Highly Efficient Protein Recovery from Food By
... the total weight of fish is considered a waste or a lowvalue product, composed mainly of heads, internal organs, tail, fins, frames and skin. Protein content and amino acid profile in these by-products are similar to that in fillets hence there is a significant amount of high quality protein current ...
... the total weight of fish is considered a waste or a lowvalue product, composed mainly of heads, internal organs, tail, fins, frames and skin. Protein content and amino acid profile in these by-products are similar to that in fillets hence there is a significant amount of high quality protein current ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... Protein Structure Contd • Tertiary Structure: The folding and twisting that results in the 3-D shape of polypeptide. – H-bonds, disulfide links (fxnl group?), Ionic bonds, and other molecular interactions between R groups. ...
... Protein Structure Contd • Tertiary Structure: The folding and twisting that results in the 3-D shape of polypeptide. – H-bonds, disulfide links (fxnl group?), Ionic bonds, and other molecular interactions between R groups. ...
Protein Analysis
... They are measured by reacting them with a compound called ninhydrin. Alpha Amino acids will be given an intense blue color while imino acids (proline, hydroproline) will be given a yellow color. The concentration of a single amino acid is proportional to the light absorbance of the solution after ad ...
... They are measured by reacting them with a compound called ninhydrin. Alpha Amino acids will be given an intense blue color while imino acids (proline, hydroproline) will be given a yellow color. The concentration of a single amino acid is proportional to the light absorbance of the solution after ad ...
Three Dimensional Protein Structures
... Three Dimensional Protein Structures Conformation: Spatial arrangement of atoms that depend on bonds and bond rotations. Proteins can change conformation, however, most proteins have a stable “native” conformation. The native protein is folded through weak interactions: a) Hydrophobic interactions ...
... Three Dimensional Protein Structures Conformation: Spatial arrangement of atoms that depend on bonds and bond rotations. Proteins can change conformation, however, most proteins have a stable “native” conformation. The native protein is folded through weak interactions: a) Hydrophobic interactions ...
Biomolecules
... It’s not just for the water cycle anymore • Macromolecules are constructed by covalently bonding monomers by condensation reactions where water is removed from the functional groups of the monomers • Dehydration synthesis (water is removed) • A hydroxyl (-OH) from one monomer and a hydrogen (-H) fro ...
... It’s not just for the water cycle anymore • Macromolecules are constructed by covalently bonding monomers by condensation reactions where water is removed from the functional groups of the monomers • Dehydration synthesis (water is removed) • A hydroxyl (-OH) from one monomer and a hydrogen (-H) fro ...
Health Science 1110-2007 Module 3 Organic Chemistry Lab 3
... c. May store hereditary information d. Both (b) and (c) e. (a), (b), and (c) 2. Sugars with the formula CnH2n0n can have: a. Hydrogen (H) atoms covalently bound to the carbon (C) of a C=0 group b. Carbon (C) atoms which are covalently bound to three H atoms c. The formula C3H6O3 d. Both (a) and (c) ...
... c. May store hereditary information d. Both (b) and (c) e. (a), (b), and (c) 2. Sugars with the formula CnH2n0n can have: a. Hydrogen (H) atoms covalently bound to the carbon (C) of a C=0 group b. Carbon (C) atoms which are covalently bound to three H atoms c. The formula C3H6O3 d. Both (a) and (c) ...
Basics Terms of Life Science Cells
... on how to make proteins, particularly enzymes that catalyses the biochemical reactions inside the body. ...
... on how to make proteins, particularly enzymes that catalyses the biochemical reactions inside the body. ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Polysaccharides - These consist of many monosaccharides bonded together. Some examples of polysaccharides are: Glycogen – this is the storage form of glucose in animals. Starch – this is the storage form of glucose in plants. Cellulose – this molecule serves as a support molecule in plants. 2. Disc ...
... Polysaccharides - These consist of many monosaccharides bonded together. Some examples of polysaccharides are: Glycogen – this is the storage form of glucose in animals. Starch – this is the storage form of glucose in plants. Cellulose – this molecule serves as a support molecule in plants. 2. Disc ...
Carbohydrates, proteins and lipids Chapter 3 MACROMOLECULES
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
... • Structural proteins provide physical stability and movement. • Transport proteins carry substances within the organism (e.g., hemoglobin ) • Genetic regulatory proteins regulate when, how, and to what extent a gene is expressed. AMINO ACIDS Amino acids have carboxyl and amino groups—so they functi ...
proteins
... • The folding of a protein from a chain of amino acids occurs spontaneously. • The function of a protein is an emergent property resulting from its specific molecular order. • Three levels of structure: primary, secondary, and tertiary structure, are used to organize the folding within a single pol ...
... • The folding of a protein from a chain of amino acids occurs spontaneously. • The function of a protein is an emergent property resulting from its specific molecular order. • Three levels of structure: primary, secondary, and tertiary structure, are used to organize the folding within a single pol ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... Protein Structure Contd • Tertiary Structure: The folding and twisting that results in the 3-D shape of polypeptide. – H-bonds, disulfide links (fxnl group?), Ionic bonds, and other molecular interactions between R groups. ...
... Protein Structure Contd • Tertiary Structure: The folding and twisting that results in the 3-D shape of polypeptide. – H-bonds, disulfide links (fxnl group?), Ionic bonds, and other molecular interactions between R groups. ...
cell division. - cis myp science
... microtubules arranged in a specific way. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at right angles. The centrioles are found in pairs and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it is time for cell division. ...
... microtubules arranged in a specific way. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at right angles. The centrioles are found in pairs and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it is time for cell division. ...
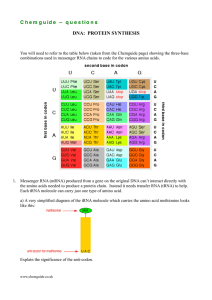
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is involved in finding the start of the a ...
... b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is involved in finding the start of the a ...
Biochemistry Study Guide – Exam 1
... Energy, entropy, enthalpy Equations for enthalpy change Free energy and free energy changes ...
... Energy, entropy, enthalpy Equations for enthalpy change Free energy and free energy changes ...
Part 2 - people.iup.edu
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
Carbon compounds - Sonoma Valley High School
... out the ‘amino’ and carboxyl group to label it? ...
... out the ‘amino’ and carboxyl group to label it? ...
Chapter 5
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
... • Enzymes are probably the most important type of protein. They act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.