File
... There are several types of lipids, but all contain subunits of glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
... There are several types of lipids, but all contain subunits of glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
Biochemistry. 4th Edition Brochure
... Fax Order Form To place an order via fax simply print this form, fill in the information below and fax the completed form to 646-607-1907 (from USA) or +353-1-481-1716 (from Rest of World). If you have any questions please visit http://www.researchandmarkets.com/contact/ ...
... Fax Order Form To place an order via fax simply print this form, fill in the information below and fax the completed form to 646-607-1907 (from USA) or +353-1-481-1716 (from Rest of World). If you have any questions please visit http://www.researchandmarkets.com/contact/ ...
The Digestive System
... liver and the gallbladder into emulsified fats. Pancreatic lipase from the pancreas takes the emulsified fats and breaks them into fatty acids and then down further into glycerol. Fat digestion is complete in the small intestine thanks to the actions of the bile and the pancreatic lipase. ...
... liver and the gallbladder into emulsified fats. Pancreatic lipase from the pancreas takes the emulsified fats and breaks them into fatty acids and then down further into glycerol. Fat digestion is complete in the small intestine thanks to the actions of the bile and the pancreatic lipase. ...
... By the end of this section you should be able to: Identify ATP as the high energy compound which transfers energy, and is produced when ADP combines with phosphate in phosphorylation, building up energy, and releases energy when broken down into ADP and phosphate once more. State that cells use high ...
Gastric Secretions
... carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids Pancreatic Amylase converts starch or glycogen into dissacharides. Pancreatic Lipase digests fats. Converts triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides Tripsin, Chyomotrypsin, and Carboxypetidase These digest proteins – no single enzyme can spli ...
... carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nucleic acids Pancreatic Amylase converts starch or glycogen into dissacharides. Pancreatic Lipase digests fats. Converts triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides Tripsin, Chyomotrypsin, and Carboxypetidase These digest proteins – no single enzyme can spli ...
medicinal-chemistry-lect-3-n-17-acid-base
... When the PH=PKa , the compound is 50% ionized (or 50% unionized). When the PKa =PH , the molar concentration of the acid equals to molar concentration of its conjugate base. When log ⌊conjugate base⌋/[acid] =1 ...
... When the PH=PKa , the compound is 50% ionized (or 50% unionized). When the PKa =PH , the molar concentration of the acid equals to molar concentration of its conjugate base. When log ⌊conjugate base⌋/[acid] =1 ...
103 Lecture Ch20a
... • Peptides are two or more amino acids linked together by amide bonds (called peptide bonds) • A peptide bond is formed when the acid group of one amino acid reacts with the amine group of another amino acid • When writing the structure of a peptide: - the amino acid with the free (unreacted) amine ...
... • Peptides are two or more amino acids linked together by amide bonds (called peptide bonds) • A peptide bond is formed when the acid group of one amino acid reacts with the amine group of another amino acid • When writing the structure of a peptide: - the amino acid with the free (unreacted) amine ...
Chapter 6 Proteins and Amino Acids I Introduction II The Structure of
... 4. Harmful to ______________ because a high protein diet is typically high in _______________ fat and __________________. 5. Environmental problems of raising lots of protein-rich foods: a. feedlot beef and pork: animal waste leaches into soil, water & air b. grazed beef: loss of native plants, soil ...
... 4. Harmful to ______________ because a high protein diet is typically high in _______________ fat and __________________. 5. Environmental problems of raising lots of protein-rich foods: a. feedlot beef and pork: animal waste leaches into soil, water & air b. grazed beef: loss of native plants, soil ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 6 Cellular Respiration
... • NAD+ and FAD (temporarily becoming NADH & FADH2) • How does the Electron transport chain, the third stage of respiration, make ATP? • By chemiosmosis, the movement of Hydrogen ions from high to low concentration via the protein ATP synthase ...
... • NAD+ and FAD (temporarily becoming NADH & FADH2) • How does the Electron transport chain, the third stage of respiration, make ATP? • By chemiosmosis, the movement of Hydrogen ions from high to low concentration via the protein ATP synthase ...
KS4 Digestion - Part Two
... If ever food accidentally got into the trachea, we would choke and try to cough it back out. ...
... If ever food accidentally got into the trachea, we would choke and try to cough it back out. ...
Special aspects of renal metabolism
... The presence of the α-amino group keeps amino acids safely locked away from oxidative breakdown Removing α-amino group is obligatory in the catabolism of all amino acids Once removed, nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons metabolized Transam ...
... The presence of the α-amino group keeps amino acids safely locked away from oxidative breakdown Removing α-amino group is obligatory in the catabolism of all amino acids Once removed, nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted, with the carbon skeletons metabolized Transam ...
The Digestive System
... ATP ADP (triphosphate to diphosphate)- loss of the phosphate releases energy Lost phos. recharges (like a battery) and bonds with an ADP to make an ATP: Energy must be available in the cells for this to occur Cellular Respiration provides the energy to regenerate ATP, ATP provides the E for cellul ...
... ATP ADP (triphosphate to diphosphate)- loss of the phosphate releases energy Lost phos. recharges (like a battery) and bonds with an ADP to make an ATP: Energy must be available in the cells for this to occur Cellular Respiration provides the energy to regenerate ATP, ATP provides the E for cellul ...
