Amino Acids
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...
... There are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. The remaining, nonprotein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. All amino acids have a common structure (see right). The only difference ...
6.8-6.10 Citric acid cycle and Oxidative phosphorylation
... • Pyruvate does not enter the citric acid cycle, but undergoes some chemical grooming in which – a carboxyl group is removed and given off as CO2, – the two-carbon compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH, – coenzyme A joins with the two-carbon group to form acetyl ...
... • Pyruvate does not enter the citric acid cycle, but undergoes some chemical grooming in which – a carboxyl group is removed and given off as CO2, – the two-carbon compound remaining is oxidized while a molecule of NAD+ is reduced to NADH, – coenzyme A joins with the two-carbon group to form acetyl ...
How do cells regulate the speed of reactions?
... Four Main Steps in Cellular Respiration 3) Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle - in matrix of mitochondria For each turn in the cycle: 2 CO2 leave 3 NADH made 1 FADH2 made 1 ATP made FADH2 = reduced form of FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide); same function as NADH = hydrogen carrier ...
... Four Main Steps in Cellular Respiration 3) Krebs (Citric Acid) Cycle - in matrix of mitochondria For each turn in the cycle: 2 CO2 leave 3 NADH made 1 FADH2 made 1 ATP made FADH2 = reduced form of FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide); same function as NADH = hydrogen carrier ...
Proteins
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
... Another major compound of living things is protein. Proteins make up the bulk of all solid material within your body and other living organisms. Proteins are the most structurally sophisticated molecules known. They vary extensively in structure with each type of protein having a unique three-dimens ...
MesoDermal Mesotherapy Cocktails
... compounds to achieve the most preventative and treatment for Androgenic Alopecia through Mesotherapy. Mesopecia contains an inhibitor of 5-alphareductase, lowering the concentrations of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in plasma and tissue. Mesopecia is a mixture of Dutasteride Biotin, Pantothenic acid and ...
... compounds to achieve the most preventative and treatment for Androgenic Alopecia through Mesotherapy. Mesopecia contains an inhibitor of 5-alphareductase, lowering the concentrations of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in plasma and tissue. Mesopecia is a mixture of Dutasteride Biotin, Pantothenic acid and ...
05 Macromoleculesl
... They don't exactly look like the saviors of our energy economy, but that's exactly what some researchers think they could be. Gribbles -- tiny crustacean pests with a knack for digesting wood -- have long been considered a marine parasite for the destruction they cause to wooden hulls and piers. But ...
... They don't exactly look like the saviors of our energy economy, but that's exactly what some researchers think they could be. Gribbles -- tiny crustacean pests with a knack for digesting wood -- have long been considered a marine parasite for the destruction they cause to wooden hulls and piers. But ...
genetics ch 7 [10-31
... Elevated serum lipid levels (hyperlipidemia) common and result from defective lipid transport mechansims Errors in metabolism of fatty acids (hydrocarbon chains with terminal carboxylate group) much less common During fasting and prolonged aerobic exercise, fatty acids mobilized from adipose t ...
... Elevated serum lipid levels (hyperlipidemia) common and result from defective lipid transport mechansims Errors in metabolism of fatty acids (hydrocarbon chains with terminal carboxylate group) much less common During fasting and prolonged aerobic exercise, fatty acids mobilized from adipose t ...
Lecture 26 - Glycolysis 2
... In addition to functioning as intermediates in the gluconeogenic pathway (production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources), many of the glycolytic metabolites provide carbon skeletons for amino acid synthesis, the pentose phosphate pathway (ribose5-P), and triacylglyceride synthesis (glycerol). ...
... In addition to functioning as intermediates in the gluconeogenic pathway (production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources), many of the glycolytic metabolites provide carbon skeletons for amino acid synthesis, the pentose phosphate pathway (ribose5-P), and triacylglyceride synthesis (glycerol). ...
