Nutrients - SBI3URHKing
... – 8 Amino Acids are considered ESSENTIAL and must be obtained from the food we eat ...
... – 8 Amino Acids are considered ESSENTIAL and must be obtained from the food we eat ...
Macromolecule Review - Mr. Dudley`s Website
... A dog gets many nutrients from its food including amino acids. Which of these can be built directly using the amino acids? ...
... A dog gets many nutrients from its food including amino acids. Which of these can be built directly using the amino acids? ...
Gel Electrophoresis
... • Breakdown the protein into amino acids – Break amide/peptide bond – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
... • Breakdown the protein into amino acids – Break amide/peptide bond – Called hydrolysis (opposite of condensation) – Acid or base and heat required ...
From Biomarkers to Companion Diagnostics: Mitochondrial
... (the Warburg effect) and as a source of precursors for generating proteins, nucleotides and lipids. Such metabolic re-programming of cancer cells includes marked over-expression of the isoforms of the mitochondrialbound glycolytic protein hexokinase (HK), required for energy production. HK also acts ...
... (the Warburg effect) and as a source of precursors for generating proteins, nucleotides and lipids. Such metabolic re-programming of cancer cells includes marked over-expression of the isoforms of the mitochondrialbound glycolytic protein hexokinase (HK), required for energy production. HK also acts ...
2 - World of Teaching
... Proteins which fold into a ball or ‘globule’ like Myoglobin are called Globular Proteins. They tend to be soluble. The most common group of Globular Proteins are ENZYMES which control the reactions in ...
... Proteins which fold into a ball or ‘globule’ like Myoglobin are called Globular Proteins. They tend to be soluble. The most common group of Globular Proteins are ENZYMES which control the reactions in ...
DHaganTalk1
... function. -The protein folding “problem” and why it has become one of the most basic intellectual challenges in Molecular Biology. ...
... function. -The protein folding “problem” and why it has become one of the most basic intellectual challenges in Molecular Biology. ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
18,5 Primory structure of proteins 18.6 Secondory stractare of proteins
... Karla sometimes experiences runner's high during her runs. \Alhat is causing this effect? Many sports physiologists believe that runner's high comes from increases in the levels of enkephalins in the brain. These increases, which remarkabie feel"* "urrr" ings of well-belng, appear to be stimulated b ...
... Karla sometimes experiences runner's high during her runs. \Alhat is causing this effect? Many sports physiologists believe that runner's high comes from increases in the levels of enkephalins in the brain. These increases, which remarkabie feel"* "urrr" ings of well-belng, appear to be stimulated b ...
Fluorescent Protein Assay
... fluorescent product that has a maximum wavelength of excitation of 340 nm and emission at 455 nm.15,16 Wavelengths from 330-375 nm have been used for excitation and 436-490 nm for measuring emission. Protein concentrations as low as 50 ng/ml can be measured with an OPA assay. The inherent sensitivit ...
... fluorescent product that has a maximum wavelength of excitation of 340 nm and emission at 455 nm.15,16 Wavelengths from 330-375 nm have been used for excitation and 436-490 nm for measuring emission. Protein concentrations as low as 50 ng/ml can be measured with an OPA assay. The inherent sensitivit ...
PPT - CBE Project Server
... o Necessary vs. Essential Nutrients o Necessary Nutrients: nutrients that can be made by the body if they are lacking in the diet o Essential Nutrients: cannot be produced by the body, must be supplied from an external source ...
... o Necessary vs. Essential Nutrients o Necessary Nutrients: nutrients that can be made by the body if they are lacking in the diet o Essential Nutrients: cannot be produced by the body, must be supplied from an external source ...
Test Review Unit 1
... 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parents)? 12) What is the cell theory? ...
... 10) What is asexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parent)? 11) What is sexual reproduction? What kind of offspring does it produce (compared to the parents)? 12) What is the cell theory? ...
Experimental phase diagrams to optimise membrane protein
... The PhD project is part of the EU Marie Skłodowska Curie Action (MSCA) network RAtionalising Membrane Protein crystallisation (RAMP). Other PhD students in the network will use multidisciplinary approaches, including structural biology, microfluidics, and coarse-grained modelling to better understan ...
