Study Guide
... 1. Competitive inhibitors Fit in active site but are not changed; prevent normal substrate from binding, prevent reaction. 2. Non-competitive inhibitors (allosteric inhibitor) Bind permanently to other site which changes molecular shape; prevents reaction. ...
... 1. Competitive inhibitors Fit in active site but are not changed; prevent normal substrate from binding, prevent reaction. 2. Non-competitive inhibitors (allosteric inhibitor) Bind permanently to other site which changes molecular shape; prevents reaction. ...
(1-4) D-glucose, a
... ZP3 Receptor on surface of sperm: ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to enter ...
... ZP3 Receptor on surface of sperm: ZP3 glycoprotein in extracellular coat of ovulated eggs a-linked galactose at the non-reducing end Binding triggers release of sperm enzymes, dissolves zona pellucida to allow sperm to enter ...
Characterization of Gametes to decide the fate of early embryo
... individual cells during early embryonic development. Here, I present our studies related to characterization of two novel representative regulatory proteins in the female germ cell, which play a key role during sperm-egg fusion and early embryonic development in mammals. I would also like to present ...
... individual cells during early embryonic development. Here, I present our studies related to characterization of two novel representative regulatory proteins in the female germ cell, which play a key role during sperm-egg fusion and early embryonic development in mammals. I would also like to present ...
lecture 5
... well as prokaryotes; not essential for viability. Yeast mutant lacking all its cyclophilins and FKBP binding proteins still alive! - bind immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin (but not cyclosporin A) - both cyclophilins and FKBP’s form complexes with the molecular chaperone Hsp90, perhaps to cataly ...
... well as prokaryotes; not essential for viability. Yeast mutant lacking all its cyclophilins and FKBP binding proteins still alive! - bind immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin (but not cyclosporin A) - both cyclophilins and FKBP’s form complexes with the molecular chaperone Hsp90, perhaps to cataly ...
FULL-TEXT - Manchester eScholar
... David N. Potier1, John R. Griffiths1, Ralf Hoffman2, Anthony D. Whetton1 1: University of Manchester, Manchester, UK; 2: Philips, Eindhoven, Netherlands Introduction Proteases have been linked to a range of different diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Many groups have monitored the amount of ...
... David N. Potier1, John R. Griffiths1, Ralf Hoffman2, Anthony D. Whetton1 1: University of Manchester, Manchester, UK; 2: Philips, Eindhoven, Netherlands Introduction Proteases have been linked to a range of different diseases, including cancer and arthritis. Many groups have monitored the amount of ...
Document
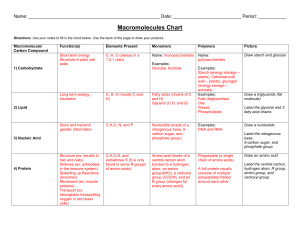
... LIPIDS- Store Energy • Lipids are formed from one glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids • 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
... LIPIDS- Store Energy • Lipids are formed from one glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids • 3 fatty acids + glycerol ...
EXPLORING PROTEIN STRUCTURE
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
GTAC bioinformatics task 4 presentation
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
... the proteins that you eat and digest. Every time you eat a burger (vege or beef), you break the proteins down into single amino acids ready for use in building new proteins. And yes, proteins have the job of digesting proteins, they are known as proteases. There are only 20 different amino acids but ...
Carbohydrates
... Macromolecule made of lipids and proteins Hydrophilic allows fats to be sheilded from the ...
... Macromolecule made of lipids and proteins Hydrophilic allows fats to be sheilded from the ...
PROTEINS - ssag.sk
... (when blood glucose levels are high, cells will transport glucose into the cells for use or storage) – Glucagon: sends message “we need more sugar in the blood” (when blood glucose is too low, cells will ...
... (when blood glucose levels are high, cells will transport glucose into the cells for use or storage) – Glucagon: sends message “we need more sugar in the blood” (when blood glucose is too low, cells will ...
The six elements that make up 99.9% of all living things include
... 1. they are lipids 2. they will react with most body chemicals 3. they can only be used once 4. they usually slow down reactions and prevent overheating of the cells 5. they usually speed up chemical reactions ...
... 1. they are lipids 2. they will react with most body chemicals 3. they can only be used once 4. they usually slow down reactions and prevent overheating of the cells 5. they usually speed up chemical reactions ...
Amino Acid Building Block Models – In Brief
... The primary sequence of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. Proteins are made up of amino acid monomers linked together by peptide bonds. Peptide bond formation between amino acids results in the release of water (dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction). The pro ...
... The primary sequence of a protein is the linear sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide. Proteins are made up of amino acid monomers linked together by peptide bonds. Peptide bond formation between amino acids results in the release of water (dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction). The pro ...
Chapter 3 Notes Set 7
... 2. Add ___________ (lacking water)_______(trifluoroacetic acid) - (analinothiazolinanone derivative) - leaves the rest of the chain with 1 less amino acid - _______________________________ - reaction does not degrade the rest of the chain 3. Selectively extract the anilinothiozolinone derivative int ...
... 2. Add ___________ (lacking water)_______(trifluoroacetic acid) - (analinothiazolinanone derivative) - leaves the rest of the chain with 1 less amino acid - _______________________________ - reaction does not degrade the rest of the chain 3. Selectively extract the anilinothiozolinone derivative int ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.