Chapter 3 PowerPoint
... • Single polynucleotide strand • RNA uses information in DNA to specify sequence of amino acids in proteins ...
... • Single polynucleotide strand • RNA uses information in DNA to specify sequence of amino acids in proteins ...
Modifications of redox-active cysteines occurring during sample
... demonstrate that redox-active cysteines can uncontrollably be modified by nominal 80 Da, as well as 32, 48, 64, 76 and -34 Da as a result of sample preparation in protein expression and proteomic workflows. Different reasons have been elucidated and not all of them are fully clarified yet. 1) β-Merc ...
... demonstrate that redox-active cysteines can uncontrollably be modified by nominal 80 Da, as well as 32, 48, 64, 76 and -34 Da as a result of sample preparation in protein expression and proteomic workflows. Different reasons have been elucidated and not all of them are fully clarified yet. 1) β-Merc ...
Polymers and Amino Acids
... Hydrolysis of peptide bonds A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
... Hydrolysis of peptide bonds A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
Nutrients and the structure of macromolecules File
... group is the only part of the amino acid that makes them different from one another. It is the combination and number of these 20 amino acids in proteins that gives us our varying traits. When peptide bonds hook amino acids together into a chain, we call the chain a polypeptide. The C=O end of the c ...
... group is the only part of the amino acid that makes them different from one another. It is the combination and number of these 20 amino acids in proteins that gives us our varying traits. When peptide bonds hook amino acids together into a chain, we call the chain a polypeptide. The C=O end of the c ...
4NucleicAcidsProteins - San Elijo Elementary School
... Enzymatic proteins regulate chemical Rxs Structural proteins support (ex. Muscles, cartilage) Storage proteins store amino acids Transport proteins move substances Hormonal proteins coordinate multicellular ...
... Enzymatic proteins regulate chemical Rxs Structural proteins support (ex. Muscles, cartilage) Storage proteins store amino acids Transport proteins move substances Hormonal proteins coordinate multicellular ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
... 22. _____________ and ______________ are the two types of nucleic acids. 23. Name the function of nucleic acids. _________________________________________ 24. Describe/Draw the structure of DNA. ( What does it look like?) ____________________________ Energy and Enzymes 25. ______________________ are ...
CHAPTER 3-Protein-In Class Activity
... Draw the structure of amino acid (aa) and label each part’s name. Draw and show how two aa bind together and go through dehydration reaction. Condensation reactions bond the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another to form a peptide bond There are _______different amino acids e ...
... Draw the structure of amino acid (aa) and label each part’s name. Draw and show how two aa bind together and go through dehydration reaction. Condensation reactions bond the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another to form a peptide bond There are _______different amino acids e ...
Organic Compounds
... Building of Structural parts of cell Non- Polar - Does not dissolve in water ...
... Building of Structural parts of cell Non- Polar - Does not dissolve in water ...
Introduction to Studying Proteins
... The instructions for how to make a protein reside in the cells DNA, found in the nucleus. The machinery for making the protein, ribosomes, are found outside the nucleus. ...
... The instructions for how to make a protein reside in the cells DNA, found in the nucleus. The machinery for making the protein, ribosomes, are found outside the nucleus. ...
E U F T DG Unfolded state, ensemble Native fold, one
... – Molten globule condenses to native fold via ...
... – Molten globule condenses to native fold via ...
Lecture 1: Fundamentals of Protein Structure
... Amino Acids Are Joined By Peptide Bonds In Peptides - -carboxyl of one amino acid is joined to -amino of a second amino acid (with removal of water) - only -carboxyl and -amino groups are used, not R-group carboxyl or amino groups ...
... Amino Acids Are Joined By Peptide Bonds In Peptides - -carboxyl of one amino acid is joined to -amino of a second amino acid (with removal of water) - only -carboxyl and -amino groups are used, not R-group carboxyl or amino groups ...
C. Protein
... certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by post-translational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes pr ...
... certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by post-translational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes pr ...
Chemistry of Life
... hydrogen and oxygen with a ratio of about two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom for every on carbon atom. Monosaccharide – This is the simplest type of carbohydrate and it is also a simple sugar. Disaccharide – This is when two monosaccharide link together. The most commonly know disaccharide i ...
... hydrogen and oxygen with a ratio of about two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom for every on carbon atom. Monosaccharide – This is the simplest type of carbohydrate and it is also a simple sugar. Disaccharide – This is when two monosaccharide link together. The most commonly know disaccharide i ...
Macromolecule Flapbook
... Macromolecule Flap Book Directions: 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
... Macromolecule Flap Book Directions: 1. Fold a sheet of paper “hot dog style.” (Landscape). 2. Divide one side of the sheet of paper into four equal sections. 3. Label each section as follows: Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids 4. Then cut each segment (top side only to form flaps!) ...
Worksheet 1 - Ch. 2, 3 - Iowa State University
... b. Peptide bonds form between __________ and ___________ functional groups. 3. This is an image of an aquaporin protein; it lets water into the cell through a tunnel. a. What structure does it have? b. Determine whether polar and nonpolar amino acids would be located on the inside or outer layer of ...
... b. Peptide bonds form between __________ and ___________ functional groups. 3. This is an image of an aquaporin protein; it lets water into the cell through a tunnel. a. What structure does it have? b. Determine whether polar and nonpolar amino acids would be located on the inside or outer layer of ...
Биологическая химия
... Peptide hormones are formed by the specific proteolysis of their peptide precursors ...
... Peptide hormones are formed by the specific proteolysis of their peptide precursors ...
I. Cells
... Note: 1. carboxylic acids can readily lose H+ in aqueous solution to form a negatively charged ion, which is denoted with suffix “-ate”, e.g. glutamate, aspartate. 2. proline is also non-polar and hydrophobic. ...
... Note: 1. carboxylic acids can readily lose H+ in aqueous solution to form a negatively charged ion, which is denoted with suffix “-ate”, e.g. glutamate, aspartate. 2. proline is also non-polar and hydrophobic. ...
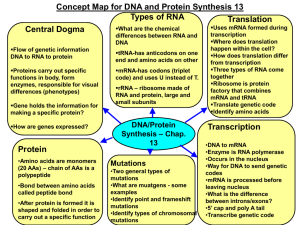
Slide 1
... •DNA to mRNA •Enzyme is RNA polymerase •Occurs in the nucleus •Way for DNA to send genetic ...
... •DNA to mRNA •Enzyme is RNA polymerase •Occurs in the nucleus •Way for DNA to send genetic ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.