Nutrition PowerPoint Presentation
... Note: Appendix is attached between small and large intestine (vestigial organ) ...
... Note: Appendix is attached between small and large intestine (vestigial organ) ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... Glycolysis is the process of Glucose break-down into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm. When pyruvate is further oxidized within the cytoplasm, we call it fermentation. Since the mitochondria are not involved, it is also referred to as anaerobic fermentation or anaerobic metabolism. What are the ...
... Glycolysis is the process of Glucose break-down into pyruvate. It occurs in the cytoplasm. When pyruvate is further oxidized within the cytoplasm, we call it fermentation. Since the mitochondria are not involved, it is also referred to as anaerobic fermentation or anaerobic metabolism. What are the ...
8 Cellular Respiration-2016 ClydeRamloch... 167KB Nov 02 2016
... in oxygen, which is then carried throughout your body by red blood cells. But, some cells grow in environments without oxygen (yeast in wine-making or the bacteria that cause botulism in canned food), and occasionally animal cells must function without sufficient oxygen (as in running sprints). In t ...
... in oxygen, which is then carried throughout your body by red blood cells. But, some cells grow in environments without oxygen (yeast in wine-making or the bacteria that cause botulism in canned food), and occasionally animal cells must function without sufficient oxygen (as in running sprints). In t ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... ● Amino acid degradation in every organ, especially in the liver and muscles ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules ...
... ● Amino acid degradation in every organ, especially in the liver and muscles ● Ammonia secretion (5-10% of whole N turnover) in kidney tubules ...
Summary of Herbicide Mechanism of Action According to the Weed
... allowing 1O2 and 3Chl to abstract a hydrogen from an unsaturated lipid (e.g. membrane fatty acid, chlorophyll) producing a lipid radical. The lipid radical interacts with O2 yielding a peroxidized lipid and another lipid radical. Thus, a self-sustaining chain reaction of lipid peroxidation is initi ...
... allowing 1O2 and 3Chl to abstract a hydrogen from an unsaturated lipid (e.g. membrane fatty acid, chlorophyll) producing a lipid radical. The lipid radical interacts with O2 yielding a peroxidized lipid and another lipid radical. Thus, a self-sustaining chain reaction of lipid peroxidation is initi ...
chapter-23
... used to power life processes because the energy of hydrolysis of ATP is ________. a. intermediate between the energies of hydrolysis of other organophosphate molecules b. small enough that ADP can easily be recycled back to ATP c. large enough to power biologically useful reactions d. All of these. ...
... used to power life processes because the energy of hydrolysis of ATP is ________. a. intermediate between the energies of hydrolysis of other organophosphate molecules b. small enough that ADP can easily be recycled back to ATP c. large enough to power biologically useful reactions d. All of these. ...
A plant has stunted growth and yellowing leaves because it is
... but does not understand that a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen atom and the hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. Aligned to: LO 2.9 CA 2.9: Represent & Model Matter Exchange ...
... but does not understand that a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen atom and the hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. Aligned to: LO 2.9 CA 2.9: Represent & Model Matter Exchange ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... isocitrate which has a secondary -OH, which can be oxidized • Aconitase uses an iron-sulfur cluster to position citrate (binds –OH and carboxyl of central carbon) ...
... isocitrate which has a secondary -OH, which can be oxidized • Aconitase uses an iron-sulfur cluster to position citrate (binds –OH and carboxyl of central carbon) ...
Final Exam, Chem 111 2012 Study Guide
... Learning goals and assessments: 1. Be familiar with reaction rates as they relate to concentrations. a) State the principal factors that control reaction rates. b) Given the rate of change of one reactant or product, calculate rates of change of other reactants or products, and the overall reaction ...
... Learning goals and assessments: 1. Be familiar with reaction rates as they relate to concentrations. a) State the principal factors that control reaction rates. b) Given the rate of change of one reactant or product, calculate rates of change of other reactants or products, and the overall reaction ...
Vertebrate digestion note
... carbohydrates – more amylase is released to continue breakdown of starches that began in the mouth – a series of disaccharide enzymes complete the breakdown of carbohydrates. proteins – trypsinogen is released by the pancreas, and is converted to trypsin by enterokinase, an enzyme ...
... carbohydrates – more amylase is released to continue breakdown of starches that began in the mouth – a series of disaccharide enzymes complete the breakdown of carbohydrates. proteins – trypsinogen is released by the pancreas, and is converted to trypsin by enterokinase, an enzyme ...
What happened to my cousin Patrick O’Neill?
... – phosphate groups require low energy to break – new bonds formed release more energy than the energy required to break the bond ...
... – phosphate groups require low energy to break – new bonds formed release more energy than the energy required to break the bond ...
16N-containing Substances
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole rings. *Distribution of side chains: different types I, II, III, IV of porphyrins. ...
... -Side chains: different porphyrins vary of the side chain that are attached to pyrrole rings. *Distribution of side chains: different types I, II, III, IV of porphyrins. ...
