GREAT CHANGES IN HEALTH CARE IN THE PAST 40 YEARS
... STAGES AND MILESTONES IN THE RESEARCH 1969-71: The degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase requires energy 1977-78: Isolation of a small protein (ubiquitin) required for energydependent protein degradation 1979-1980: Discovery of ligation of ubiquitin to proteins; proposal of the ubiquitin tagging ...
... STAGES AND MILESTONES IN THE RESEARCH 1969-71: The degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase requires energy 1977-78: Isolation of a small protein (ubiquitin) required for energydependent protein degradation 1979-1980: Discovery of ligation of ubiquitin to proteins; proposal of the ubiquitin tagging ...
Polymers - Sierra Vista Chemistry
... to form a polymer. Polymer - A substance that has a molecular structure built from a large number of similar units (monomers) bonded together. ...
... to form a polymer. Polymer - A substance that has a molecular structure built from a large number of similar units (monomers) bonded together. ...
20 Proteins - mrhortonbiology
... decided to help them out. I conducted a test for starch, sugar, and protein to try to determine what the food is (it isn’t necessarily one we tested in class). The starch test was brown but not black. The sugar and protein test are shown below. Based on these results, what food do you think it could ...
... decided to help them out. I conducted a test for starch, sugar, and protein to try to determine what the food is (it isn’t necessarily one we tested in class). The starch test was brown but not black. The sugar and protein test are shown below. Based on these results, what food do you think it could ...
Molecules of life
... In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold ...
... In some individuals, protein appears to have correct amino acid sequence but fails to fold ...
Proteins…
... ATP synthase – helps to make ATP Structural Proteins – provide support ex: elastin, horn, silk (web), keratin (hair & nails) Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
... ATP synthase – helps to make ATP Structural Proteins – provide support ex: elastin, horn, silk (web), keratin (hair & nails) Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream ...
Protein and Amino Acid
... Amino acids are the basis units of proteins and are held together by peptide linkages to form long protein chains. Protein chains can range in size. Simple proteins yield only amino acids. Eg. Albumin in blood plasma, keratin, collagen and elastin. Complex or conjugated proteins are made up of a ...
... Amino acids are the basis units of proteins and are held together by peptide linkages to form long protein chains. Protein chains can range in size. Simple proteins yield only amino acids. Eg. Albumin in blood plasma, keratin, collagen and elastin. Complex or conjugated proteins are made up of a ...
A1 B1 C1 D1 A2 B2 C2 D2 A1 B1 C1 A2 B2 C2
... structures are repetitive patterns found in proteins and usually give a clue about the function of the protein. In this activity, students are making alpha-helix structures which are rod-like shapes around a rotational axis. ...
... structures are repetitive patterns found in proteins and usually give a clue about the function of the protein. In this activity, students are making alpha-helix structures which are rod-like shapes around a rotational axis. ...
High Nucleotide Yeast Specification
... ß-glucans and ß-mannans. It is high in free nucleotides which are essential building blocks for cell regeneration and replication. These free nucleotides are most important for young animals which have yet to develop endogenous enzyme systems to release free nucleotides from dietary materials. They ...
... ß-glucans and ß-mannans. It is high in free nucleotides which are essential building blocks for cell regeneration and replication. These free nucleotides are most important for young animals which have yet to develop endogenous enzyme systems to release free nucleotides from dietary materials. They ...
Artificial Enzyme Design, written by Emily Coyte
... been used outside of their natural context for decades, but the range for utility is limited by what evolution on this planet has given us. Enhancing that range with new, man-made proteins has huge potential for human health and understanding. Two options present themselves: adapt some of the huge d ...
... been used outside of their natural context for decades, but the range for utility is limited by what evolution on this planet has given us. Enhancing that range with new, man-made proteins has huge potential for human health and understanding. Two options present themselves: adapt some of the huge d ...
Flexibility of a polypeptide chain
... most abundant protein in mammals, main fibrous component of skin, bone, teeth, cartilage and tendon extracellular protein, rod shape, ~3000 Å long/15 Å in diameter, 3 helical protein chains (~1000 residues each, every 3rd residue is Gly, Gly-Pro-(Pro-OH) triad is frequent, Pro-OH (4-hydroxyproline) ...
... most abundant protein in mammals, main fibrous component of skin, bone, teeth, cartilage and tendon extracellular protein, rod shape, ~3000 Å long/15 Å in diameter, 3 helical protein chains (~1000 residues each, every 3rd residue is Gly, Gly-Pro-(Pro-OH) triad is frequent, Pro-OH (4-hydroxyproline) ...
College 5
... Protein folding in a living cell is often assisted by special proteins called molecular chaperones. These proteins bind to partly folded polypeptide chains and help them progress along the energetically most favorable folding pathway. Chaperones are vital in the crowded conditions of the cytoplasm, ...
... Protein folding in a living cell is often assisted by special proteins called molecular chaperones. These proteins bind to partly folded polypeptide chains and help them progress along the energetically most favorable folding pathway. Chaperones are vital in the crowded conditions of the cytoplasm, ...
Chapter 4 - Open Yale Courses
... • There are four levels of structure for proteins. The amino acid sequence is the primary structure, the local domains are the secondary structure, the overall three-dimensional shape is the tertiary structure, and the formation of a complex with other polypeptide chains is the quaternary structure. ...
