Announcements - Hiram College
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
... What does it do? How similar is it to something else? How does it fold? Where does it go in a cell? What does it interact with? How it is regulated? Level of confidence? ...
Protein Structure and Bioinformatics
... • What is protein structure? • What are proteins made of? • What forces determines protein structure? • What is protein secondary structure? • What are the primary secondary structures? • How are protein structures determined experimentally? • How can structures be predicted in silico? ...
... • What is protein structure? • What are proteins made of? • What forces determines protein structure? • What is protein secondary structure? • What are the primary secondary structures? • How are protein structures determined experimentally? • How can structures be predicted in silico? ...
so, where do you get all your protein? investigating
... Proteins are the most complex and functionally diverse molecules of living organisms. Proteins compose enzymes, hormones, hair, skin, blood cells and muscle tissue just to name a few and are therefore associated with meat products. The basic elements of proteins are carbon (C) hydrogen (H), oxygen ( ...
... Proteins are the most complex and functionally diverse molecules of living organisms. Proteins compose enzymes, hormones, hair, skin, blood cells and muscle tissue just to name a few and are therefore associated with meat products. The basic elements of proteins are carbon (C) hydrogen (H), oxygen ( ...
any molecule that is present in living organisms. Carbohydrates
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
Biomolecules - Pearland ISD
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
... Unsaturated: at least 1 C = C double bond Triglyceride: 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
The Biology of
... (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held together by hydrogen bonds. • When the protein folds onto itself completely it is said to make a “ha ...
... (dotted lines) are between oxygen atoms (red) and hydrogen atoms (white) (shown in this case as occurring every fourth pair of amino acids along the protein). • (B) shows examples of beta-sheets held together by hydrogen bonds. • When the protein folds onto itself completely it is said to make a “ha ...
Slide 1
... Translates the genetic message in RNA into the production of protein. (It is the site of protein synthesis.) ...
... Translates the genetic message in RNA into the production of protein. (It is the site of protein synthesis.) ...
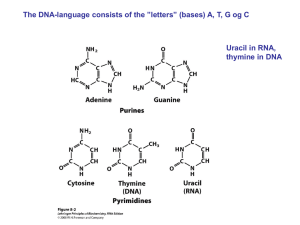
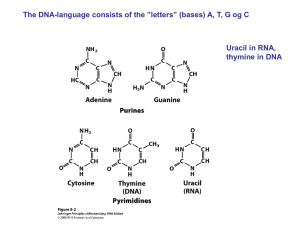
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
... Lipids typically have long chains of carbon atoms, but exist in many forms, also linked to polysaccharides (lipopolysacchariders), phosphate (phospholipids) and as triglycerides. They are typically found in cell membranes and as stored fat (do you see it on yourself?). Candle-lights are composed of ...
(DNA) and ribose (RNA)
... DNA can replicate itself by the help of numerous proteins. This is perhaps the most important characteristic of life! Life anywhere (in the universe!) without copying is difficult to envision ...
... DNA can replicate itself by the help of numerous proteins. This is perhaps the most important characteristic of life! Life anywhere (in the universe!) without copying is difficult to envision ...
Ubiquitin-proteosome protein degradation ppt
... First, Ubiquitin is activated by forming a link to “enzyme 1” (E1). Then, ubiquitin is transferred to one of several types of “enzyme 2” (E2). Then, “enzyme 3” (E3) catalizes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to a Lys e-amino group of the “condemned” ...
... First, Ubiquitin is activated by forming a link to “enzyme 1” (E1). Then, ubiquitin is transferred to one of several types of “enzyme 2” (E2). Then, “enzyme 3” (E3) catalizes the transfer of ubiquitin from E2 to a Lys e-amino group of the “condemned” ...
Lecture 6
... Proteins are the building blocks from which cells are assemble, and they constitute most of the cell’s dry mass. But in addition to providing cell with shape and structure, proteins also execute nearly all its diverse functions. Some examples of protein functions: 1. Enzyme: Catalyze covalent bond ...
... Proteins are the building blocks from which cells are assemble, and they constitute most of the cell’s dry mass. But in addition to providing cell with shape and structure, proteins also execute nearly all its diverse functions. Some examples of protein functions: 1. Enzyme: Catalyze covalent bond ...
