Review 1 - Allen ISD
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...
... group, is formed. c. Energy is released, which can be used by the cell. d. Energy is lost in the ...
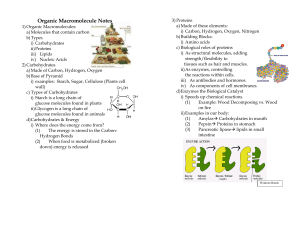
Organic Macromolecule Notes
... i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies and hormones. iv) As components of cell membranes. d) Enzymes the Biological Catalyst i) Speeds up chemical reactions ...
... i) As structural molecules, adding strength/flexibility to tissues such as hair and muscles. ii) As enzymes, controlling the reactions within cells. iii) As antibodies and hormones. iv) As components of cell membranes. d) Enzymes the Biological Catalyst i) Speeds up chemical reactions ...
Biochemistry PPT
... Plants make their energy from the sun, animals get their energy from foods eaten ...
... Plants make their energy from the sun, animals get their energy from foods eaten ...
Introduction to Molecular forces and Macromolecules
... onto jello surface. .examine during next two hours (effect of gelatinase from plant origin on the jell-O . ...
... onto jello surface. .examine during next two hours (effect of gelatinase from plant origin on the jell-O . ...
Protein Synthesis Review
... Proteins are polymers, made up of monomers called amino acids There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
... Proteins are polymers, made up of monomers called amino acids There are 20 different types of amino acids ...
If we are composed of cells, what are cells made of? Building Blocks
... 3. Proteins- the workhorse molecules. Made up of chains of amino acids that twist and fold into certain shapes. ...
... 3. Proteins- the workhorse molecules. Made up of chains of amino acids that twist and fold into certain shapes. ...
1. The formation of a peptide bond between two amino acids is an
... Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure None of the above ...
... Primary structure Secondary structure Tertiary structure Quaternary structure None of the above ...
Making Proteins - Foothill Technology High School
... Steps to Translation Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between th ...
... Steps to Translation Making proteins from mRNA 1. Ribosomes attach to the “start” codon of mRNA (AUG), signaling the beginning of the protein chain 2. mRNA codons are matched to corresponding tRNA anticodons and appropriate amino acids are strung together. 3. Dehydration synthesis occurs between th ...
biological_molecules_facts
... The linking bond between two monosaccharides is a glycosidic link. Maltose is formed from two glucose molecules. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. It must be hydrolysed with warm hydrochloric acid before it gives a positive reducing sugar test. Sucrose is formed from a glucose and a fructose. Starch ...
... The linking bond between two monosaccharides is a glycosidic link. Maltose is formed from two glucose molecules. Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. It must be hydrolysed with warm hydrochloric acid before it gives a positive reducing sugar test. Sucrose is formed from a glucose and a fructose. Starch ...
Chapter 1 Study Questions
... acidic amino acid (such as glutamic acid). Show the charges on the side chains at pH 7. 4. Compare the chemical structure of a small non-polar amino acid (such as alanine) to one with a bulky hydrocarbon side chain (such as isoleucine). What kind of chemical interactions are non-polar side chains in ...
... acidic amino acid (such as glutamic acid). Show the charges on the side chains at pH 7. 4. Compare the chemical structure of a small non-polar amino acid (such as alanine) to one with a bulky hydrocarbon side chain (such as isoleucine). What kind of chemical interactions are non-polar side chains in ...
@ tin Scruppsfusrencu Iusrnurs
... All cells employ mechanisms termed "checkpointcontrols" to preventinappropriatecell cycle progressionwhen essentialeventsare blockedor incomplete. For example,cells exposedto radiationor chemotherapy undergorepairprior to DNA synthesisand must completethe synthesisbeforecell division. This regulator ...
... All cells employ mechanisms termed "checkpointcontrols" to preventinappropriatecell cycle progressionwhen essentialeventsare blockedor incomplete. For example,cells exposedto radiationor chemotherapy undergorepairprior to DNA synthesisand must completethe synthesisbeforecell division. This regulator ...
Flow of Matter_04_Sample Quiz Questions_Key
... Add your favorite cellular structure here – it probably has some protein in it!] A protein is a polymer of many monomers called amino acids that are linked together by covalent bonds. The structure of a protein is held together by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polymer (remember prima ...
... Add your favorite cellular structure here – it probably has some protein in it!] A protein is a polymer of many monomers called amino acids that are linked together by covalent bonds. The structure of a protein is held together by hydrogen bonds between the amino acids in the polymer (remember prima ...