No Slide Title
... does not change and determines the atoms identity. When P = 5 the element is B (boron) Mass Number (atomic mass)- ( P + N) This is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotope - This is an atom of an element where the number of neutrons have ...
... does not change and determines the atoms identity. When P = 5 the element is B (boron) Mass Number (atomic mass)- ( P + N) This is the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotope - This is an atom of an element where the number of neutrons have ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... amino acids, nucleobases, sugars, lipids, oligomers of biochemical compounds ...
... amino acids, nucleobases, sugars, lipids, oligomers of biochemical compounds ...
Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth
... Disaccharides are formed between glucose and other monosaccharides Glucose liberated through hydrolysis enters glycolysis Other monosaccharide modified before metabolism ...
... Disaccharides are formed between glucose and other monosaccharides Glucose liberated through hydrolysis enters glycolysis Other monosaccharide modified before metabolism ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Amino acids can form amide bonds by condensation between carboxyl group and amino group as shown in Fig. 2.1. The amide bonds are specifically called the peptide bonds. If two amino acids are condensed, the product is called as dipeptide. When another amino acid condenses to this dipeptide, a tripep ...
... Amino acids can form amide bonds by condensation between carboxyl group and amino group as shown in Fig. 2.1. The amide bonds are specifically called the peptide bonds. If two amino acids are condensed, the product is called as dipeptide. When another amino acid condenses to this dipeptide, a tripep ...
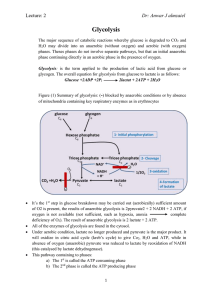
Dr: Anwar J almzaiel Glycolysis
... It’s the 1st step in glucose breakdown may be carried out (aerobically) sufficient amount of O2 is present, the results of anaerobic glycolysis is 2pyruvate2 + 2 NADH + 2 ATP, if oxygen is not available (not sufficient, such as hypoxia, anoxia complete deficiency of O2). The result of anaerobic glyc ...
... It’s the 1st step in glucose breakdown may be carried out (aerobically) sufficient amount of O2 is present, the results of anaerobic glycolysis is 2pyruvate2 + 2 NADH + 2 ATP, if oxygen is not available (not sufficient, such as hypoxia, anoxia complete deficiency of O2). The result of anaerobic glyc ...
Friday`s presentation.
... energy stored in the concentration gradient of H+ ions (i.e., protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP ...
... energy stored in the concentration gradient of H+ ions (i.e., protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP ...
Bio150 Chapter 7
... •During the first 2 phases of glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, a molecule of glucose is gradually broken apart in 20 sequential biochemical reactions which transforms the glucose into different carbohydrate intermediates as bonds are broken or rearranged -4 molecules of ATP are synthesized as a resu ...
... •During the first 2 phases of glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, a molecule of glucose is gradually broken apart in 20 sequential biochemical reactions which transforms the glucose into different carbohydrate intermediates as bonds are broken or rearranged -4 molecules of ATP are synthesized as a resu ...
Slide 1
... energy stored in the concentration gradient of H+ ions (i.e., protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP ...
... energy stored in the concentration gradient of H+ ions (i.e., protons) across the inner membrane, which is relatively impermeable to H+. b. The H+ ions tend to move down their concentration gradient toward the matrix of the mitochondrion. Movement through the ATP synthase is used to generate the ATP ...
Chapter 7 - Medical Image Analysis
... regulation of the activity of transporters and enzymes involved in glucose and fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle. We know that the activity of transporters and enzymes is not only modulated by means of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, but also by translocation from one subcellular compartme ...
... regulation of the activity of transporters and enzymes involved in glucose and fatty acid metabolism in skeletal muscle. We know that the activity of transporters and enzymes is not only modulated by means of phosphorylation/dephosphorylation, but also by translocation from one subcellular compartme ...
DOMALKYD 1666 75 D-60 Alkyd resin modified with
... Domalkyd 1666 75 D-60 is a low viscosity drying alkyd resin for high quality air drying gloss paints. Due to the low viscosity and good pigment wetting properties paints have good flow, excellent brushability and fullness. It is used as a general purpose binder in enamels for wood and metal, for ind ...
... Domalkyd 1666 75 D-60 is a low viscosity drying alkyd resin for high quality air drying gloss paints. Due to the low viscosity and good pigment wetting properties paints have good flow, excellent brushability and fullness. It is used as a general purpose binder in enamels for wood and metal, for ind ...
What Do I already know about Prehistoric Cultures?
... •amino acids are the building blocks of protein • human tissue contains 22 different amino acids • 13 can be made by the body • 9 of the 22 must be obtained from foods ...
... •amino acids are the building blocks of protein • human tissue contains 22 different amino acids • 13 can be made by the body • 9 of the 22 must be obtained from foods ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology II
... Used immediately for ATP production Stored as glycogen in liver or skeletal muscle Leftover: forms triglycerides in adipose tissue ...
... Used immediately for ATP production Stored as glycogen in liver or skeletal muscle Leftover: forms triglycerides in adipose tissue ...