Multiple Choice:
... natural state, and thus cannot be stretched further. α-helices are naturally compact and spring-like, and stretch considerably. Chaperones are proteins the increase the rate of protein folding into their native state. Hydrophobic forces are actually due to the increase in entropy resulting from the ...
... natural state, and thus cannot be stretched further. α-helices are naturally compact and spring-like, and stretch considerably. Chaperones are proteins the increase the rate of protein folding into their native state. Hydrophobic forces are actually due to the increase in entropy resulting from the ...
honors Chapter 2.3-2.4 teaching
... •Those chemicals that enter into a reaction are the “reactants”, those that are made are the “products” •Chemical reactions change the bonding patterns in the reactants •Energy is released or absorbed when chemical bonds are formed or broken during a reaction •Rxns releasing energy generally happen ...
... •Those chemicals that enter into a reaction are the “reactants”, those that are made are the “products” •Chemical reactions change the bonding patterns in the reactants •Energy is released or absorbed when chemical bonds are formed or broken during a reaction •Rxns releasing energy generally happen ...
Revealing the Genetic Code
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
... Gene = sequence of nucleotides (bases) Protein = sequence of amino acids Sequence of bases determines sequence of amino acids (protein’s primary structure) Protein’s primary structure determines its secondary & tertiary (3D) structures Protein’s 3D structure determines its function!! ...
A1988Q982800002
... obtain distance constraints by experimentalphysical chemical methods to determine the three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease in aqueous solution. For example, three specific Tyr...Asp interactions were identified, and subsequently verified when the crystal structure was determined (see Fig. 5 o ...
... obtain distance constraints by experimentalphysical chemical methods to determine the three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease in aqueous solution. For example, three specific Tyr...Asp interactions were identified, and subsequently verified when the crystal structure was determined (see Fig. 5 o ...
Notes_Biochemistry_Short_Course
... INORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Define: do ______ contain Carbon with Hydrogen together (may have either one but NOT at the same time) - ___________________ compounds I. (pgs 36-37) Water - ___________________ % of body Match each property of water with its description/importance _____attracts molecules & form ...
... INORGANIC COMPOUNDS: Define: do ______ contain Carbon with Hydrogen together (may have either one but NOT at the same time) - ___________________ compounds I. (pgs 36-37) Water - ___________________ % of body Match each property of water with its description/importance _____attracts molecules & form ...
Answers to Progress 2 Practice Questions
... acids that BEGIN to form the 3-dimensional shape of the protein. Typically this forms alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets. Tertiary structure of a protein is a result of the interactions between the Rgroups/side-chains of the amino acids such as disulfide bonds (very strong), acid-base bonds, more ...
... acids that BEGIN to form the 3-dimensional shape of the protein. Typically this forms alpha-helices and beta-pleated sheets. Tertiary structure of a protein is a result of the interactions between the Rgroups/side-chains of the amino acids such as disulfide bonds (very strong), acid-base bonds, more ...
Biochemistry Test Review (Vocabulary on the back page
... contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds that also store energy. However, that energy must be transferred to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to be usable by the cell. B2.2 Organic Molecules There are four major categories of organic molecules that make up living systems: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nu ...
... contain many carbon-hydrogen bonds that also store energy. However, that energy must be transferred to ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to be usable by the cell. B2.2 Organic Molecules There are four major categories of organic molecules that make up living systems: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and nu ...
02 DNA and RNA and protein synthesis
... 2) NAD, FAD, GDP and NADP, which are high energy electron ...
... 2) NAD, FAD, GDP and NADP, which are high energy electron ...
Biomolecules Review
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
... 15. Draw the structure of a generic dipeptide using H3N+-CHR-CO2-. What type of bond links the amino acids? Draw an arrow to this bond. 16. What are the four levels of protein structure? What level is given for this tripeptide? alanine–lysine–aspartic acid 17. What is denaturation of protein? What c ...
Chapter 5 notes cont.
... At any moment in the cell's life, the specific enzymes that are present and active determine which reactions occur. ...
... At any moment in the cell's life, the specific enzymes that are present and active determine which reactions occur. ...
Learning Objectives handouts
... 12. Name the principal energy storage molecules of plants and animals. Proteins have Many Structures, Resulting in a Wide Range of Functions 13. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide. 14. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 15. List and describe the four major compone ...