... • There are four levels of structure for proteins. The amino acid sequence is the primary structure, the local domains are the secondary structure, the overall three-dimensional shape is the tertiary structure, and the formation of a complex with other polypeptide chains is the quaternary structure. ...
Chapter 3
... • Antibodies can be isolated from serum (blood) (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
... • Antibodies can be isolated from serum (blood) (polyclonal), or from a single B cell colony (monoclonal). • Every different antibody has a unique Fab region. • All antibodies isolated from the same species of animal have nearly identical Fc regions. ...
Biotechnology Unit 3: DNA to Proteins Essential Cell Biology
... ii. Each protein will fold into a final shape called a conformation based on its amino acid sequence 1. Proteins will naturally fold into the lowest possible energy conformation 2. Each protein has one single stable conformation, but there can be slight changes based on interactions with other molec ...
... ii. Each protein will fold into a final shape called a conformation based on its amino acid sequence 1. Proteins will naturally fold into the lowest possible energy conformation 2. Each protein has one single stable conformation, but there can be slight changes based on interactions with other molec ...
Biochemistry http://www.brainpop.com/science/matterandchemistry
... When the product is released the enzyme is free to work again. (Catalysts are not used up in reaction!) ...
... When the product is released the enzyme is free to work again. (Catalysts are not used up in reaction!) ...
Basic Biochemistry
... Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) Low density proteins (LDL) – ‘bad cholesterol’ High density lipoproteins (HDL) – ‘good ...
... Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) Low density proteins (LDL) – ‘bad cholesterol’ High density lipoproteins (HDL) – ‘good ...
BIO SOL Review 10 - Macromolecules - Enzymes
... 6. (2004-16) Enzymes only work with specific substrates because each substrate — a. actively interferes with other substrates around it b. destroys its specific enzyme c. can only use a specific ionic bond with the enzyme d. has a specific activation site for enzyme attachment 7. (2005-40) Most cell ...
... 6. (2004-16) Enzymes only work with specific substrates because each substrate — a. actively interferes with other substrates around it b. destroys its specific enzyme c. can only use a specific ionic bond with the enzyme d. has a specific activation site for enzyme attachment 7. (2005-40) Most cell ...
Text 3
... solvent on both sides of the membrane. […] The [...] protein molecules are postulated to be amphipathic2 as are the phospholipids. That is, they are structurally asymmetric, with one highly polar end and one nonpolar end. 'The highly polar region [...] is in contact with the hydrophilic phase in the ...
... solvent on both sides of the membrane. […] The [...] protein molecules are postulated to be amphipathic2 as are the phospholipids. That is, they are structurally asymmetric, with one highly polar end and one nonpolar end. 'The highly polar region [...] is in contact with the hydrophilic phase in the ...
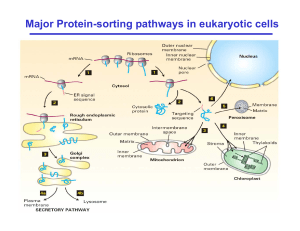
Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
... Major topological classes of integral membrane proteins synthesized on the rough ER ...
Contractile Proteins
... Enzymes - are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions. They are often referred to as catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions. Examples include the enzymes lactase and pepsin. Lactase breaks down the sugar lactose found in milk. Pepsin is a digestive enzyme that works in the stomach ...
... Enzymes - are proteins that facilitate biochemical reactions. They are often referred to as catalysts because they speed up chemical reactions. Examples include the enzymes lactase and pepsin. Lactase breaks down the sugar lactose found in milk. Pepsin is a digestive enzyme that works in the stomach ...
03 - summer worksheet
... B. Circle and identify all of the functional groups seen in this ATP molecule shown below. (note: ATP is an incredibly important energy molecule that we will talk about a lot in this class. Take a couple of minutes to get to know it….). ...
... B. Circle and identify all of the functional groups seen in this ATP molecule shown below. (note: ATP is an incredibly important energy molecule that we will talk about a lot in this class. Take a couple of minutes to get to know it….). ...
Characterisation of glycogenic and ketogenic metabolic pathways
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
... Background: The use of whey protein as a source of amino acids and its effect on reducing risks of diseases such as heart disease, cancer and diabetes [6,7] is the focus of ongoing research [8]. Whey is an abundant source of branched-chain amino acids that stimulates protein synthesis. In particular ...
Attomole Detection of Proteins in a Complex Mixture Using the
... T h e s olu t i o n A standard protein mixture containing equal molar amounts of yeast enolase, bovine serum albumin, rabbit glycogen phosphorylase B, and yeast alcohol dehydrogenase, were spiked at various concentrations into 100 ng of digested E.coli cell lysate. This provided a dilution series r ...
... T h e s olu t i o n A standard protein mixture containing equal molar amounts of yeast enolase, bovine serum albumin, rabbit glycogen phosphorylase B, and yeast alcohol dehydrogenase, were spiked at various concentrations into 100 ng of digested E.coli cell lysate. This provided a dilution series r ...
Core Concept Cheat Sheet
... ! Macromolecule: A molecule having a molecular weight in the range of a few thousands to many millions. ! Functional group: The specific atom or group of atoms that confers a particular chemical property on a biomolecule. ! Organic Compounds: Molecules containing covalently bonded carbon backbones a ...
... ! Macromolecule: A molecule having a molecular weight in the range of a few thousands to many millions. ! Functional group: The specific atom or group of atoms that confers a particular chemical property on a biomolecule. ! Organic Compounds: Molecules containing covalently bonded carbon backbones a ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.