Macromolecules: Proteins
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid H ...
Designer enzymes Donald Hilvert ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
... understand the rules of protein folding, and our knowledge of structure-function relationships in these macromolecules is at best incomplete. Nature has solved the problem of protein design through the mechanism of Darwinian evolution. From primitive precursors, recursive cycles of mutation, selecti ...
ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins ...
... Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins ...
Chapter01 Introduction Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins (绪论
... Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The hydrophobic tail of dodecylsulfate interacts strongly with polypeptide chains. Each dodecylsulfate contribute two negative charges. Thus all protein samples undergone electrophoresis are negatively charged. Sulfhydryl-reducing agents such as -mercaptoethanol is a ...
... Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The hydrophobic tail of dodecylsulfate interacts strongly with polypeptide chains. Each dodecylsulfate contribute two negative charges. Thus all protein samples undergone electrophoresis are negatively charged. Sulfhydryl-reducing agents such as -mercaptoethanol is a ...
FST 123 - Enzymology Homework IS `13
... c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 (State any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel.) d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a sa ...
... c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 (State any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel.) d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a sa ...
Exam II Review: - Texas Tech University
... RF-2: Recognizes UAA + UGA stop codons. RF-3: Stimulates RF- 1 & 2 release via GTP hydrolysis. RRF: Together with EF-G, induces ribosomal dissociation of small and large subunits. ...
... RF-2: Recognizes UAA + UGA stop codons. RF-3: Stimulates RF- 1 & 2 release via GTP hydrolysis. RRF: Together with EF-G, induces ribosomal dissociation of small and large subunits. ...
Unit 2 Test Retake Review Sheet – Cell Biology Answer questions
... Why are macromolecules important components of living things? Macromolecules are polymers composed of repeating sub-units called ___________. Identify the basic monomer for each type of macromolecule. Describe the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Distinguish the functi ...
... Why are macromolecules important components of living things? Macromolecules are polymers composed of repeating sub-units called ___________. Identify the basic monomer for each type of macromolecule. Describe the structure of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids Distinguish the functi ...
Organic Molecules
... • Made up of monomers called amino acids • 20 essential amino acids form polypeptide bonds to form protein ...
... • Made up of monomers called amino acids • 20 essential amino acids form polypeptide bonds to form protein ...
G-protein linked receptors
... • The addition of Pi to a protein, which activates the protein. • Usually adds Pi to Serine or Threonine. ...
... • The addition of Pi to a protein, which activates the protein. • Usually adds Pi to Serine or Threonine. ...
Introduction, ppt file - Cheriton School of Computer Science
... It is unclear why Dform was not chosen ...
... It is unclear why Dform was not chosen ...
Question 2:
... enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase and beta–galactosidase in live bacteria. In contrast, D-Pyrrhocoricin, magainin 2, or buforin II, an antimicrobial peptide involved in binding to bacterial nucleic acids (see below), had only negligible effect. Example 2: Binding to DNA and inhibit DNA synt ...
... enzymatic activity of alkaline phosphatase and beta–galactosidase in live bacteria. In contrast, D-Pyrrhocoricin, magainin 2, or buforin II, an antimicrobial peptide involved in binding to bacterial nucleic acids (see below), had only negligible effect. Example 2: Binding to DNA and inhibit DNA synt ...
BIOS 1300 SI WORKSHEET 2 (Chapter 2) SI Leader: Merrin Jeffries
... 21.List (from simplest to most complex) the four levels of structural complexity that proteins can have: ...
... 21.List (from simplest to most complex) the four levels of structural complexity that proteins can have: ...
Cellular compartmentalization
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
... Here is an illustration of how proteins targeted to the mitochondria are delivered. First the protein must carry the appropriate signal sequence. Then, it attaches to a receptor protein on the outer membrane. This complex diffuses until it reaches a contact site, where it is treaded through both ch ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
... from monomers called amino acids. Hundreds of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds and fold into a specific shape to make up a protein. There are 20 different types of amino acids. ...
02/13
... Nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) are located in interior of proteins such as DNA and RNA polymerases. They are recognized by nuclear pore proteins for transport into nucleus. ...