... The PhD project is part of the EU Marie Skłodowska Curie Action (MSCA) network RAtionalising Membrane Protein crystallisation (RAMP). Other PhD students in the network will use multidisciplinary approaches, including structural biology, microfluidics, and coarse-grained modelling to better understan ...
slides
... particular catalytic or structural function. • Proteins are so precisely built that the change of even a few atoms in one amino acid can sometimes disrupt the structure and the function of a protein. • Proteins can be grouped into families with very similar sequences and structures, probably due to ...
... particular catalytic or structural function. • Proteins are so precisely built that the change of even a few atoms in one amino acid can sometimes disrupt the structure and the function of a protein. • Proteins can be grouped into families with very similar sequences and structures, probably due to ...
Macromolecule Review (PP)
... Function: Provide structure for tissues and organs, allow muscles to contract, transport oxygen, and make up enzymes which carry out chemical reactions. ...
... Function: Provide structure for tissues and organs, allow muscles to contract, transport oxygen, and make up enzymes which carry out chemical reactions. ...
Protein structure - Wikispaces
... Proteins which fold into a ball or ‘globule’ like Myoglobin are called Globular Proteins. They tend to be soluble. The most common group of Globular Proteins are ENZYMES which control the reactions in ...
... Proteins which fold into a ball or ‘globule’ like Myoglobin are called Globular Proteins. They tend to be soluble. The most common group of Globular Proteins are ENZYMES which control the reactions in ...
Chemistry Comes Alive: Part B Classes of Compounds • Inorganic
... • pH change interferes with cell function and may damage living tissue • Slight change in pH can be fatal • pH is regulated by kidneys, lungs, and buffers Buffers • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) o ...
... • pH change interferes with cell function and may damage living tissue • Slight change in pH can be fatal • pH is regulated by kidneys, lungs, and buffers Buffers • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) o ...
Unit 5 Proteins PPT
... Vegans do not eat meat of any kind and also do not eat eggs, dairy products, or processed foods containing these or other animal-derived ingredients such as gelatin. Many vegans also refrain from eating foods that are made using animal products that may not contain animal products in the finished pr ...
... Vegans do not eat meat of any kind and also do not eat eggs, dairy products, or processed foods containing these or other animal-derived ingredients such as gelatin. Many vegans also refrain from eating foods that are made using animal products that may not contain animal products in the finished pr ...
Biomolecules
... • Chemical properties and reactivity are a result of functional groups- a configuration of atoms attached to the carbon skeleton • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which or ...
... • Chemical properties and reactivity are a result of functional groups- a configuration of atoms attached to the carbon skeleton • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which or ...
7. Protein Function
... There are two classes of MHC proteins which differ in their distribution among cell types and in the source of digested proteins Class I MHC - are found on the surface of virtually all vertebrate cells. These complexes of peptides and class I MHC proteins are the recognition targets of the T-cell re ...
... There are two classes of MHC proteins which differ in their distribution among cell types and in the source of digested proteins Class I MHC - are found on the surface of virtually all vertebrate cells. These complexes of peptides and class I MHC proteins are the recognition targets of the T-cell re ...
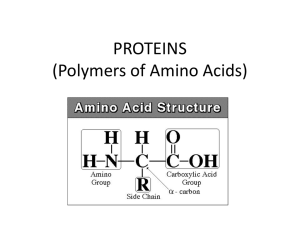
PROTEINS (Polymers of Amino Acids)
... 20 Amino Acids • Grouped by properties of their side chains – Non-polar (hydrophobic) – Polar (hydrophilic) – Acidic (-COOH grp) – Basic (-NH2) ...
... 20 Amino Acids • Grouped by properties of their side chains – Non-polar (hydrophobic) – Polar (hydrophilic) – Acidic (-COOH grp) – Basic (-NH2) ...
R–groups
... e. disulfide bridges― covalent bonds between two cysteine amino acids with sulfhydryl groups are brought close enough together by the folding of the protein D. Quaternary Structure― when two or more polypeptide chains are joined together by bonds or interactions of their R–groups. Same as a–e above. ...
... e. disulfide bridges― covalent bonds between two cysteine amino acids with sulfhydryl groups are brought close enough together by the folding of the protein D. Quaternary Structure― when two or more polypeptide chains are joined together by bonds or interactions of their R–groups. Same as a–e above. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.