File
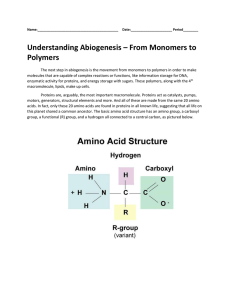
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
... The next step in abiogenesis is the movement from monomers to polymers in order to make molecules that are capable of complex reactions or functions, like information storage for DNA, enzymatic activity for proteins, and energy storage with sugars. These polymers, along with the 4th macromolecule, l ...
Peptides - Alfred State College
... Affinity for a ligand Solubility Hydrophobicity Thermal stability ...
... Affinity for a ligand Solubility Hydrophobicity Thermal stability ...
Building Materials of Life
... bonds than carbohydrates and therefore contain more chemical energy. Lipids store more than twice the energy per grams as carbohydrates or proteins.) ...
... bonds than carbohydrates and therefore contain more chemical energy. Lipids store more than twice the energy per grams as carbohydrates or proteins.) ...
From Genes to Proteins
... 1. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. (Use chart on p. 211.) 2. Determine the anticodon of each tRNA molecule that will bind to this mRNA segment. 3. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA from which the mRNA ...
... 1. Determine the sequence of amino acids that will result from the translation of the segment of mRNA above. (Use chart on p. 211.) 2. Determine the anticodon of each tRNA molecule that will bind to this mRNA segment. 3. Determine the sequence of nucleotides in the segment of DNA from which the mRNA ...
Prot Structure - USD Home Pages
... • Relate the two general classes of proteins to their respective structure and function • Discriminate between the four levels of protein structure in terms of the “focus-level”, bonds and roles each part of the amino acid/peptide backbone/aa side group plays in the structure • Understand the primar ...
... • Relate the two general classes of proteins to their respective structure and function • Discriminate between the four levels of protein structure in terms of the “focus-level”, bonds and roles each part of the amino acid/peptide backbone/aa side group plays in the structure • Understand the primar ...
Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
... Abstract The cytoskeleton is a cellular structure comprised of three types of protein filaments called microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules respectively. These filaments are highly dynamic and can change their organisation and properties according to the current needs of a cell. T ...
amino acids - Wando High School
... The carbon atom has four electrons available for bonding in its outer energy level. When two carbons bond, they can form a single, double or triple bond (sharing 1, 2, or 3 electrons) Carbons can form short chains, long chains, rings, or branched chains ...
... The carbon atom has four electrons available for bonding in its outer energy level. When two carbons bond, they can form a single, double or triple bond (sharing 1, 2, or 3 electrons) Carbons can form short chains, long chains, rings, or branched chains ...
Extraction and Purification
... • Density gradient centrifugation; – Exploits the different density of organelles – Density gradients are formed by using sucrose as solute – Can be step gradient or continuous – Centrifuge for set time at a know force and determine where your compound is or run it until it reaches equilibrium. Samp ...
... • Density gradient centrifugation; – Exploits the different density of organelles – Density gradients are formed by using sucrose as solute – Can be step gradient or continuous – Centrifuge for set time at a know force and determine where your compound is or run it until it reaches equilibrium. Samp ...
Protein Synthesis II
... ! Matches codons with amino acids (called “adaptor” or “translator” molecule). ! Generally a cloverleaf with secondary and tertiary structure; has “anticodon” at one end (3 bases complementary to codon), corresponding amino acid hooked onto the other end. ...
... ! Matches codons with amino acids (called “adaptor” or “translator” molecule). ! Generally a cloverleaf with secondary and tertiary structure; has “anticodon” at one end (3 bases complementary to codon), corresponding amino acid hooked onto the other end. ...
3 - University High School
... _____ 6. All enzymes are proteins that give energy to a cell. _____ 7. An enzyme is a protein that causes chemical reactions to occur in a cell. _____ 8. Muscles are made of protein. _____ 9. Some proteins are hormones. _____ 10. Proteins can serve many different functions. _____ 11. Proteins are ma ...
... _____ 6. All enzymes are proteins that give energy to a cell. _____ 7. An enzyme is a protein that causes chemical reactions to occur in a cell. _____ 8. Muscles are made of protein. _____ 9. Some proteins are hormones. _____ 10. Proteins can serve many different functions. _____ 11. Proteins are ma ...
