custom protein production service
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
... CUSTOM PROTEIN PRODUCTION SERVICE Highly specialized custom production service Our experience in recombinant protein production for your research! ...
bioinformatics lec10student
... Fewer than 50 aa called peptide More than 50 is called protein Insulin is 53 aa long Is it a peptide or protein hormone? ...
... Fewer than 50 aa called peptide More than 50 is called protein Insulin is 53 aa long Is it a peptide or protein hormone? ...
Protein Digestion and Absorption
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
... Proteins are sequences of amino acids (AA) linked by peptide bonds. There are twenty amino acids of which nine are essential and eleven are non-essential. Essential amino acids include phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, isoleucine, methionine, leucine, lysine, and histidine. These AA are ...
analysis of a local huntington protein interaction network
... protein. This study sheds light on possible functions for the huntingtin protein though analysis of a local protein-protein interaction network consisting of the huntingtin protein, proteins called primaries that have been found to interact with the huntingtin protein and secondary proteins that int ...
... protein. This study sheds light on possible functions for the huntingtin protein though analysis of a local protein-protein interaction network consisting of the huntingtin protein, proteins called primaries that have been found to interact with the huntingtin protein and secondary proteins that int ...
Learning Target: I can analyze and teach my classmates about Radon.
... • In the respiratory system, hemoglobin (composed of four protein subunits) transports oxygen for use in cellular metabolism. • The proteins actin and tubulin form cellular structures , while keratin forms the structural support for the dead cells that become fingernails and hair. • Antibodies help ...
... • In the respiratory system, hemoglobin (composed of four protein subunits) transports oxygen for use in cellular metabolism. • The proteins actin and tubulin form cellular structures , while keratin forms the structural support for the dead cells that become fingernails and hair. • Antibodies help ...
Protein Synthesis Project - Lin
... below, remember A-U and C-G. t-RNA : ________________________________________________________________________ _____ ________________________________________________________________________ _____ ...
... below, remember A-U and C-G. t-RNA : ________________________________________________________________________ _____ ________________________________________________________________________ _____ ...
Organic Biomolecules Fill in Notes 2016
... • Commonly called sugars • Only contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio of 1:2:1 Example: formula for glucose is C6H12O6 ...
... • Commonly called sugars • Only contain the elements carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a specific ratio of 1:2:1 Example: formula for glucose is C6H12O6 ...
CH 107 SI Summer 2015 Worksheet 13 Answers What are the two
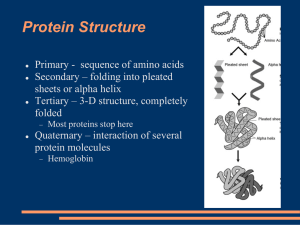
... 1. What are the two major types of secondary protein structure and what bonds are present in each? α-helices and β-sheets Hydrogen bonds 2. What types of interactions can be present in tertiary protein structure? Rank the interactions from strongest to weakest. disulfide bonds >> salt bridges > hydr ...
... 1. What are the two major types of secondary protein structure and what bonds are present in each? α-helices and β-sheets Hydrogen bonds 2. What types of interactions can be present in tertiary protein structure? Rank the interactions from strongest to weakest. disulfide bonds >> salt bridges > hydr ...
Digestion Review Outline
... Digestion Review Outline I. Nutrients Some compounds (food) we eat are too large to diffuse into cells so they need to be digested (broken down). A. Carbohydrates or starches (broken down into building blocks simple sugars, or glucose) B. Proteins (broken down into building blocks amino acids) C. Li ...
... Digestion Review Outline I. Nutrients Some compounds (food) we eat are too large to diffuse into cells so they need to be digested (broken down). A. Carbohydrates or starches (broken down into building blocks simple sugars, or glucose) B. Proteins (broken down into building blocks amino acids) C. Li ...
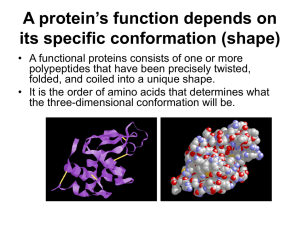
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
PDF - Available Technologies
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
... Production of recombinant protein or gene products in bacteria or other cells is dramatically increased when the TEnBOX is incorporated into the plasmid vector. The efficiency of the protein expression from the TEnBOX is much higher than reported with the best commercial vectors (pET-21 and pTriEX-3 ...
Proteins and Nucleic Acids
... • Is the active site the same for all enzymes and substrates? NO! Only a certain substrate fits into a particular active site ...
... • Is the active site the same for all enzymes and substrates? NO! Only a certain substrate fits into a particular active site ...
Chapter 2 SWBATS Content Standards Cell Biology 1. The
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
... What are the two main types of chemical bonds? Give an example of each. Why are water molecules polar? What are acidic solutions? What are basic solutions? Give an example of each. What are the functions of each group of organic compounds? What happens to chemical bonds during chemical reactions? Ho ...
Competition
... together There are only 20 types of amino acids, but there are millions of proteins. Therefore the number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, nuts). These 8 are called Essential Amino ...
... together There are only 20 types of amino acids, but there are millions of proteins. Therefore the number of amino acids, and their sequence determine the protein. Only 12 of the amino acids can be made by our body, the rest have to come from our food (meat, nuts). These 8 are called Essential Amino ...
Chapter 3 - Proteins
... • Name one polar and one nonpolar amino acid, then make a list of all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or gr ...
... • Name one polar and one nonpolar amino acid, then make a list of all the additional amino acids that you remember. • What are the four weak (noncovalent) interactions that determine the conformation of a protein? • (True/False) A protein is at a near entropy minimum (point of lowest disorder, or gr ...
Proteins
... Functional molecules – like integral proteins and hemoglobin to transport molecules Enzymes – biological catalysts speeding up chemical reactions within the body Protection – immunoglobulins in the immune system protect against bacterial infections and diseases like cancer Also Protection – fibrin i ...
... Functional molecules – like integral proteins and hemoglobin to transport molecules Enzymes – biological catalysts speeding up chemical reactions within the body Protection – immunoglobulins in the immune system protect against bacterial infections and diseases like cancer Also Protection – fibrin i ...
Chapter 5 – Proteins and Amino Acids
... D. Protein Recommendations and Nitrogen Balance 1. Protein on Food Labels 2. Nitrogen Balance Protein in Foods A. Protein Quality 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetaria ...
... D. Protein Recommendations and Nitrogen Balance 1. Protein on Food Labels 2. Nitrogen Balance Protein in Foods A. Protein Quality 1. Digestibility 2. Amino Acid Composition 3. High-Quality Proteins 4. Complementary Proteins B. Protein Sparing Nutrition in Practice – Vegetarian Diets A. Are vegetaria ...
Proteolysis
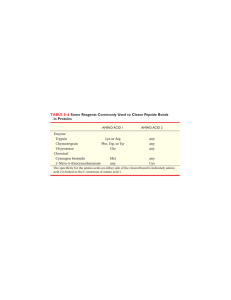
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.