103 Lecture Ch20b
... held together by the same forces involved in tertiary structure • For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein that consists of four subunits, of two different types - each subunit contains a heme group for O2 binding ...
... held together by the same forces involved in tertiary structure • For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein that consists of four subunits, of two different types - each subunit contains a heme group for O2 binding ...
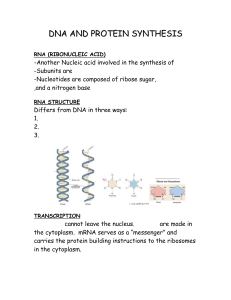
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Proteins
... Defensive (Protect): antibodies (IgG), fibrinogen & thrombin, snake venoms, bacterial toxins Regulatory (Signal): regulate metabolic processes, hormones, transcription factors & enhancers, growth factor proteins ...
... Defensive (Protect): antibodies (IgG), fibrinogen & thrombin, snake venoms, bacterial toxins Regulatory (Signal): regulate metabolic processes, hormones, transcription factors & enhancers, growth factor proteins ...
1.Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an
... 1. Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an unsaturated fat. 2. Identify and describe the four levels of protein structure. 3. Speculate (predict) on why a change in pH or Na+ concentration could cause a protein to lose its secondary or tertiary structure and denature. 4. Disc ...
... 1. Contrast and compare the structure of a saturated fat versus an unsaturated fat. 2. Identify and describe the four levels of protein structure. 3. Speculate (predict) on why a change in pH or Na+ concentration could cause a protein to lose its secondary or tertiary structure and denature. 4. Disc ...
MCB Lecture 2 – Amino Acids and Proteins
... Quaternary Structure – Multiple protein subunits bound together to form a 3dimensional shape. Hydropathy Plot – A plot that determines how hydrophobic particular amino acids are in a chain. Above the x-axis is most hydrophobic, and below the xaxis is hydrophilic. What is the maximal UV absorption of ...
... Quaternary Structure – Multiple protein subunits bound together to form a 3dimensional shape. Hydropathy Plot – A plot that determines how hydrophobic particular amino acids are in a chain. Above the x-axis is most hydrophobic, and below the xaxis is hydrophilic. What is the maximal UV absorption of ...
Name__________________________________
... 7. Organisms can have thousands of types of proteins that form cellular structures or act as chemical messengers. Describe how a cell can create so many kinds of proteins. ...
... 7. Organisms can have thousands of types of proteins that form cellular structures or act as chemical messengers. Describe how a cell can create so many kinds of proteins. ...
The Synthesis and Expression of Peptide CbnY Thomas Doerksen
... recently isolated and reported, but initial structural studies and sequence homology suggests that it is part of a two-component bacteriocin. To test this hypothesis, the proposed second component CbnY, a 33 amino acid peptide predicted by genetics, was prepared by both solid phase peptide synthesis ...
... recently isolated and reported, but initial structural studies and sequence homology suggests that it is part of a two-component bacteriocin. To test this hypothesis, the proposed second component CbnY, a 33 amino acid peptide predicted by genetics, was prepared by both solid phase peptide synthesis ...
`Super yeasts` produce 300 times more protein than
... amino acids to make proteins. Scientists have made additional amino acids, the UAAs, which show promise for building new proteins with a broad range of medical and industrial applications. However, researchers had had difficulty in efficiently incorporating these UAAs into useful protein products. W ...
... amino acids to make proteins. Scientists have made additional amino acids, the UAAs, which show promise for building new proteins with a broad range of medical and industrial applications. However, researchers had had difficulty in efficiently incorporating these UAAs into useful protein products. W ...
Slide 1 - helmricht
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
... Denaturation- the loss of the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of a protein by chemical or physical agent that leaves the primary structure intact Enzymes lose their catalytic activity and other proteins can’t carry out their biological functions when denatured ...
Section 2 Molecules of Life
... histidine hydroxyproline isoleucine leucine lysine methionine phenylalanine proline serine threonine tryptophan tyrosine valine ...
... histidine hydroxyproline isoleucine leucine lysine methionine phenylalanine proline serine threonine tryptophan tyrosine valine ...
Self Test Quiz-1 Given below are some questions related to protein
... Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain carbon, hydrogen, ox ...
... Given below are some questions related to protein and enzymes in general. Each statement is followed by 4 choices. Choose a single correct answer for each question. 1. How many different types of amino acid are used to make proteins? a. 4 b. 20 c. 23 d. 38 2. Amino acids contain carbon, hydrogen, ox ...
Biological Catalysts
... covalent bonds (disulphide bridges) & hydrophobic interactions between the amino acid side chains. Enzymes are tertiary structures, and not quaternary as they contain just one polypeptide chain rather than several polypeptides that make up the quaternary structure. ...
... covalent bonds (disulphide bridges) & hydrophobic interactions between the amino acid side chains. Enzymes are tertiary structures, and not quaternary as they contain just one polypeptide chain rather than several polypeptides that make up the quaternary structure. ...
proteins - SD57 Mail
... • Ex. Keratin in hair and nails; collagen in skin; actin and myosin in muscle ...
... • Ex. Keratin in hair and nails; collagen in skin; actin and myosin in muscle ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
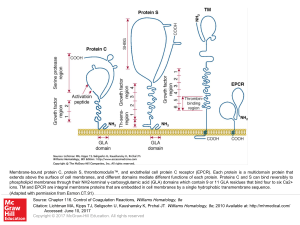
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
... Membrane-bound protein C, protein S, thrombomodulin™, and endothelial cell protein C receptor (EPCR). Each protein is a multidomain protein that extends above the surface of cell membranes, and different domains mediate different functions of each protein. Proteins C and S can bind reversibly to pho ...
Name: Ch 6 Take Home Quiz Due: 3/22/13 Multiple
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to provide energy. 9) A rare genetic disorder, phenyl ...
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true of non-essential amino acids? A) They are synthesized by the body. B) They are not necessary for protein synthesis. C) There are 11 amino acids that belong to this group. D) They can be broken down to provide energy. 9) A rare genetic disorder, phenyl ...
Macromolecules Review Worksheet Answer Key
... Part A. Classify each as a carbohydrate or protein 1. C ...
... Part A. Classify each as a carbohydrate or protein 1. C ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
Proteinler - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... cleaves at COOH end of Lys and Arg cleaves at COOH end of Phe, Tyr, Trp ...
... cleaves at COOH end of Lys and Arg cleaves at COOH end of Phe, Tyr, Trp ...
Digestion of Biomolecules
... Hydrolysis Reactions • Proteins amino acids – Proteases, peptidases ...
... Hydrolysis Reactions • Proteins amino acids – Proteases, peptidases ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.