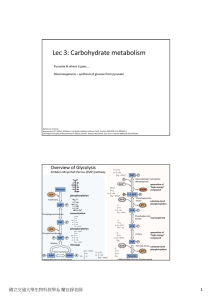
Lec 3: Carbohydrate metabolism
... In humans, glucose can be synthesized from pyruvate (or lactate, or oxaloacetate, or certain amino acids) through this pathway (mainly occurring in the liver). Particularly important for converting human diet intake to glucose ...
... In humans, glucose can be synthesized from pyruvate (or lactate, or oxaloacetate, or certain amino acids) through this pathway (mainly occurring in the liver). Particularly important for converting human diet intake to glucose ...
Chapter 30
... • tRNA “charged” with amino acid • Carries out codon recognition through anticodon loop • Delivers amino acid to ribosomes • Amino acid has no role in codon recognition ...
... • tRNA “charged” with amino acid • Carries out codon recognition through anticodon loop • Delivers amino acid to ribosomes • Amino acid has no role in codon recognition ...
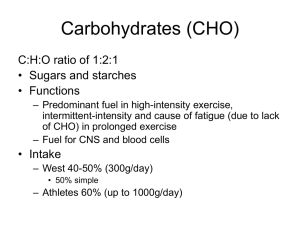
Carbohydrates (CHO)
... • 3-15 monosaccharide units joined to form polysaccharides • Maltodextrins – partially hydrolysed starch – Include starch oligosaccharides and maltose – Less osmotically active than glucose and less ...
... • 3-15 monosaccharide units joined to form polysaccharides • Maltodextrins – partially hydrolysed starch – Include starch oligosaccharides and maltose – Less osmotically active than glucose and less ...
Sources of enzyme
... catalytic functions and are not used with either a pure substrate or a completely defined ...
... catalytic functions and are not used with either a pure substrate or a completely defined ...
Biology 123 SI-Dr. Raut`s Class Session 10
... from NADH to the first molecule of the electron transport chain in complex one. From there the electrons flow down the electron transport chain. Every time the electrons move to a molecule, that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is o ...
... from NADH to the first molecule of the electron transport chain in complex one. From there the electrons flow down the electron transport chain. Every time the electrons move to a molecule, that particular molecule is reduced. When the electrons move on to the next molecule, the first molecule is o ...
Chapter 6 Proteins and Amino Acids I Introduction II The Structure of
... Measures of Protein Quality in a food: digestibility and how well the amino acid pattern of the protein supports growth. A. Digestibility Animal protein is more digestible than plant protein. B. Amino Acid Pattern 1. Complete protein a. Definition: a protein in food that has all the ESSENTIAL amino ...
... Measures of Protein Quality in a food: digestibility and how well the amino acid pattern of the protein supports growth. A. Digestibility Animal protein is more digestible than plant protein. B. Amino Acid Pattern 1. Complete protein a. Definition: a protein in food that has all the ESSENTIAL amino ...
protein
... Diet Carbohydrates RDA • Is set at 130 g/day for adults & children based on the amount of glucose used by carbohydrate dependent tissues (as brain & RBCs). • However, this level of intake is usually exceeded to meet energy needs. • Adults should consume 45 – 65 % of their total calories from carboh ...
... Diet Carbohydrates RDA • Is set at 130 g/day for adults & children based on the amount of glucose used by carbohydrate dependent tissues (as brain & RBCs). • However, this level of intake is usually exceeded to meet energy needs. • Adults should consume 45 – 65 % of their total calories from carboh ...
answer key
... B. Give an example of a membrane with a low protein-to-lipid ratio and an example of a membrane with a high protein-to-lipid ratio. Briefly explain why these membranes have such different ratios. Myelin has a low protein-to-lipid ratio because it electrically insulates axons, which doesn't require p ...
... B. Give an example of a membrane with a low protein-to-lipid ratio and an example of a membrane with a high protein-to-lipid ratio. Briefly explain why these membranes have such different ratios. Myelin has a low protein-to-lipid ratio because it electrically insulates axons, which doesn't require p ...
Chapter 3 – The Molecules of Cells
... depend upon the size and shape of its carbon skeleton and the groups of atoms that are attached to that skeleton. Of the six groups of atoms that are essential to life, five serve as functional groups. Functional groups affect a molecule’s function by participating in chemical reactions in character ...
... depend upon the size and shape of its carbon skeleton and the groups of atoms that are attached to that skeleton. Of the six groups of atoms that are essential to life, five serve as functional groups. Functional groups affect a molecule’s function by participating in chemical reactions in character ...
PPT3 - Ycmou
... intermediates and energy generated from catabolic reactions to synthesize the cells components. Anabolic reactions require input of energy in the forms of ATP molecules or reduced co enzymes, NADH and NADPH. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. ...
... intermediates and energy generated from catabolic reactions to synthesize the cells components. Anabolic reactions require input of energy in the forms of ATP molecules or reduced co enzymes, NADH and NADPH. © 2007, YCMOU. All Rights Reserved. ...
Cholesterol
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...
... LYSOLECITHIN + CHOLESTEROL ESTER • LCAT is activated by apo-A1 and deficiency in LCAT means that HDL can’t take ...