The amino acids, peptide bonds, and the primary structure of proteins
... • If you know the pH and pKa, you can determine whether an amino acid is charged or uncharged ...
... • If you know the pH and pKa, you can determine whether an amino acid is charged or uncharged ...
Covalent Reactions Atoms SHARE electrons
... • Collagen- ligaments, tendons, skin • Many hormones • Actin and Myosin- allow muscles to contract • Hemoglobin- transport oxygen in blood • Antibodies in the blood • Allow movement through cell membrane • Enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) ...
... • Collagen- ligaments, tendons, skin • Many hormones • Actin and Myosin- allow muscles to contract • Hemoglobin- transport oxygen in blood • Antibodies in the blood • Allow movement through cell membrane • Enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) ...
" Exploring the Unique Dual Function and the Evolutionary
... Instituto Mercedes y Martín Ferreyra, Argentina Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of G ...
... Instituto Mercedes y Martín Ferreyra, Argentina Endocytosis and lysosomal protein trafficking is essential in pathogenic parasites since it is directly linked to vital parasite-specific processes, e.g. host cell invasion, nutrition, and cell differentiation into resistant stages, as in the case of G ...
MTC25 - Intracellular Processing
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
... Once inside the rough ER, new proteins undergo a series of post-translational modifications depending on their ultimate destination and function, including glycosylation of 14 N-linked sugars and formation of tertiary structure under the supervision of chaperones (a large class of ATP-hydrolysing pr ...
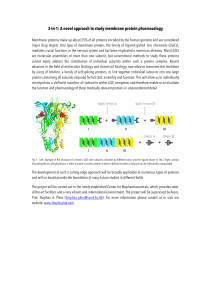
3-in-1: A novel approach to study membrane protein pharmacology
... major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGICs are molecular assemblies of more than one subunit, but conventional methods to study these prote ...
... major drug targets. One type of membrane protein, the family of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs), mediates crucial functions in the nervous system and has been implicated a numerous diseases. Most LGICs are molecular assemblies of more than one subunit, but conventional methods to study these prote ...
A Crash Course on Enzymology
... unaffected. What could be a cause why Todd is affected but Kevin isn’t? ...
... unaffected. What could be a cause why Todd is affected but Kevin isn’t? ...
Document
... How do amino acids bind together to form a dipeptide? Draw the process • Condensation synthesis! Peptide Bonds: – form between amino acids & join them – Amine group combines with carboxyl group of next amino acid – Atoms of O,C, C & H share electrons (unevenly) – Polar bond (O is more neg, H is mor ...
... How do amino acids bind together to form a dipeptide? Draw the process • Condensation synthesis! Peptide Bonds: – form between amino acids & join them – Amine group combines with carboxyl group of next amino acid – Atoms of O,C, C & H share electrons (unevenly) – Polar bond (O is more neg, H is mor ...
amino acids
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
... ● results in a “backbone” with a repeating pattern of sugar-phosphatesugar-phosphate... ...
A dead-end street of protein folding
... A dead-end street of protein folding? András Perczel, Villő Pálfi and Péter Hudáky Laboratory of Structural Chemistry and Biology, Institute of Chemistry; Eötvös University, Budapest 112, P.O. Box 32, H-1518, HUNGARY Amino acid sequences of globular proteins encode their 3D-structures linked to thei ...
... A dead-end street of protein folding? András Perczel, Villő Pálfi and Péter Hudáky Laboratory of Structural Chemistry and Biology, Institute of Chemistry; Eötvös University, Budapest 112, P.O. Box 32, H-1518, HUNGARY Amino acid sequences of globular proteins encode their 3D-structures linked to thei ...
04b Carbohydrates-student note
... can be produced by __________________________ organisms from CO2, H2O, sunlight store ____________ in chemical bonds, which is released during cellular respiration Characteristics of a sugar: An _____________________ attached to each carbon except one, which double bonded to an oxygen (_______ ...
