Bio160 ExIII Sp09
... 6. A non-polar substance is not soluble in oil. 7. An electrically unbalanced atom has an equal number of protons and electrons. 8. An isotope is a version of an atom for an element which has extra neutrons. 9. Hydrogen bonds involve the sharing of electrons. 10. Fatty acids have an amino functional ...
... 6. A non-polar substance is not soluble in oil. 7. An electrically unbalanced atom has an equal number of protons and electrons. 8. An isotope is a version of an atom for an element which has extra neutrons. 9. Hydrogen bonds involve the sharing of electrons. 10. Fatty acids have an amino functional ...
lec32_F2015
... CoA is a central intermediate Anabolic role: TCA cycle provides starting material for fats and amino acids. Note: carbohydrates cannot be synthesized from acetyl-CoA by humans. PyruvateAcetyl CoA is one way! In contrast to glycolysis, none of the intermediates are phosphorylated; but all are ei ...
... CoA is a central intermediate Anabolic role: TCA cycle provides starting material for fats and amino acids. Note: carbohydrates cannot be synthesized from acetyl-CoA by humans. PyruvateAcetyl CoA is one way! In contrast to glycolysis, none of the intermediates are phosphorylated; but all are ei ...
PATHWAYS THAT HARVEST CHEMICAL ENERGY CHAPTER 9
... • Links glycolysis and the citric acid cycle; occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • Pyruvate is oxidized to acetate and CO2 is released • NAD+ is reduced to NADH, capturing energy • Some energy is stored by combining acetate and Coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA ...
... • Links glycolysis and the citric acid cycle; occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • Pyruvate is oxidized to acetate and CO2 is released • NAD+ is reduced to NADH, capturing energy • Some energy is stored by combining acetate and Coenzyme A (CoA) to form acetyl CoA ...
3 MoleculesCells
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
... monomers are they made of? What types of glycosidic bonds do they have? What is the structural differences between the storage polysaccharides? Where are each found in nature? 4. Which polysaccharides are used for structural support in living things? How are they constructed with regards to monosacc ...
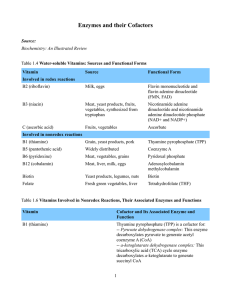
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... decarboxylates pyruvate to generate acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) -- a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: This tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzyme decarboxylates a-ketoglutarate to generate succinyl CoA ...
... decarboxylates pyruvate to generate acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) -- a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex: This tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzyme decarboxylates a-ketoglutarate to generate succinyl CoA ...
Study Guide Exam #2 1) What are the 2 stages of
... 1) What are the 2 stages of food consumption in animals? What is the difference between them? ...
... 1) What are the 2 stages of food consumption in animals? What is the difference between them? ...
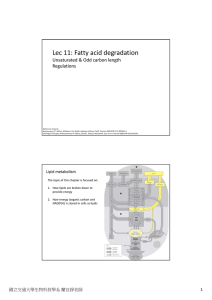
Lec 11: Fatty acid degradation
... Since H2O2 is strong oxidizing agent, it is immediately cleaved to O2 and H2O by catalase. 2. Since peroxisome does not contain ETC, ATP generated is dissipated as heat. For plants, when seeds are germinating, they will use glyoxysome (same as peroxisome) to break the lipid stored in seeds to ...
... Since H2O2 is strong oxidizing agent, it is immediately cleaved to O2 and H2O by catalase. 2. Since peroxisome does not contain ETC, ATP generated is dissipated as heat. For plants, when seeds are germinating, they will use glyoxysome (same as peroxisome) to break the lipid stored in seeds to ...
THE MOLECULES OF LIFE - Christian Heritage School
... Glycogen, cellulose, and starch are three types of polysaccharides found in food. Though all three polymers are composed of the same monomer, glucose, the way the glucose monomers link together is different for each. ...
... Glycogen, cellulose, and starch are three types of polysaccharides found in food. Though all three polymers are composed of the same monomer, glucose, the way the glucose monomers link together is different for each. ...
CHEM 214 Elementary Biochemistry
... There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of ...
... There are no make-up quizzes or exams. An hourly exam missed for a valid reason (first discussed with the instructor) will be replaced by the corresponding grade on the final (Final is then 65% of your total grade). The learning objectives for Chem 214 are the following: To gain an understanding of ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Dietary Sources of Major Nutrients Basics of Cellular Respiration Metabolism of Carbos, Fats, and Protein Central Role of the Liver in Digestion/Metabolism Cholesterol and Lipid Transport Absorptive and Postabsorptive States Developmental Aspects of Metabolism ...
... Dietary Sources of Major Nutrients Basics of Cellular Respiration Metabolism of Carbos, Fats, and Protein Central Role of the Liver in Digestion/Metabolism Cholesterol and Lipid Transport Absorptive and Postabsorptive States Developmental Aspects of Metabolism ...
terminal end
... The energy of hydrolysis of a phosphoanhydride bond (shown as squiggles) is greater than that of a phosphate ester and will have significance in Chapter 5 (Section 5.8) ...
