac muscle, although these tissues do not make ketones (9). Interestingly, we subsequently discovered that the interaction of malonyl-CoA and carnitine with CPT1 are different in liver and muscle. Inhibition of liver CPT1 requires ten times the concentration of malonyl-CoA as does the inhibi ...
... and cardiac muscle, although these tissues do not make ketones (9). Interestingly, we subsequently discovered that the interaction of malonyl-CoA and carnitine with CPT1 are different in liver and muscle. Inhibition of liver CPT1 requires ten times the concentration of malonyl-CoA as does the inhibi ...
Organic Compounds - tanyabshank
... bring two (or more) reactants together more quickly and force them to react stress bonds in a single substrate and cause it to break apart more easily ...
... bring two (or more) reactants together more quickly and force them to react stress bonds in a single substrate and cause it to break apart more easily ...
Bio 7
... Uses for plants?...Uses for animals? Lipids/fats – single glycerol and three free-fatty acids Uses in animals? Proteins – amino acid chains Used as enzymes and structural components of the cell Fold into unique 3D shape that gives each protein’s its function DNA and RNA Nucleotides (nucleic acids) c ...
... Uses for plants?...Uses for animals? Lipids/fats – single glycerol and three free-fatty acids Uses in animals? Proteins – amino acid chains Used as enzymes and structural components of the cell Fold into unique 3D shape that gives each protein’s its function DNA and RNA Nucleotides (nucleic acids) c ...
and fatty acids
... from triacylglycerols for our use …………….. • The initial event in the mobilization and utilization of stored fat as an energy source is the release of free fatty acids and glycerol by hydrolysis of triacylglycerols by lipases, an event referred to as lipolysis or the breakdown of fats . • Two metabol ...
... from triacylglycerols for our use …………….. • The initial event in the mobilization and utilization of stored fat as an energy source is the release of free fatty acids and glycerol by hydrolysis of triacylglycerols by lipases, an event referred to as lipolysis or the breakdown of fats . • Two metabol ...
Honors Biology Name Biochemistry Exam Review #1 Period _____
... The pocket or groove where the substrate fits into on the enzyme is called the active site. (See diagram in enzyme notes for enzyme structure) Enzymes are named for the substrate that they work with. Names usually end in –ase (ex. Lactase, Helicase) Enzymes can be denatured (a change in shape) by a ...
... The pocket or groove where the substrate fits into on the enzyme is called the active site. (See diagram in enzyme notes for enzyme structure) Enzymes are named for the substrate that they work with. Names usually end in –ase (ex. Lactase, Helicase) Enzymes can be denatured (a change in shape) by a ...
Organic Molecules
... The carbon chain is saturated with all the hydrogens it can hold Account for the solid nature of fats, like butter, at room temperature ...
... The carbon chain is saturated with all the hydrogens it can hold Account for the solid nature of fats, like butter, at room temperature ...
Ch. 5 Organic Chem
... • The unique sequence of the bases on a DNA polymer is in the 5’ to 3’ end • sequence determines amino acid sequence of genes passed to next generation and evolutionary links • DNA Strands are antiparallel • Each strand used as a template in DNA replication ...
... • The unique sequence of the bases on a DNA polymer is in the 5’ to 3’ end • sequence determines amino acid sequence of genes passed to next generation and evolutionary links • DNA Strands are antiparallel • Each strand used as a template in DNA replication ...
Biological Chemistry
... molecules) covalently bonded together 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. _______ (amylose) - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to _______ in our bodies 3 ...
... molecules) covalently bonded together 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. _______ (amylose) - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to _______ in our bodies 3 ...
Cholesterol
... Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) is the precursor for cholesterol synthesis. • HMG-CoA is also an intermediate on the pathway for synthesis of ketone bodies from acetyl-CoA. ...
... Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) is the precursor for cholesterol synthesis. • HMG-CoA is also an intermediate on the pathway for synthesis of ketone bodies from acetyl-CoA. ...
View as PDF - Helen Money Nutrition
... musculoskeletal pain and 82% of those with back pain return to work. Reducing recovery time is therefore financially beneficial to employers. Physiotherapy is commonly used to restore pre-injury health which together with a preventative exercise program can help reduce the chances of the same proble ...
... musculoskeletal pain and 82% of those with back pain return to work. Reducing recovery time is therefore financially beneficial to employers. Physiotherapy is commonly used to restore pre-injury health which together with a preventative exercise program can help reduce the chances of the same proble ...
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid
... cholesterol starts with acetyl groups and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed. Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
... cholesterol starts with acetyl groups and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed. Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
Power point presentation
... When many amino acids bond together to create long chains, the structure is called a polypeptide because it contains many peptide bonds. Polypeptides form ...
... When many amino acids bond together to create long chains, the structure is called a polypeptide because it contains many peptide bonds. Polypeptides form ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Alfred State College
... Acid Cycle Occurs in Mitochondria • Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm • Citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix† • Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner membrane ...
... Acid Cycle Occurs in Mitochondria • Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm • Citric acid cycle occurs in the mitochondrial matrix† • Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner membrane ...
AP Chapter 5A WS - TJ
... 9. Polymers of sugars form 10. Which forms of polysaccharide is best for each function: a. Strength of structure b. Storage and sugar release c. What biological theme is this addressing? ...
... 9. Polymers of sugars form 10. Which forms of polysaccharide is best for each function: a. Strength of structure b. Storage and sugar release c. What biological theme is this addressing? ...
B4 Lipids
... The fatty acid hydrocarbon chains, R1, R2, R3, may be identical (as in tristearin with three oleic acids. However, R1, R2, R3, are generally different ...
... The fatty acid hydrocarbon chains, R1, R2, R3, may be identical (as in tristearin with three oleic acids. However, R1, R2, R3, are generally different ...
Review 1 - Allen ISD
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...