... can be produced by __________________________ organisms from CO2, H2O, sunlight store ____________ in chemical bonds, which is released during cellular respiration Characteristics of a sugar: An _____________________ attached to each carbon except one, which double bonded to an oxygen (_______ ...
TABLE 3–1 Some Common Types of Enzymes
... general name used for enzymes that synthesize molecules in anabolic reactions by condensing two smaller molecules together. catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups ...
... general name used for enzymes that synthesize molecules in anabolic reactions by condensing two smaller molecules together. catalyze the rearrangement of bonds within a single molecule. catalyze polymerization reactions such as the synthesis of DNA and RNA. catalyze the addition of phosphate groups ...
Proteins - TC Online
... function This shape is dependant on the amino acid sequence (primary structure), the kinking and twisting of the chain (secondary structure), the folding of the chain (tertiary structure), and interaction with other proteins (quaternary structure) Hemoglobin example ...
... function This shape is dependant on the amino acid sequence (primary structure), the kinking and twisting of the chain (secondary structure), the folding of the chain (tertiary structure), and interaction with other proteins (quaternary structure) Hemoglobin example ...
Chapt 2
... 1. polar, non-charged 2. polar, charged 3. nonpolar 4. glycine 5. proline Hydrogen bonds can occur between which of the following molecules: 1. The sulfhydral in cysteine and the hydroxyl of serine 2. Two parts of the peptide backbone of a protein 3. The phosphodiester backbone of two strands of nuc ...
... 1. polar, non-charged 2. polar, charged 3. nonpolar 4. glycine 5. proline Hydrogen bonds can occur between which of the following molecules: 1. The sulfhydral in cysteine and the hydroxyl of serine 2. Two parts of the peptide backbone of a protein 3. The phosphodiester backbone of two strands of nuc ...
Nanoscale localisation of a Candida albicans peptide
... Institute of Physical Chemistry and Abbe center of Photonics, Friedrich Schiller University Lessingstrasse 10, 07743 Jena, Germany ...
... Institute of Physical Chemistry and Abbe center of Photonics, Friedrich Schiller University Lessingstrasse 10, 07743 Jena, Germany ...
BIO 6.3 Carbon - Steinbach Science
... Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) or C—H bonds and less oxygen than carbohydrates (e.g., beef fat has the formula C57H110O6) Lipids are commonly call ...
... Lipids are organic compounds that have a large portion (much greater than 2 to 1) or C—H bonds and less oxygen than carbohydrates (e.g., beef fat has the formula C57H110O6) Lipids are commonly call ...
aliphatic amino acid structures
... Cleaving the polypeptide chain Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Locating disulfide bond ...
... Cleaving the polypeptide chain Sequencing of peptides Ordering peptide fragments Locating disulfide bond ...
Proteins
... 8) What is the general name of a protein that catalyzes (speeds up) chemical reactions? _enzyme____ 9) Give a more specific name for a protein in your digestive system that speeds hydrolysis of lipids. ___lipase __________ 10) What happens to the structure of a protein as it is heated to a high temp ...
... 8) What is the general name of a protein that catalyzes (speeds up) chemical reactions? _enzyme____ 9) Give a more specific name for a protein in your digestive system that speeds hydrolysis of lipids. ___lipase __________ 10) What happens to the structure of a protein as it is heated to a high temp ...
of proteins
... A typical example of a quaternary structure of the protein is hemoglobin or the protein that is responsible to carry oxygen, contained in our red blood cells. It consists of two different types of peptide chains (alpha and beta). Furthermore, each chain contains in its interior a non-protein molecu ...
... A typical example of a quaternary structure of the protein is hemoglobin or the protein that is responsible to carry oxygen, contained in our red blood cells. It consists of two different types of peptide chains (alpha and beta). Furthermore, each chain contains in its interior a non-protein molecu ...
Homeostasis and Biochemistry
... Proteins So what are the building blocks of enzymes Amino Acids Every enzymes acts upon only One Substance ...
... Proteins So what are the building blocks of enzymes Amino Acids Every enzymes acts upon only One Substance ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.