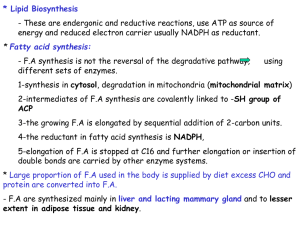
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... exergonic decarboxylation reaction drives the condensation reaction. The CO2 group added to acetyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase is given up in this reaction. In effect this reaction is driven by ATP. ATP was used to activate bicarbonate in the acetyl CoA carboxylase reaction. The free energy was co ...
... exergonic decarboxylation reaction drives the condensation reaction. The CO2 group added to acetyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase is given up in this reaction. In effect this reaction is driven by ATP. ATP was used to activate bicarbonate in the acetyl CoA carboxylase reaction. The free energy was co ...
103 Lecture Ch23b
... Conversion of Pyruvate to Lactate • For aerobic organisms under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate, which replenishes NAD+ to continue glycolysis • During strenuous exercise, muscle cells quickly use up their stored oxygen, creating anaerobic conditions - lactate accumulates, lead ...
... Conversion of Pyruvate to Lactate • For aerobic organisms under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate is reduced to lactate, which replenishes NAD+ to continue glycolysis • During strenuous exercise, muscle cells quickly use up their stored oxygen, creating anaerobic conditions - lactate accumulates, lead ...
A. glycolysis
... 1. oxidative phosphorylation – electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen – the energy released from this process is used to turn ADP into ATP – use of an electron transport chain (chemiosmosis) 2. substrate level phosphorylation – addition of a phosphate gro ...
... 1. oxidative phosphorylation – electrons are transferred from electron donors to electron acceptors such as oxygen – the energy released from this process is used to turn ADP into ATP – use of an electron transport chain (chemiosmosis) 2. substrate level phosphorylation – addition of a phosphate gro ...
Geoff Barton`s Protein Structure: A quick reminder
... Other helix structures also occur with different pitch. ...
... Other helix structures also occur with different pitch. ...
File
... Autotrophs: synthesise organic molecules from inorganic forms to obtain energy. Examples water and carbon dioxide ...
... Autotrophs: synthesise organic molecules from inorganic forms to obtain energy. Examples water and carbon dioxide ...
13synthesis
... lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
... lipids) they transferred to different cell membranes by Golgi apparatus in form of vesicles. ...
Glycolysis - medscistudents
... Provide carbon skeletons for the synthesis of nonessential amino acids. Most of the reactions of glycolysis are reversible The entry of glucose from ECF to cell (ICF) is under the control of insulin Glycolysis occurrence is the pre-requisite for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrates Aerob ...
... Provide carbon skeletons for the synthesis of nonessential amino acids. Most of the reactions of glycolysis are reversible The entry of glucose from ECF to cell (ICF) is under the control of insulin Glycolysis occurrence is the pre-requisite for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrates Aerob ...
Ketone ester effects on metabolism and
... increases the energy of ATP hydrolysis by reducing the mitochondrial NAD couple and oxidizing the coenzyme Q couple, thus increasing the redox span between site I and site II. In contrast, metabolism of fatty acids leads to a reduction of both mitochondrial NAD and mitochondrial coenzyme Q causing a ...
... increases the energy of ATP hydrolysis by reducing the mitochondrial NAD couple and oxidizing the coenzyme Q couple, thus increasing the redox span between site I and site II. In contrast, metabolism of fatty acids leads to a reduction of both mitochondrial NAD and mitochondrial coenzyme Q causing a ...
Ch 18
... • DHF must be reduced to THF by DHF reductase • NADPH dependent • Chemotherapy target – DHF analogs such as methotrexate ...
... • DHF must be reduced to THF by DHF reductase • NADPH dependent • Chemotherapy target – DHF analogs such as methotrexate ...
Studies on the Fate of Isotopically Labeled
... property of tumor cells has emerged from such studies (6, 12). Because of the unregulated growth, which is an inherent feature of malignancy, atten tion has been focused particularly on the problem of energy production in tumors; and it is in this area of cancer research that metabolic exploration ...
... property of tumor cells has emerged from such studies (6, 12). Because of the unregulated growth, which is an inherent feature of malignancy, atten tion has been focused particularly on the problem of energy production in tumors; and it is in this area of cancer research that metabolic exploration ...