... 12. Name the principal energy storage molecules of plants and animals. Proteins have Many Structures, Resulting in a Wide Range of Functions 13. Distinguish between a protein and a polypeptide. 14. Explain how a peptide bond forms between two amino acids. 15. List and describe the four major compone ...
Ass4_ans - The University of Sydney
... filling in the relevant circles on the grid provided. Grids can be collected from under the green notice boards in the BCHM2 labs. ...
... filling in the relevant circles on the grid provided. Grids can be collected from under the green notice boards in the BCHM2 labs. ...
H - Bioinf!
... There are alternatives to the helix configuration giving more constrained or less constrained structures: -310 helices, in which hydrogen bonds form between residues i and i + 3 - -helices, in which hydrogen bonds form between residues i and i + 5 This configurations are much rarer due to the cons ...
... There are alternatives to the helix configuration giving more constrained or less constrained structures: -310 helices, in which hydrogen bonds form between residues i and i + 3 - -helices, in which hydrogen bonds form between residues i and i + 5 This configurations are much rarer due to the cons ...
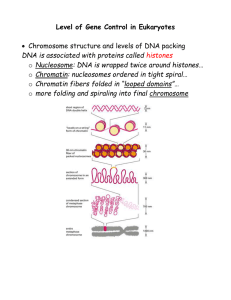
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... Regulation at translational level - Initiation of Translation o Regulatory proteins can bind to mRNA at 5’ end preventing initiation of translation (ribosomes can’t attach) o Stored mRNA’s in an egg lack poly-A tails = can’t initiate translation. - At right developmental times, A’s are added so t ...
... Regulation at translational level - Initiation of Translation o Regulatory proteins can bind to mRNA at 5’ end preventing initiation of translation (ribosomes can’t attach) o Stored mRNA’s in an egg lack poly-A tails = can’t initiate translation. - At right developmental times, A’s are added so t ...
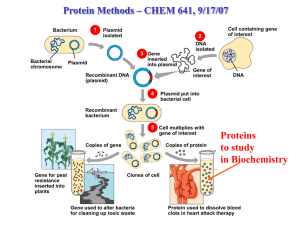
Computational protein design
... engineer protein hormones and enzymes to perform existing functions under a wider range of conditions, or to perform entirely new functions, • knowledge obtained is likely to be linked to a more complete understanding of the forces underlying protein folding, enabling more rapid interpretation of th ...
... engineer protein hormones and enzymes to perform existing functions under a wider range of conditions, or to perform entirely new functions, • knowledge obtained is likely to be linked to a more complete understanding of the forces underlying protein folding, enabling more rapid interpretation of th ...
Key to Exam 2
... conjunction with gel electrophoresis to identify specific proteins or subunits recognized by antibodies. Many times the two methods will provide the same information about a protein and can be used interchangeably. In other situations one of the methods will work better or be more appropriate. For e ...
... conjunction with gel electrophoresis to identify specific proteins or subunits recognized by antibodies. Many times the two methods will provide the same information about a protein and can be used interchangeably. In other situations one of the methods will work better or be more appropriate. For e ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... attendees will receive a detailed step-by-step description for performinig practical molecular modelling on the PC by using appropriate software. Using the X,Y, Z coordinates of atoms, as deposited in the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank, PDB, students can „create“ the 3D structure of crystallographical ...
... attendees will receive a detailed step-by-step description for performinig practical molecular modelling on the PC by using appropriate software. Using the X,Y, Z coordinates of atoms, as deposited in the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank, PDB, students can „create“ the 3D structure of crystallographical ...
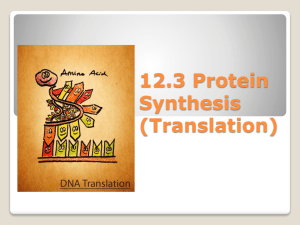
Protein Synthesis (Translation)
... Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... Translation or protein synthesis is the process of making a protein Proteins are made up of amino acids (small building blocks) There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
Carbon Compounds
... Organic Compound -A compound that contains the element carbon and is made by living organisms In order for life to occur, many organisms require complex organic molecules (macromolecules) • Organisms get these organic molecules via the nutrients they take in or by producing the organic molecules ...
... Organic Compound -A compound that contains the element carbon and is made by living organisms In order for life to occur, many organisms require complex organic molecules (macromolecules) • Organisms get these organic molecules via the nutrients they take in or by producing the organic molecules ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.