CHAPTER 5 THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF LARGE
... 26. List the major components of a nucleotide, and describe how these monomers are linked to form a nucleic acid. Name the type of bond that holds two nucleotides together. 27. Distinguish between: a. pyrimidine and purine b. nucleotide and nucleoside c. ribose and deoxyribose d. 5’ end and 3’ end o ...
... 26. List the major components of a nucleotide, and describe how these monomers are linked to form a nucleic acid. Name the type of bond that holds two nucleotides together. 27. Distinguish between: a. pyrimidine and purine b. nucleotide and nucleoside c. ribose and deoxyribose d. 5’ end and 3’ end o ...
$doc.title
... monosaccharides can join to form one disaccharide (a dehydration synthesis reaction) ...
... monosaccharides can join to form one disaccharide (a dehydration synthesis reaction) ...
Practice Questions
... In the absence of trophic factors, __apoptosis____ is triggered when Bad binds to Bcl proteins and allows _____bax_________ to form channels and let ions move into the mitochondria. This ion flux leads to both the release of ____cytochrome C______ from the mitochondria and its binding to Apaf1 and t ...
... In the absence of trophic factors, __apoptosis____ is triggered when Bad binds to Bcl proteins and allows _____bax_________ to form channels and let ions move into the mitochondria. This ion flux leads to both the release of ____cytochrome C______ from the mitochondria and its binding to Apaf1 and t ...
Defining immortality of stem cells to identify novel anti
... cellular protein content. This ability declines during the aging process, inducing the accumulation of damaged and misfolded proteins that can lead to cell death or malfunction. Several neurodegenerative age-related disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are linked to a d ...
... cellular protein content. This ability declines during the aging process, inducing the accumulation of damaged and misfolded proteins that can lead to cell death or malfunction. Several neurodegenerative age-related disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or Huntington’s disease are linked to a d ...
Why teach a course in bioinformatics?
... • It's amazing that not only do proteins selfassemble -- fold -- but they do so amazingly quickly: some as fast as a millionth of a second. While this time is very fast on a person's timescale, it's remarkably long for computers to simulate. In fact there is a 1000 fold gap between the simulation ti ...
... • It's amazing that not only do proteins selfassemble -- fold -- but they do so amazingly quickly: some as fast as a millionth of a second. While this time is very fast on a person's timescale, it's remarkably long for computers to simulate. In fact there is a 1000 fold gap between the simulation ti ...
Proteins_Fats
... build and maintain lean body mass. It also maintains strong hair, skin, and teeth. But it doesn’t stop there – protein is also vitally important in maintaining blood, organs, tendons, and in the production and smooth functioning of hormones, enzymes, immune cells and brain neurotransmitters. In shor ...
... build and maintain lean body mass. It also maintains strong hair, skin, and teeth. But it doesn’t stop there – protein is also vitally important in maintaining blood, organs, tendons, and in the production and smooth functioning of hormones, enzymes, immune cells and brain neurotransmitters. In shor ...
PP-Protein Synthesis
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
... Proteins have MANY different functions Enzymes to help control/speed up chemical reactions Help to build and repair cell structures Determine the structure & function of living organisms ...
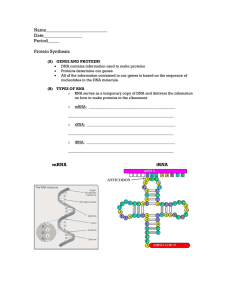
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
... Protein Synthesis (A) GENES AND PROTEINS DNA contains information used to make proteins ...
Chem for Bio 9, part 2- Biological Macromolecules
... amino acid sequence • Determined by the sequence of amino acids • Amino acids linked by peptide bonds • Chain is called polypeptide • Sequence proceeds from “Nterminus” to “C-terminus” • Amino acid sequence determined by DNA code ...
... amino acid sequence • Determined by the sequence of amino acids • Amino acids linked by peptide bonds • Chain is called polypeptide • Sequence proceeds from “Nterminus” to “C-terminus” • Amino acid sequence determined by DNA code ...
Bonding is more than attraction
... • What is a nucleic acid? - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
... • What is a nucleic acid? - It is a long chain of smaller molecules called nucleotides. • What is a nucleotide? - A nucleotide has three parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group, which contains phosphorus and oxygen atoms. ...
Protein Degradation
... because they can form non-physiological interactions with other proteins. – If a damaged protein is not repaired, it is degraded in specialized organelles such as the lysosome, and by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. ...
... because they can form non-physiological interactions with other proteins. – If a damaged protein is not repaired, it is degraded in specialized organelles such as the lysosome, and by the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.