Chemistry 695C Fall 2001 Exam 1 Key
... b) “corners” between α-helical regions invariably contained a glycine residue, which, because of its unique properties, cannot fit into the helix. c) highly polar or charged amino acid residues tended to be located at the interior of the protein d) the structure was very compact, with virtually no i ...
... b) “corners” between α-helical regions invariably contained a glycine residue, which, because of its unique properties, cannot fit into the helix. c) highly polar or charged amino acid residues tended to be located at the interior of the protein d) the structure was very compact, with virtually no i ...
Protein Structure Prediction (10 points total)
... domains has evolved by the combinatorial assembly and/or exchange of smaller polypeptide segments. To investigate this proposal, we fused DNA encoding the N-terminal half of a beta-barrel domain (from cold shock protein CspA) with fragmented genomic Escherichia coli DNA and cloned the repertoire of ...
... domains has evolved by the combinatorial assembly and/or exchange of smaller polypeptide segments. To investigate this proposal, we fused DNA encoding the N-terminal half of a beta-barrel domain (from cold shock protein CspA) with fragmented genomic Escherichia coli DNA and cloned the repertoire of ...
Chapter 5.tst - HCC Learning Web
... D) primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary E) tertiary 8) What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins? A) chaperonin B) enzyme protein C) tertiary protein D) renaturing protein E) denaturing protein 9) One of the primary functions of RNA mol ...
... D) primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary E) tertiary 8) What is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins? A) chaperonin B) enzyme protein C) tertiary protein D) renaturing protein E) denaturing protein 9) One of the primary functions of RNA mol ...
Proteins - Northern Highlands
... different conformations determined by the primary sequence of amino acids. α-Helix: formation is stabilized by H-bonds between amino nitrogens and carbonyl carbons of the peptide bonds every 4 amino acids apart. Helical coiling of the peptide backbone results - Keratin (hair), Myosin (muscles), Fibr ...
... different conformations determined by the primary sequence of amino acids. α-Helix: formation is stabilized by H-bonds between amino nitrogens and carbonyl carbons of the peptide bonds every 4 amino acids apart. Helical coiling of the peptide backbone results - Keratin (hair), Myosin (muscles), Fibr ...
B2 - Enzymes
... B2 - Enzymes Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? Answer: Photosynthesis, digestion, respiration and biological washing powders all use enzymes! ...
... B2 - Enzymes Starter: Which of these uses enzymes? Answer: Photosynthesis, digestion, respiration and biological washing powders all use enzymes! ...
Organic Compounds
... • Proteins are the building materials for the body. – Hair, skin, muscles, and organs are made mostly of proteins. ...
... • Proteins are the building materials for the body. – Hair, skin, muscles, and organs are made mostly of proteins. ...
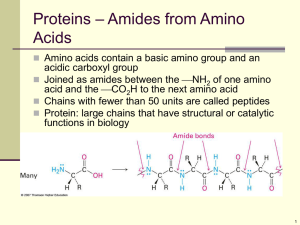
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... acid and the CO2H to the next amino acid Chains with fewer than 50 units are called peptides Protein: large chains that have structural or catalytic functions in biology ...
... acid and the CO2H to the next amino acid Chains with fewer than 50 units are called peptides Protein: large chains that have structural or catalytic functions in biology ...
Conformational Analysis of a Set of Peptides Corresponding
... Introduction to Ribosome Ribosome contains one mRNA and two tRNA ...
... Introduction to Ribosome Ribosome contains one mRNA and two tRNA ...
A non-conventional nuclear import pathway Sandra Korge1, Bert
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
... Generating a 24 hour rhythm of the molecular circadian clock is influenced by transcriptional and translational regulation as well as post-translational processes as nucleocytoplasmic protein shuttling. As it is known for Period (PER), Cryptochrome (CRY) and other clock proteins to carry classical n ...
Chapter 14 Oxidative Phosphorylation Prokaryotes are bacteria
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
... Eukaryotes contain multiple chromosomes surrounded by a membrane (nucleus) and membrane-bound organelles. Some organelles such as the nucleus and mitochondrion have two membranes. Animal Cell ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... ____________________ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. ____________________ 2. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of ...
... ____________________ 1. This measures the hydrogen ion level of a solution. ____________________ 2. This is the name for a compound with many sugar subunits linked together. ____________________ 3. This is the name given to an amino acid added to a dipeptide. ____________________ 4. Of what kind of ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
... Two types of nucleic acids – 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) – double strand of genetic information 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) – single strand copy of DNA used to build proteins Examples of nongenetic nucleotides - plays a major role in cell metabolism 1. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) – carries energy ...
biochem study guide
... proteins are so sensitive to changes in temperature and pH. 8. Diagram an individual nucleotide, identify the five-carbon sugar, the phosphate group and the nitrogenous base. 9. Identify examples of each of the four main classes of organic molecules and the building block components of each. 10. Exp ...
... proteins are so sensitive to changes in temperature and pH. 8. Diagram an individual nucleotide, identify the five-carbon sugar, the phosphate group and the nitrogenous base. 9. Identify examples of each of the four main classes of organic molecules and the building block components of each. 10. Exp ...
Lecture 12
... • Activation of proteases – Pepsinogen (stomach) to pepsin – Trypsinogen (pancrease) to trypsin – Chymotrypsinogen (pancrease) to chymotrypsin – Procarboxypeptidase (pancrease) to carboxypeptidase – Proelastase (pancrease ) to elastase ...
... • Activation of proteases – Pepsinogen (stomach) to pepsin – Trypsinogen (pancrease) to trypsin – Chymotrypsinogen (pancrease) to chymotrypsin – Procarboxypeptidase (pancrease) to carboxypeptidase – Proelastase (pancrease ) to elastase ...
Document
... the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition and puzzle-solving abilities make them more efficient than existing computer programs at pattern-folding tasks. If this turns out to be true, we can the ...
... the folds of unsolved proteins as well as designing new proteins to cure diseases. We’re collecting data to find out if humans' pattern-recognition and puzzle-solving abilities make them more efficient than existing computer programs at pattern-folding tasks. If this turns out to be true, we can the ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.