Document
... they influence membrane fluidity. Know the general structure of membrane lipids. Know the names of the fatty acids and lipids presented in class. You do NOT need to memorize the structure of the individual fatty acids, ethanolamine, or serine. 2. Compare and contrast bacterial,eukaryal, and archaeal ...
... they influence membrane fluidity. Know the general structure of membrane lipids. Know the names of the fatty acids and lipids presented in class. You do NOT need to memorize the structure of the individual fatty acids, ethanolamine, or serine. 2. Compare and contrast bacterial,eukaryal, and archaeal ...
NOTES: Ch 9, part 4
... ● Fats are digested to glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ● An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
... ● Fats are digested to glycerol (used in glycolysis) and fatty acids (used in generating acetyl CoA) ● An oxidized gram of fat produces more than twice as much ATP as an oxidized gram of carbohydrate ...
Lh6Ch11aMembranes
... – The function of biological membranes – The structure and composition membranes and their molecules – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
... – The function of biological membranes – The structure and composition membranes and their molecules – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... or w/o presence of O2 • 2 phases: – Investment phase: use 2 ATP to break up glucose into 2 PGAL (C-C-C-p) – Payoff phase: each PGAL turns into pyruvate (C-C-C) • Each PGAL pyruvate change makes 2 ATPs via substrate level phosphorylation and 1 NADH via redox ...
... or w/o presence of O2 • 2 phases: – Investment phase: use 2 ATP to break up glucose into 2 PGAL (C-C-C-p) – Payoff phase: each PGAL turns into pyruvate (C-C-C) • Each PGAL pyruvate change makes 2 ATPs via substrate level phosphorylation and 1 NADH via redox ...
The Pancreas and Its Functions
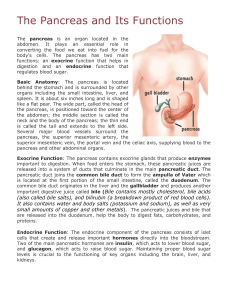
... like a flat pear. The wide part, called the head of the pancreas, is positioned toward the center of the abdomen; the middle section is called the neck and the body of the pancreas; the thin end is called the tail and extends to the left side. Several major blood vessels surround the pancreas, the s ...
... like a flat pear. The wide part, called the head of the pancreas, is positioned toward the center of the abdomen; the middle section is called the neck and the body of the pancreas; the thin end is called the tail and extends to the left side. Several major blood vessels surround the pancreas, the s ...
Pod photosynthesis and seed dark CO2 fixation support oil
... such as phosphofructokinase, phosphoglucoisomerase, glyceraldehyde-3-P-dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate phosphokinase and pyruvate kinase; though showed higher activity in cytosolic fraction, were present in both cytoplasmic and leucoplasitc fractions. These results are consistent with the proposal t ...
... such as phosphofructokinase, phosphoglucoisomerase, glyceraldehyde-3-P-dehydrogenase, phosphoglycerate phosphokinase and pyruvate kinase; though showed higher activity in cytosolic fraction, were present in both cytoplasmic and leucoplasitc fractions. These results are consistent with the proposal t ...
Skill Builder _3a Cellular Respiration 10 Feb 2014
... I. Background: All cells break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules before they can use them. This break down occurs through a series of complex chemical reactions referred to as metabolism. One of the most important of these reactions is known as cellular respiration. Cellular resp ...
... I. Background: All cells break down complex organic compounds into simpler molecules before they can use them. This break down occurs through a series of complex chemical reactions referred to as metabolism. One of the most important of these reactions is known as cellular respiration. Cellular resp ...
Honors Biology Unit 1 Objectives: The Chemistry of Life
... concentration gradients and how kinetic molecular theory explains the motion of the particles described. 4. Given necessary information regarding the concentration of substances (water, gasses, particles, etc.), predict the direction of diffusion (some particles may not be able to diffuse… why?). If ...
