Cell Bio/Physio Lecture 6 Objectives Sunday, August 14, 2011 11:41
... Motifs: Each individual protein has a segment that binds to the DNA molecules, and a different segment that binds to its partner protein; DNA binding is highly specific; The geometry of the amino acid sequence matches exactly the geometry of the DNA sequence, allowing for this specific binding. Zi ...
... Motifs: Each individual protein has a segment that binds to the DNA molecules, and a different segment that binds to its partner protein; DNA binding is highly specific; The geometry of the amino acid sequence matches exactly the geometry of the DNA sequence, allowing for this specific binding. Zi ...
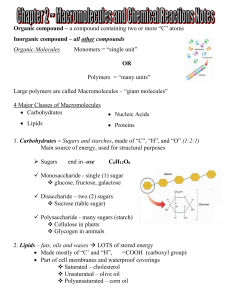
Amino Acids
... Amino Acids • Amino acids are building blocks for proteins • They have a central α-carbon and α-amino and αcarboxyl groups • 20 different amino acids • Same core structure, but different side group (R) • The α-C is chiral (except glycine); proteins contain only L-isoforms. • Amino acids are ampholyt ...
... Amino Acids • Amino acids are building blocks for proteins • They have a central α-carbon and α-amino and αcarboxyl groups • 20 different amino acids • Same core structure, but different side group (R) • The α-C is chiral (except glycine); proteins contain only L-isoforms. • Amino acids are ampholyt ...
Exam 1
... 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate bindi ...
... 27. The technique called the Edman Degradation can be used to sequence polypeptides by identifying the amino acid at the _______________________ end of the peptide. 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate bindi ...
Classification of Amino Acids
... Translation from DNA sequence DNA sequence protein sequence Protein sequence cloning of the gene ...
... Translation from DNA sequence DNA sequence protein sequence Protein sequence cloning of the gene ...
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Compounds - Linn
... Proteins that carry other molecules from one place to another ...
... Proteins that carry other molecules from one place to another ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
... Hypotheses for molecular basis of bipolar disorder •Suggest problem lies in protein targeting Proteins made in cytosol (cytosolic and membrane ones) Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 2. What are the monomers of proteins? 3. Draw and label the levels of organization of the protein structure. 4. What types of atoms are found in proteins? 5. Draw the general structure for an amino acid and label its functional groups. 6. Which part of an amino acid determines its specific propertie ...
... 2. What are the monomers of proteins? 3. Draw and label the levels of organization of the protein structure. 4. What types of atoms are found in proteins? 5. Draw the general structure for an amino acid and label its functional groups. 6. Which part of an amino acid determines its specific propertie ...
proteins and protein structure
... Hemoglobin is comprised of four polypeptide subunits (each has tertiary structure). All four components carry a heme group that can bind to oxygen, and all four components must be present to form hemoglobin. The shape of the hemoglobin affects its ability to carry oxygen, and travel freely throughou ...
... Hemoglobin is comprised of four polypeptide subunits (each has tertiary structure). All four components carry a heme group that can bind to oxygen, and all four components must be present to form hemoglobin. The shape of the hemoglobin affects its ability to carry oxygen, and travel freely throughou ...
Biochemistry File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
... 4. Proteins – polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds Used to build cells, transport molecules, and control the rate of reactions Made of “C”, “H”, “O”, and “N” 20 different amino acids ...
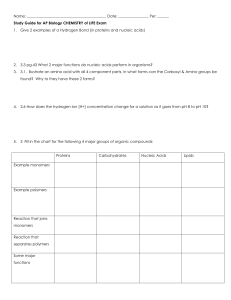
Name: Date: Per: ______ Study Guide for AP Biology CHEMISTRY
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
... 1. Give 2 examples of a Hydrogen Bond (in proteins and nucleic acids) ...
How Did Life Begin? Unit Objectives Vocabulary: Miller
... o List the two components of cell theory and explain how they apply to the fossil record explored in unit 1 and the origin of life itself. o Explain the origin of organic molecules from inorganic matter. o Describe the Miller-Urey experiment, what it tested, and what the results indicate. o Describe ...
... o List the two components of cell theory and explain how they apply to the fossil record explored in unit 1 and the origin of life itself. o Explain the origin of organic molecules from inorganic matter. o Describe the Miller-Urey experiment, what it tested, and what the results indicate. o Describe ...
Chapter 17 (part 2) - University of Nevada, Reno
... ubiquitin marks that protein for destruction ...
... ubiquitin marks that protein for destruction ...
Proteins are made of subunits called amino acids and are
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
... COLOR and LABEL the parts of a nucleotide --- sugar (5-sided)-green, phosphate group (round)yellow, and nitrogen base (6-sided)-blue. ATP used for cellular energy is a high energy nucleotide with three phosphate groups. Color code the ATP and LABEL THE PHOSPHATES. ...
martakmalina proteins
... the building blocks of proteins. Mammals cannot synthesize all 20 amino acids, so protein from the diet is necessary for life and the amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body are known as essential amino acids. The exact amount of dietary protein needed for life may vary widely depending o ...
... the building blocks of proteins. Mammals cannot synthesize all 20 amino acids, so protein from the diet is necessary for life and the amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body are known as essential amino acids. The exact amount of dietary protein needed for life may vary widely depending o ...
Study Guide-Carbon, monomers, polymers, amino acids, proteins
... -How many monomers are there if given amount of water removed or added? -What bond forms between monomers? -In order for both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis to proceed fast enough to be of value, what is needed? c. Structure of amino acids -What is the monomer of a protein? -How many amino aci ...
... -How many monomers are there if given amount of water removed or added? -What bond forms between monomers? -In order for both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis to proceed fast enough to be of value, what is needed? c. Structure of amino acids -What is the monomer of a protein? -How many amino aci ...
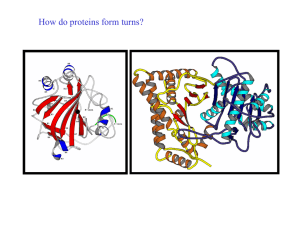
How do proteins form turns? - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
... A reverse turn is region of the polypeptide having a hydrogen bond from one main chain carbonyl oxygen to the main chain N-H group 3 residues along the chain (i.e. O(i) to N(i+3)) Helical regions are excluded from this definition (see later) Reverse turns are very abundant in globular proteins and g ...
$doc.title
... Understanding protein folding is essential in biochemical research. Several diseases are a result of incorrect protein folding and can ultimately lead to the formation of protein aggregates1. Chaperone proteins can assist proper protein folding as a protein matures, but once protein aggregates form ...
... Understanding protein folding is essential in biochemical research. Several diseases are a result of incorrect protein folding and can ultimately lead to the formation of protein aggregates1. Chaperone proteins can assist proper protein folding as a protein matures, but once protein aggregates form ...
18.1 Macromolecules
... As food travels through the digestive system, it is exposed to a variety of pH levels. The stomach has a pH of 2 due to the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl), and the small intestine has a pH ranging from 7 to 9. HCl? HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin, an enzyme that digests proteins in the sto ...
... As food travels through the digestive system, it is exposed to a variety of pH levels. The stomach has a pH of 2 due to the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl), and the small intestine has a pH ranging from 7 to 9. HCl? HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin, an enzyme that digests proteins in the sto ...
Document
... G. Importance of lipids- alternate energy source other than monosaccharides; fats are lighter than polysacc. and take up less space ...
... G. Importance of lipids- alternate energy source other than monosaccharides; fats are lighter than polysacc. and take up less space ...
Test #4: Biomolecule Foldable
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
... subunits called nucleotides has which of these functions in the cell? F ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.