Chapter 3: The Molecules of Cells
... contain double bonds – These prevent them from solidifying at room temperature ...
... contain double bonds – These prevent them from solidifying at room temperature ...
Week 2 Handout with No answers
... The number of ordered water molecules, and therefore the magnitude of the entropy decrease, depends on the surface area of the hydrophobic molecule enclosed with the cage of water. I.e. more lipid surface area = more organized water = less entropy which is energetically un favorable. Water is capabl ...
... The number of ordered water molecules, and therefore the magnitude of the entropy decrease, depends on the surface area of the hydrophobic molecule enclosed with the cage of water. I.e. more lipid surface area = more organized water = less entropy which is energetically un favorable. Water is capabl ...
Chapter 3 (part 2) – Protein Function
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
College 5
... Protein folding in a living cell is often assisted by special proteins called molecular chaperones. These proteins bind to partly folded polypeptide chains and help them progress along the energetically most favorable folding pathway. Chaperones are vital in the crowded conditions of the cytoplasm, ...
... Protein folding in a living cell is often assisted by special proteins called molecular chaperones. These proteins bind to partly folded polypeptide chains and help them progress along the energetically most favorable folding pathway. Chaperones are vital in the crowded conditions of the cytoplasm, ...
Las proteínas que `resisten` a la sal
... with different salts, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, etc. This was a very basic interest. From early studies of different mutants that we obtained from a protein, and taking into account the existing literature, we realised that this problem was not solved. We established the hypothesis and fr ...
... with different salts, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, etc. This was a very basic interest. From early studies of different mutants that we obtained from a protein, and taking into account the existing literature, we realised that this problem was not solved. We established the hypothesis and fr ...
Proteomics_Overview_BB_3_09_rev1
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
... Technological Advances Help Us See Both the Forest and the Trees ...
Proteins
... • the haem group is not made of AA, but is an integral part of the protein – prosthetic grp. • Each haem group contains an ion of iron ...
... • the haem group is not made of AA, but is an integral part of the protein – prosthetic grp. • Each haem group contains an ion of iron ...
Unit 1 Rev 2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly work, what does the cell have (use) in order to help it build thes ...
... ___ 2. Name the three main nutrient groups/chemicals used by cells. ___ 3. What are the basic building blocks that make up a protein molecule? ___ 4. Many of the proteins/enzymes that a cell makes are crucial for the cell to properly work, what does the cell have (use) in order to help it build thes ...
What`s so great about Protein
... Proteins are compounds that are made by linking together amino acids into chains-like structures called peptides. One amino acid is joined to a second; a third is then added to the first two and so on. The bonds between amino acids are called peptide bonds. Peptides are then linked together into lon ...
... Proteins are compounds that are made by linking together amino acids into chains-like structures called peptides. One amino acid is joined to a second; a third is then added to the first two and so on. The bonds between amino acids are called peptide bonds. Peptides are then linked together into lon ...
Cells as Molecular Factories
... The damaged protein is brought to a _________________ where enzymes digest the protein into amino acids which can be used to synthesize new proteins. A new protein to replace the damaged protein is synthesized by a ___________________ . The instructions for making the replacement protein are provide ...
... The damaged protein is brought to a _________________ where enzymes digest the protein into amino acids which can be used to synthesize new proteins. A new protein to replace the damaged protein is synthesized by a ___________________ . The instructions for making the replacement protein are provide ...
Lh6Ch04aProt
... biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is a cost in conformational entropy of folding the protein into one specific native fold ...
... biological function • This structure is called the native fold • The native fold has a large number of favorable interactions within the protein • There is a cost in conformational entropy of folding the protein into one specific native fold ...
Protein Structures
... groups in amino acids are either hydrophobic or hydrophilic and will seek aquatic or non-aquatic environments accordingly, which determines their location within the protein. Hydrogen bonds facilitate stabilization within the proteins based on the shape established by the hydrophobic interactions. I ...