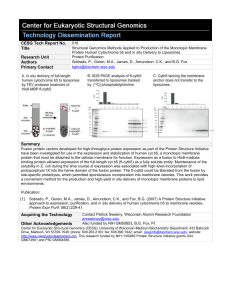
Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics (CESG)
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
... Fusion protein vectors developed for high-throughput protein expression as part of the Protein Structure Initiative have been investigated for use in the expression and stabilization of human cyt b5, a monotopic membrane protein that must be attached to the cellular membrane for function. Expression ...
Night Time Muscle Growth
... Protein shake (Casein) before bed stimulates muscle growth Many athletes like to consume a last protein shake just before turning in for the night. This provides their muscles with extra amino acids while they sleep, and that's good for muscle growth, they say. And they're right too: Dutch nutrition ...
... Protein shake (Casein) before bed stimulates muscle growth Many athletes like to consume a last protein shake just before turning in for the night. This provides their muscles with extra amino acids while they sleep, and that's good for muscle growth, they say. And they're right too: Dutch nutrition ...
The endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi
... taken from NADPH Hepatocytes are really good at making NADPH P-450 destroys carcinogens/toxins System increases solubility/removal of metabolites Water soluble toxins no longer reabsorbed BASIC RXN: R-H+NADPH+H++O2R-OH+NADP+H2O Cells make more P-450 if stimulus continues! This is called enzyme or P ...
... taken from NADPH Hepatocytes are really good at making NADPH P-450 destroys carcinogens/toxins System increases solubility/removal of metabolites Water soluble toxins no longer reabsorbed BASIC RXN: R-H+NADPH+H++O2R-OH+NADP+H2O Cells make more P-450 if stimulus continues! This is called enzyme or P ...
Worksheet Answer Key
... The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. They are each polymers made up from the monomer of a nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of 3 parts: nitrogen base, a five carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. There are 5 types of bases. The purines are two ring structures and include adenine and g ...
... The two main types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. They are each polymers made up from the monomer of a nucleotide. A nucleotide consists of 3 parts: nitrogen base, a five carbon sugar, and a phosphate group. There are 5 types of bases. The purines are two ring structures and include adenine and g ...
Presentation Title Goes Right Here
... Nathan Edwards Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology University of Maryland, College Park ...
... Nathan Edwards Center for Bioinformatics and Computational Biology University of Maryland, College Park ...
Organic compounds Carbon compounds are also called organic
... Steroids are also a type of lipid. There are many different types of steroids with different functions, but all can be recognized by their 4 fused carbon-ring structure. Proteins contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Proteins are large folded molecules made of amino acid sub-units ...
... Steroids are also a type of lipid. There are many different types of steroids with different functions, but all can be recognized by their 4 fused carbon-ring structure. Proteins contain nitrogen as well as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Proteins are large folded molecules made of amino acid sub-units ...
Proteins: 3D-Structure Protein Structure Terminology
... Number of repeating units per turn = n d = p/n = Rise per repeating unit (distance) α-helix is right-handed – point your thumb up and curl your fingers on your right hand for α-helix. Several types α, 2.27 ribbon, 310 , π-helices, or the most common is the α-helix. ...
... Number of repeating units per turn = n d = p/n = Rise per repeating unit (distance) α-helix is right-handed – point your thumb up and curl your fingers on your right hand for α-helix. Several types α, 2.27 ribbon, 310 , π-helices, or the most common is the α-helix. ...
Document
... Uses of Absorbance Spectra: Quantitating Protein by Amino Acid absorption Why not just weigh the protein? * Most samples are typically quantities of milligrams or even micrograms, not grams, and thus, it is difficult to transfer and measure such small amounts * Water is present in proteins, and it ...
... Uses of Absorbance Spectra: Quantitating Protein by Amino Acid absorption Why not just weigh the protein? * Most samples are typically quantities of milligrams or even micrograms, not grams, and thus, it is difficult to transfer and measure such small amounts * Water is present in proteins, and it ...
Chapter 3: Molecules of Life The molecules of life contain a high
... ______________________________: two or more polypeptide chains that are closely associated or covalently bonded together Enzymes often attach sugars to proteins (____________________) or lipids to proteins (____________________) Heat, some salts, shifts in pH, or detergents can denature (unravel) a ...
... ______________________________: two or more polypeptide chains that are closely associated or covalently bonded together Enzymes often attach sugars to proteins (____________________) or lipids to proteins (____________________) Heat, some salts, shifts in pH, or detergents can denature (unravel) a ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.