... The energy of hydrolysis of a phosphoanhydride bond (shown as squiggles) is greater than that of a phosphate ester and will have significance in Chapter 5 (Section 5.8) ...
Cells Are Made Of Molecules
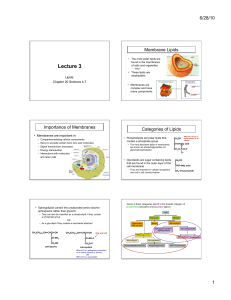
... Lipids, including fats, are nonpolar and hydrophobic macromolecules that serve as long term energy storage, insulations, & cushioning OBJECTIVES: 1. SWBAT describe the structure and function of fats 2. SWBAT distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids 3. SWBAT explain the hydrophobic n ...
... Lipids, including fats, are nonpolar and hydrophobic macromolecules that serve as long term energy storage, insulations, & cushioning OBJECTIVES: 1. SWBAT describe the structure and function of fats 2. SWBAT distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids 3. SWBAT explain the hydrophobic n ...
Chapter 25: Metabolism
... • Glycerol pyruvic acid TCA cycle • FA acetyl-CoA (via beta oxidation) TCA cycle ...
... • Glycerol pyruvic acid TCA cycle • FA acetyl-CoA (via beta oxidation) TCA cycle ...
Energy Production
... It produces ATP to support continuos muscle activity for longer than 90-120 seconds. The availability of oxygen through the process of respiration is vital. Without oxygen ATP cannot be supplied. Through glycolysis, pyruvic acid is supplied, with the presence of oxygen, it is converted to acetyl Coe ...
... It produces ATP to support continuos muscle activity for longer than 90-120 seconds. The availability of oxygen through the process of respiration is vital. Without oxygen ATP cannot be supplied. Through glycolysis, pyruvic acid is supplied, with the presence of oxygen, it is converted to acetyl Coe ...
Bacterial Physiology Lec-8 Catabolism: Tricarboxylic acid cycle
... ,balance is maintained and no net carbon is lost. Cycle now enters the four carbon stage during which 2 oxidation steps yield; 1FADH2 and 3NADH per acetyl –CoA . GTP (a high – energy molecule equivalent to ATP) is produced from succinyl–CoA by substrate–level phosphorylation. Oxaloacetate is reforme ...
... ,balance is maintained and no net carbon is lost. Cycle now enters the four carbon stage during which 2 oxidation steps yield; 1FADH2 and 3NADH per acetyl –CoA . GTP (a high – energy molecule equivalent to ATP) is produced from succinyl–CoA by substrate–level phosphorylation. Oxaloacetate is reforme ...
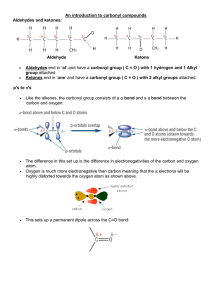
An introduction to carbonyl compounds Aldehydes and ketones
... If its melting point is above room temperature it is a solid which makes it a fat, eg margarine and butter. If its melting point is below room temperature it is a solid which makes it an oil, eg olive oil. ...
... If its melting point is above room temperature it is a solid which makes it a fat, eg margarine and butter. If its melting point is below room temperature it is a solid which makes it an oil, eg olive oil. ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology
... – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea; metabolizes drugs, hormones; has the Cytochrome P-450 enzyme system. ...
... – Hepatocytes remove ammonia and convert to urea; metabolizes drugs, hormones; has the Cytochrome P-450 enzyme system. ...
Molecules - Chapter 2
... acids they make the cis forms Food manufacturers found that foods like chips with the trans form have a longer “shelf ...
... acids they make the cis forms Food manufacturers found that foods like chips with the trans form have a longer “shelf ...
Overview of Carbohydrate Digestion and Metabolism
... 1. Control enzyme levels 2. Control of enzyme activity (activation or inhibition) 3. Compartamentalization Fatty acid oxidation occurs in mitochondrial matrix Fatty acid synthesis occurs in endoplasmic reticulum membrane exposed to the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
... 1. Control enzyme levels 2. Control of enzyme activity (activation or inhibition) 3. Compartamentalization Fatty acid oxidation occurs in mitochondrial matrix Fatty acid synthesis occurs in endoplasmic reticulum membrane exposed to the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
Overview of Carbohydrate Digestion and Metabolism
... 1. Control enzyme levels 2. Control of enzyme activity (activation or inhibition) 3. Compartamentalization Fatty acid oxidation occurs in mitochondrial matrix Fatty acid synthesis occurs in endoplasmic reticulum membrane exposed to the cytoplasm of the cell. ...
... 1. Control enzyme levels 2. Control of enzyme activity (activation or inhibition) 3. Compartamentalization Fatty acid oxidation occurs in mitochondrial matrix Fatty acid synthesis occurs in endoplasmic reticulum membrane exposed to the cytoplasm of the cell. ...