Chapter Summary for Nutrition: Concepts and
... proteins. Each type of protein has a distinctive sequence of amino acids and so has great specificity. Often, cells specialize in synthesizing particular types of proteins in addition to the proteins necessary to all cells. Nutrients can greatly affect genetic expression. Proteins can be denatured b ...
... proteins. Each type of protein has a distinctive sequence of amino acids and so has great specificity. Often, cells specialize in synthesizing particular types of proteins in addition to the proteins necessary to all cells. Nutrients can greatly affect genetic expression. Proteins can be denatured b ...
lecture2-Proteins2014-08
... • Each amino acid in a chain makes two peptide bonds • The amino acids at the two ends of a chain make only one peptide bond • The aa with a free amino group is called amino terminus or N-terminus • The aa with a free carboxylic group is called carboxyl terminus or C-terminus ...
... • Each amino acid in a chain makes two peptide bonds • The amino acids at the two ends of a chain make only one peptide bond • The aa with a free amino group is called amino terminus or N-terminus • The aa with a free carboxylic group is called carboxyl terminus or C-terminus ...
Biological Chemistry II: Problem Set 1
... identical length, if you assume that all 20 proteinogenic amino acids occur with equal frequency and are distributed uniformly over the length of the protein? (c) BLAST searches are performed to identify proteins having similar amino acid sequences. A BLAST tutorial can be found at http://www.ncbi.n ...
... identical length, if you assume that all 20 proteinogenic amino acids occur with equal frequency and are distributed uniformly over the length of the protein? (c) BLAST searches are performed to identify proteins having similar amino acid sequences. A BLAST tutorial can be found at http://www.ncbi.n ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins provide structure for cells as well as the whole organism, examples ...
... Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins provide structure for cells as well as the whole organism, examples ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins provide structure for cells as well as the whole organism, examples ...
... Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport, Enzymes and Movement). Proteins provide structure for cells as well as the whole organism, examples ...
How does DNA control cell activities?
... acids are found in your cells? • DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid – 5-Carbon Sugar = Deoxyribose – Double-stranded ...
... acids are found in your cells? • DNA – Deoxyribonucleic Acid – 5-Carbon Sugar = Deoxyribose – Double-stranded ...
Protein Structure Activity
... 5) Walk around the room and polymerize a polypeptide chain by carrying out dehydration synthesis with your amino acids. You’ll need scissors and tape to do this. NOTE: Save the water molecules you make in the process! ...
... 5) Walk around the room and polymerize a polypeptide chain by carrying out dehydration synthesis with your amino acids. You’ll need scissors and tape to do this. NOTE: Save the water molecules you make in the process! ...
The Role of Leucine-doc
... weight loss continues to expand. Often this debate centers on the relative merits or risks of carbohydrates vs. fats; however, there is increasing interest in the optimal level of dietary protein for weight loss. Diets with a reduced ratio of carbohydrates/protein are reported to be beneficial for w ...
... weight loss continues to expand. Often this debate centers on the relative merits or risks of carbohydrates vs. fats; however, there is increasing interest in the optimal level of dietary protein for weight loss. Diets with a reduced ratio of carbohydrates/protein are reported to be beneficial for w ...
Final Report
... This proposal aimed to create expression vectors for two forms of a protein: Noxo1 and Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant function of these enzyme complexes lead ...
... This proposal aimed to create expression vectors for two forms of a protein: Noxo1 and Noxo1. Noxo1 (NOX Organizer 1) is a protein that serves as an “organizer” in a multiprotein enzyme complex that is involved in a wide range of cellular functions. Aberrant function of these enzyme complexes lead ...
Proteins
... • Peptide bonds = covalent bonds between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on an adjacent amino acid ...
... • Peptide bonds = covalent bonds between the carboxyl group on one amino acid and the amino group on an adjacent amino acid ...
Protein Purification - Bio 5068
... • Preserve the structure during purification • Consider that the structure may be lost • Activity assay a good test ...
... • Preserve the structure during purification • Consider that the structure may be lost • Activity assay a good test ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.