Biomolecules Review Game
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
... What are the names of these functional Groups found at either end of every Amino acid molecule? ...
proteinszednii
... function performed by a cell, including regulation of cellular functions such as signal transduction and metabolism • The protein involved in functions control almost all the molecular processes of the ...
... function performed by a cell, including regulation of cellular functions such as signal transduction and metabolism • The protein involved in functions control almost all the molecular processes of the ...
Abstract - BMB Reports
... The ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy lysosome system are the two major protein degradation machineries in eukaryotic cells. These two systems coordinate the removal of unwanted intracellular materials, but the mechanism by which they achieve this coordination is largely unknown. The ubi ...
... The ubiquitin-proteasome system and the autophagy lysosome system are the two major protein degradation machineries in eukaryotic cells. These two systems coordinate the removal of unwanted intracellular materials, but the mechanism by which they achieve this coordination is largely unknown. The ubi ...
Biochem-5012.3B - Center for Structural Biology
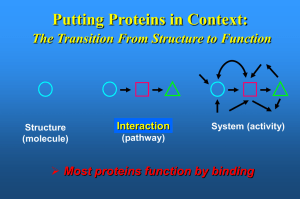
... Putting Proteins in Context: The Transition From Structure to Function ...
... Putting Proteins in Context: The Transition From Structure to Function ...
intracellular protein synthesis, post
... The proteasome is the primary site in cells for the complete degradation of cell proteins and for production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into th ...
... The proteasome is the primary site in cells for the complete degradation of cell proteins and for production of most antigenic peptides presented to the immune system on MHC-class I molecules. In this process, intracellular proteins are degraded to 8-9 residue fragments, are then transported into th ...
Protein Metabolism
... •Occurred by proteolytic enzymes (proteases), synthesised as larger, inactive forms known as zymogens. After zymogens are secreted into the digestive tract, they are cleaved to produce the active proteases. •Dietary proteins are denatured as a result of acidic environment of the stomach (pH is about ...
... •Occurred by proteolytic enzymes (proteases), synthesised as larger, inactive forms known as zymogens. After zymogens are secreted into the digestive tract, they are cleaved to produce the active proteases. •Dietary proteins are denatured as a result of acidic environment of the stomach (pH is about ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
... molecules such as the muscle protein titin, with 34,350 amino acids. ...
Moonlighting and pleiotropy among regulators of the degradation
... features. Each of the two complexes is involved in a distinct cellular activity: the CSN promotes the function of a large family of ubiquitin E3 ligases known as CRLs, while the proteasome lid is required for ubiquitin hydrolysis from proteasome substrates before degradation. Both complexes determin ...
... features. Each of the two complexes is involved in a distinct cellular activity: the CSN promotes the function of a large family of ubiquitin E3 ligases known as CRLs, while the proteasome lid is required for ubiquitin hydrolysis from proteasome substrates before degradation. Both complexes determin ...
IB2.14.3 Building a protein
... proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
... proteins. Skin, muscles, bone, cartilage, ligaments and cell membranes all contain a lot of protein. In addition, other proteins do important jobs in cells. All protein molecules contain the elements: Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Nitrogen ...
organic molecules : proteins - Mr. Lesiuk
... - The second or Secondary Structure takes place as the chains of amino acids get longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
... - The second or Secondary Structure takes place as the chains of amino acids get longer they begin to twist into a spiral. (called an alpha helix). ...
Functions
... Regulating cell processes (enzymes). •Enough amino acids connected together will Forming bones and muscles. cause the protein to fold and create a new Transporting substances into or out of cells. shape Helping to fight disease (antibodies). Function is determined by shape! Elements: ...
... Regulating cell processes (enzymes). •Enough amino acids connected together will Forming bones and muscles. cause the protein to fold and create a new Transporting substances into or out of cells. shape Helping to fight disease (antibodies). Function is determined by shape! Elements: ...
3.2 Proteins - Biology with Radjewski
... • Transport proteins carry substances (e.g., hemoglobin) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed ...
... • Transport proteins carry substances (e.g., hemoglobin) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed ...
Amino acids
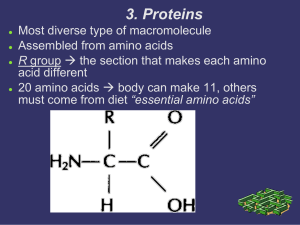
... Video: http://viewpure.com/2Jgb_DpaQhM • Proteins • most diverse of all biological molecules • made by bonding amino acids together is specific orders • Amino acids • monomers (building blocks) of proteins • over 500 different AA are known • 20 AA are standard and make many different kinds of prote ...
... Video: http://viewpure.com/2Jgb_DpaQhM • Proteins • most diverse of all biological molecules • made by bonding amino acids together is specific orders • Amino acids • monomers (building blocks) of proteins • over 500 different AA are known • 20 AA are standard and make many different kinds of prote ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
... o Hydrophobic side chains orient themselves so that they are minimally exposed to water in the protein’s interior ...
Proteins*
... Two amino acids linked together are called dipeptides More than 2 linked together are called polypeptides polypeptides can be thousands of amino acids long ...
... Two amino acids linked together are called dipeptides More than 2 linked together are called polypeptides polypeptides can be thousands of amino acids long ...
BL 616 Test 1 study guide. The test will probably have 20 multiple
... Ch 6-7 amino acids, protein structure Be able to draw generic amino acid, peptide bond between two amino acids You will be provided with a diagram of the amino acid side chains if that is needed Describe the different levels of protein structure – what is quaternary What is difference between a poly ...
... Ch 6-7 amino acids, protein structure Be able to draw generic amino acid, peptide bond between two amino acids You will be provided with a diagram of the amino acid side chains if that is needed Describe the different levels of protein structure – what is quaternary What is difference between a poly ...
Life’s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon 8/25/2011 1
... fibers that make up connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments. • Contractile proteins: Found in muscles • Defensive proteins: The antibodies of the immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
... fibers that make up connective tissues such as tendons and ligaments. • Contractile proteins: Found in muscles • Defensive proteins: The antibodies of the immune system • Signal proteins: Such as hormones that coordinate body activity ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.