AP Chemistry Acid-‐Base and Solution Equilibrium
... Chemical equilibrium reasoning can be used to describe the proton6.C.1: transfer reactions of acid-base chemistry. The pH is an important characteristic of aqueous solutions that can be controlled with buffers. Comparing pH to pKa allows one to determine the rotonation state of a molecule with a lab ...
... Chemical equilibrium reasoning can be used to describe the proton6.C.1: transfer reactions of acid-base chemistry. The pH is an important characteristic of aqueous solutions that can be controlled with buffers. Comparing pH to pKa allows one to determine the rotonation state of a molecule with a lab ...
Insulin and glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue
... stored in vesicles are transferred to the cell membrane which leads to uptake of glucose • Glucose is stored in muscles as glycogen and in adipose tissue as fat • ~ 90 % of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake occurs in skeletal muscle • ~ 10% in adipose tissue ...
... stored in vesicles are transferred to the cell membrane which leads to uptake of glucose • Glucose is stored in muscles as glycogen and in adipose tissue as fat • ~ 90 % of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake occurs in skeletal muscle • ~ 10% in adipose tissue ...
Cellular Respiration
... d. It produces more energy per glucose molecule than does aerobic respiration. 2. Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis? a. an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell b. an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it c. an a ...
... d. It produces more energy per glucose molecule than does aerobic respiration. 2. Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis? a. an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell b. an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it c. an a ...
A chemist has discovered a drug that blocks
... catalyzes the second reaction in glycolysis. He wants to use the drug to kill bacteria in people with infections. Which statement below explains why this is not possible: a. bacteria are prokaryotes; they usually don't need to perform glycolysis b. glycolysis produces so little ATP that the drug wil ...
... catalyzes the second reaction in glycolysis. He wants to use the drug to kill bacteria in people with infections. Which statement below explains why this is not possible: a. bacteria are prokaryotes; they usually don't need to perform glycolysis b. glycolysis produces so little ATP that the drug wil ...
Abnormalities of Intermediary Metabolism in Barth Syndrome
... Is Barth Syndrome a Mitochondrial Disease? 1. Muscle biopsies often have normal mitochondrial enzymology and histology 2. Profound muscle fatigue and weakness occur without biochemical signs of mitochondrial dysfunction 3. Severity of growth delay is out of proportion to biochemical signs of mitoch ...
... Is Barth Syndrome a Mitochondrial Disease? 1. Muscle biopsies often have normal mitochondrial enzymology and histology 2. Profound muscle fatigue and weakness occur without biochemical signs of mitochondrial dysfunction 3. Severity of growth delay is out of proportion to biochemical signs of mitoch ...
The Human Digestive System
... • Carbohydrates are broken down to simple sugars during digestion such as glucose, fructose and galactose • Their main function is to provide a source of energy. The excess carbohydrates are converted to fat and stored. • Some food sources would be glucose, rice, bread, pasta, etc. ...
... • Carbohydrates are broken down to simple sugars during digestion such as glucose, fructose and galactose • Their main function is to provide a source of energy. The excess carbohydrates are converted to fat and stored. • Some food sources would be glucose, rice, bread, pasta, etc. ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism - BITS Academic Resource Center
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. The most important carbohydrate is glucose, which can be broken down via glycolysis, enter into the Kreb's cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate A ...
... Carbohydrate Metabolism Carbohydrate metabolism is a fundamental biochemical process that ensures a constant supply of energy to living cells. The most important carbohydrate is glucose, which can be broken down via glycolysis, enter into the Kreb's cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to generate A ...
6.8-6.10 Citric acid cycle and Oxidative phosphorylation
... • Pyruvate does not enter the citric acid cycle, but undergoes some chemical grooming in which – a carboxyl group is removed and given off as CO2, – the two-carbon compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH, – coenzyme A joins with the two-carbon group to form acetyl ...
... • Pyruvate does not enter the citric acid cycle, but undergoes some chemical grooming in which – a carboxyl group is removed and given off as CO2, – the two-carbon compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH, – coenzyme A joins with the two-carbon group to form acetyl ...
Amino Acids - Chavis Biology
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...
Chapter 13
... Triose Phosphate Isomerase (TIM) Reversible and driven towards GAP due to product depletion ...
... Triose Phosphate Isomerase (TIM) Reversible and driven towards GAP due to product depletion ...
Amino Acids - Chavis Biology
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...