... concentration gradients and how kinetic molecular theory explains the motion of the particles described. 4. Given necessary information regarding the concentration of substances (water, gasses, particles, etc.), predict the direction of diffusion (some particles may not be able to diffuse… why?). If ...
Chapter 1
... and adaptation to different environments suggest a wide range of restrictions on protein design, native and non-native alike. In many cases it is necessary to investigate the problem including its environment and the sequence of an individual molecule will not provide sufficient information on its i ...
... and adaptation to different environments suggest a wide range of restrictions on protein design, native and non-native alike. In many cases it is necessary to investigate the problem including its environment and the sequence of an individual molecule will not provide sufficient information on its i ...
PRACTICE SET 6 - UC Davis Plant Sciences
... synthesizing oxidation step. Unsaturations at an even C require both the 2,4-dienoylCoA reductase and an isomerase. This consumes one NADPH. Total 120 + 14 + 27 = 161-2 for activation = 159 ATP ...
... synthesizing oxidation step. Unsaturations at an even C require both the 2,4-dienoylCoA reductase and an isomerase. This consumes one NADPH. Total 120 + 14 + 27 = 161-2 for activation = 159 ATP ...
CHM 303 - Unaab.edu.ng
... fat), which serves as a depot or storage site for lipids. Monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols also exist, but are far less common than the triacylglycerols. Most natural plant and animal fat is composed of mixtures of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. Acylglycerols can be hydrolyzed by heating wi ...
... fat), which serves as a depot or storage site for lipids. Monoacylglycerols and diacylglycerols also exist, but are far less common than the triacylglycerols. Most natural plant and animal fat is composed of mixtures of simple and mixed triacylglycerols. Acylglycerols can be hydrolyzed by heating wi ...
Proteins - chem.uwec.edu
... I prefer to use the term polypeptide to refer to a long chain of amino acids connected by peptide bonds and to reserver the term protein to refer to polypeptides that form a well defined 3-dimensional structure and have a well-defined ...
... I prefer to use the term polypeptide to refer to a long chain of amino acids connected by peptide bonds and to reserver the term protein to refer to polypeptides that form a well defined 3-dimensional structure and have a well-defined ...
ATP
... Only about 1/10th of one percent of the human genome differs from person to person Inborn Errors of Metabolism • Occurs from inheriting a mutation that ...
... Only about 1/10th of one percent of the human genome differs from person to person Inborn Errors of Metabolism • Occurs from inheriting a mutation that ...
7 energy for cells
... c. How many ATP are produced per glucose molecule as a direct result of the citric acid cycle? _____________ d. What coenzymes carry out oxidation of substrates in the citric acid cycle? ______________ e. Considering your answers to these questions, what are the outputs of the citric acid cycle? ___ ...
... c. How many ATP are produced per glucose molecule as a direct result of the citric acid cycle? _____________ d. What coenzymes carry out oxidation of substrates in the citric acid cycle? ______________ e. Considering your answers to these questions, what are the outputs of the citric acid cycle? ___ ...
Amino Acid and Fatty Acid Profile of Twenty Wild Plants
... *Source: Abdou Bouba et al. (2012). Mean values that have the same superscripts letters in the same column are not significantly different level; Mean ± standard deviation; n = 3. ND = Non Detected ...
... *Source: Abdou Bouba et al. (2012). Mean values that have the same superscripts letters in the same column are not significantly different level; Mean ± standard deviation; n = 3. ND = Non Detected ...
Micronutrients - Functions - University of Alaska Fairbanks
... • Vitamin D receptors (VDR) have been identified in cells that play a critical role in the immune system. Specialized white blood cells, known as T-lymphocytes or T-cells, are involved in the recognition of foreign pathogens known as antigens, and coordinating the immune response. • Immune responses ...
... • Vitamin D receptors (VDR) have been identified in cells that play a critical role in the immune system. Specialized white blood cells, known as T-lymphocytes or T-cells, are involved in the recognition of foreign pathogens known as antigens, and coordinating the immune response. • Immune responses ...