... Nuclear localization sequences (NLSs) are located in interior of proteins such as DNA and RNA polymerases. They are recognized by nuclear pore proteins for transport into nucleus. ...
Lecture 4
... interact with the non polar lipid bilayers, they have hydrophobic amino acid residues on the surface. These proteins do not have stable structures in aqueous solution. ...
... interact with the non polar lipid bilayers, they have hydrophobic amino acid residues on the surface. These proteins do not have stable structures in aqueous solution. ...
ERT320 BIOSEPARATION ENGINEERING
... aggregated protein, and undissolved nutrients. Common operations for this purpose are sedimentation, centrifugation, and filtration. Isolation and Concentration. Generally refers to the isolation of the desired product from unrelated impurities. Significant concentration is achieved in the early s ...
... aggregated protein, and undissolved nutrients. Common operations for this purpose are sedimentation, centrifugation, and filtration. Isolation and Concentration. Generally refers to the isolation of the desired product from unrelated impurities. Significant concentration is achieved in the early s ...
Ribosome and Endoplasmic Reticulum
... What is a Ribosome? A Ribosome is a cluster of proteins and nucleic acids that constructs proteins in a cell. They are found in the cytoplasm of a cell or on the endoplasmic reticulum and in both animal and plant cells. ...
... What is a Ribosome? A Ribosome is a cluster of proteins and nucleic acids that constructs proteins in a cell. They are found in the cytoplasm of a cell or on the endoplasmic reticulum and in both animal and plant cells. ...
Can use more than once
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
... Hydrophobic Tails Cell membrane Hydrophilic Head Chemical Signals Steak ...
Ch6PROTEIN
... • Otherwise, the resulting conditions of acidosis or alkalosis could lead to coma or death Transport Functions • Lipoproteins • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transferrin transports iron (hemoglobin – a protein, contains iron, but it transports oxyg ...
... • Otherwise, the resulting conditions of acidosis or alkalosis could lead to coma or death Transport Functions • Lipoproteins • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transferrin transports iron (hemoglobin – a protein, contains iron, but it transports oxyg ...
Protein Structure HW Key
... 1. Give three roles of proteins in an organism. nutrition, structure, motility, enzymes, regulatory, defense, recognition.... 2. What are prosthetic groups? non amino acid parts of a protein (heme in hemoglobin, for example) 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? glycoproteins are proteins with ...
... 1. Give three roles of proteins in an organism. nutrition, structure, motility, enzymes, regulatory, defense, recognition.... 2. What are prosthetic groups? non amino acid parts of a protein (heme in hemoglobin, for example) 3. What are glycoproteins and lipoproteins? glycoproteins are proteins with ...
Honors Biology Name Biochemistry Exam Review #1 Period _____
... The pocket or groove where the substrate fits into on the enzyme is called the active site. (See diagram in enzyme notes for enzyme structure) Enzymes are named for the substrate that they work with. Names usually end in –ase (ex. Lactase, Helicase) Enzymes can be denatured (a change in shape) by a ...
... The pocket or groove where the substrate fits into on the enzyme is called the active site. (See diagram in enzyme notes for enzyme structure) Enzymes are named for the substrate that they work with. Names usually end in –ase (ex. Lactase, Helicase) Enzymes can be denatured (a change in shape) by a ...
Review Sheet - Phillips Scientific Methods
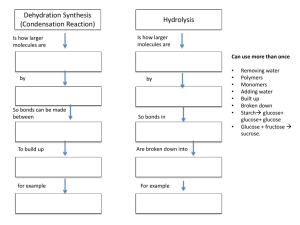
... o Proteins can have polymers and monomers o Polypeptide is a polymer of amine o Kinks can occur where double bond is present o Some can be acidic or basic –depending on balance of functional groups o Some hydrophilic, some hydrophobic o A peptide bond is formed during dehydration synthesis Bond be ...
... o Proteins can have polymers and monomers o Polypeptide is a polymer of amine o Kinks can occur where double bond is present o Some can be acidic or basic –depending on balance of functional groups o Some hydrophilic, some hydrophobic o A peptide bond is formed during dehydration synthesis Bond be ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.