... groups in amino acids are either hydrophobic or hydrophilic and will seek aquatic or non-aquatic environments accordingly, which determines their location within the protein. Hydrogen bonds facilitate stabilization within the proteins based on the shape established by the hydrophobic interactions. I ...
Uncommon amino acids, amino acids forming proteins
... An example of this is how bovine insulin is used for instant injections for humans. Even though the insulin is not identical in structure to human insulin it still performs the same task when introduced into a human. Although it does perform the same task it is not as ...
... An example of this is how bovine insulin is used for instant injections for humans. Even though the insulin is not identical in structure to human insulin it still performs the same task when introduced into a human. Although it does perform the same task it is not as ...
A new strategy for quantitative proteomics using isotope
... determination is not accurate and the reproducibility of the 2D-gels is very poor. Recent developments, like the ICAT reagent [1] or GIST [2] methodology have shown to be powerful alternatives to comparative 2D gel imaging analysis. Nevertheless, these methods also have their limitations. Here we de ...
... determination is not accurate and the reproducibility of the 2D-gels is very poor. Recent developments, like the ICAT reagent [1] or GIST [2] methodology have shown to be powerful alternatives to comparative 2D gel imaging analysis. Nevertheless, these methods also have their limitations. Here we de ...
Unit 3 Biology - moleculesoflife2
... Two types include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA. (Ribonucleic acid) Both are created from long chains of units known as nucleotides. DNA carries genetic instructions required to assemble the proteins. ...
... Two types include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA. (Ribonucleic acid) Both are created from long chains of units known as nucleotides. DNA carries genetic instructions required to assemble the proteins. ...
They do NOT like water!
... metabolism by moderating chemical reactions. – All proteins are structurally complex in 3 dimensions. – All are constructed from the same set of 20 monomers, called amino acids. ...
... metabolism by moderating chemical reactions. – All proteins are structurally complex in 3 dimensions. – All are constructed from the same set of 20 monomers, called amino acids. ...
MolBioIntro
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
Translation (Protein Synthesis)
... • Brings amino acids to the ribosome so it can build proteins • It has Anticodons – 3 nucleotide sequence complementary to the mRNA codon ...
... • Brings amino acids to the ribosome so it can build proteins • It has Anticodons – 3 nucleotide sequence complementary to the mRNA codon ...
PP Ch_ 2-3 Modified - Maria Regina High School
... 1 Monomer of a Protein = 1 amino acid A large chain (polymer) of amino acids is a Polypeptide ...
... 1 Monomer of a Protein = 1 amino acid A large chain (polymer) of amino acids is a Polypeptide ...
AP Biology 2 -
... Denaturing impact that heat and pH can have on protein structure Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Structure and function of organelles in both plant and animal cells Organelles found only in plant or animal cells Why membranes are selectively permeable Role of phospholipids and p ...
... Denaturing impact that heat and pH can have on protein structure Differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Structure and function of organelles in both plant and animal cells Organelles found only in plant or animal cells Why membranes are selectively permeable Role of phospholipids and p ...
GLYCOGEN – energy storage in ANIMALS • Stored as cytoplasmic
... Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence (glu → ala) Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped FACTORS AFFECTING CONFORMATION Folding occurs a ...
... Since shape is determined by amino acid sequence; changing sequence changes 3D shape EX: Sickle cell anemia mutation changes one amino acid in the sequence (glu → ala) Abnormal hemoglobin molecules crystallize; cause blood cells to become sickle shaped FACTORS AFFECTING CONFORMATION Folding occurs a ...
Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
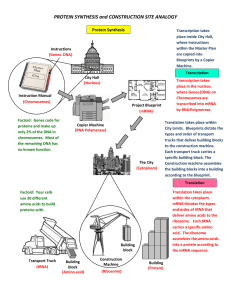
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
... Transcription takes place in the nucleus, where Genes (DNA) on Chromosomes are transcribed into mRNA by RNA Polymerase. Translation takes place within City Limits. Blueprints dictate the types and order of transport trucks that deliver building blocks to the construction machine. Each transport truc ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.