ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SEMINAR Professor Jeff Kelly Biological and Chemical Approaches to Adapt
... proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, proteindegradation and the like. Stress responsive signaling pathways match proteostasis network capacity with demand in each subcellular compartment to maintain cellular ...
... proteome function by controlling ribosomal protein synthesis, chaperone and enzyme mediated protein folding, protein trafficking, proteindegradation and the like. Stress responsive signaling pathways match proteostasis network capacity with demand in each subcellular compartment to maintain cellular ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins 1. At very low pH most amino acids is have a _____ charge. 2. Disulfide bonds are formed between two ______________________ amino acids. 3. In the condensation of two amino acids one molecule of ___________ is lost. 4. Amino acids linked together in a chain are cal ...
... Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins 1. At very low pH most amino acids is have a _____ charge. 2. Disulfide bonds are formed between two ______________________ amino acids. 3. In the condensation of two amino acids one molecule of ___________ is lost. 4. Amino acids linked together in a chain are cal ...
Intracellular Protein Degradation
... for degradation of intracellular proteins Poole et al were studying the mode of action anti-malaria drugs Chloroquine and other lysosomotropic (weak bases) block the activity of lysosomal proteases by neutralizing the low pH of the lysosome. Treat macrophages labeled with 3H-leucine with chlor ...
... for degradation of intracellular proteins Poole et al were studying the mode of action anti-malaria drugs Chloroquine and other lysosomotropic (weak bases) block the activity of lysosomal proteases by neutralizing the low pH of the lysosome. Treat macrophages labeled with 3H-leucine with chlor ...
A1987J365500002
... Chou P Y. Welts M & Fasmimu G 0. Conformational studies on copolymcrs of hydroxypropyl-L.glatamine and L-leucine. Circutar-dichroism studies. Biochemistry—USA t 1:3028-343. 1972. Ch,tu P V & Fasman G 0. Structural and functional rote of leucine residues in proteins, J. Mo), Rio!. 74:263-81. 972. - C ...
... Chou P Y. Welts M & Fasmimu G 0. Conformational studies on copolymcrs of hydroxypropyl-L.glatamine and L-leucine. Circutar-dichroism studies. Biochemistry—USA t 1:3028-343. 1972. Ch,tu P V & Fasman G 0. Structural and functional rote of leucine residues in proteins, J. Mo), Rio!. 74:263-81. 972. - C ...
Part 4
... contains peptides or proteins. A violet color is produced when at least two peptide bonds are present in the peptide or protein. This means that the test will not be positive for amino acids or dipeptides. ...
... contains peptides or proteins. A violet color is produced when at least two peptide bonds are present in the peptide or protein. This means that the test will not be positive for amino acids or dipeptides. ...
Word - LangdonBiology.org
... When sugar is placed in water, the individual sugar molecules move apart, but the molecule itself stays together. What type of bonds must be present in lithium chloride? What functional group is found on sugars that make them dissolve in water? Many ionic attractions disassociate (break apart) in wa ...
... When sugar is placed in water, the individual sugar molecules move apart, but the molecule itself stays together. What type of bonds must be present in lithium chloride? What functional group is found on sugars that make them dissolve in water? Many ionic attractions disassociate (break apart) in wa ...
Protein Structure:
... 1. Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. The construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a p ...
... 1. Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. The construction of a vast array of macromolecules from a limited number of monomer building blocks is a recurring theme in biochemistry. Does protein function depend on the linear sequence of amino acids? The function of a p ...
Principles of Protein Structure
... α Helix • If N-terminus is at bottom, then all peptide N-H bonds point “down” and all peptide C=O bonds point “up”. • N-H of residue n is H-bonded to C=O of residue n+4. • a-Helix has: ...
... α Helix • If N-terminus is at bottom, then all peptide N-H bonds point “down” and all peptide C=O bonds point “up”. • N-H of residue n is H-bonded to C=O of residue n+4. • a-Helix has: ...
Proteins - UF Macromolecular Structure Group
... Proteins can bind to: Substrate Molecules (small molecules) Cell Receptors Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Polysaccharides Lipids ...
... Proteins can bind to: Substrate Molecules (small molecules) Cell Receptors Nucleic Acids (DNA/RNA) Polysaccharides Lipids ...
Document
... oligosaccharide of composition Glc3Man9GlcNAc2. The outermost two glucoses are rapidly removed through the action of glucosidases I and II to reveal the monoglucosylated species recognized by the lectin sites of calnexin/calreticulin. In their ATP-bound state, calnexin bind to the monoglucosylated o ...
... oligosaccharide of composition Glc3Man9GlcNAc2. The outermost two glucoses are rapidly removed through the action of glucosidases I and II to reveal the monoglucosylated species recognized by the lectin sites of calnexin/calreticulin. In their ATP-bound state, calnexin bind to the monoglucosylated o ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... functions: structure, transport, defense, movement, messengers, catalysts monomer – amino acid: carbon, amino, carboxyl, H and variable (R group) R group – how many – 20; important – cross links hold 3-D shape of protein Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – ...
... functions: structure, transport, defense, movement, messengers, catalysts monomer – amino acid: carbon, amino, carboxyl, H and variable (R group) R group – how many – 20; important – cross links hold 3-D shape of protein Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – ...
Chapter 10 Section 3 Notes Answer Key
... 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to bu ...
... 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins to the nucleus for the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acid bond. b. Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to bu ...
File
... • What is a chemical reaction? • Do they happen on their own? – If we stare at the piece of paper, are we going to be able to make the oxygen molecules in the air collide with the cellulose in the paper? – What do we need to do? ...
... • What is a chemical reaction? • Do they happen on their own? – If we stare at the piece of paper, are we going to be able to make the oxygen molecules in the air collide with the cellulose in the paper? – What do we need to do? ...
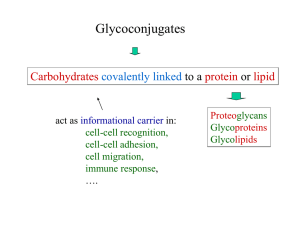
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
... • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features of glycans act as destination l ...
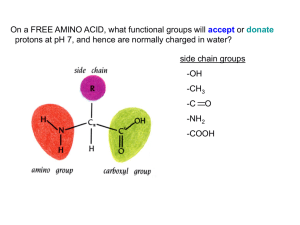
Lab 1 activity, AMINO ACIDS - Cal State LA
... Proline has a nitrogen in an aliphatic ring system • Proline (Pro, P) - has a three carbon side chain bonded to the a-amino nitrogen • The heterocyclic pyrrolidine ring restricts the geometry of polypeptides ...
... Proline has a nitrogen in an aliphatic ring system • Proline (Pro, P) - has a three carbon side chain bonded to the a-amino nitrogen • The heterocyclic pyrrolidine ring restricts the geometry of polypeptides ...
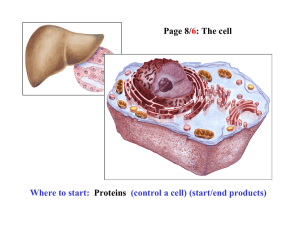
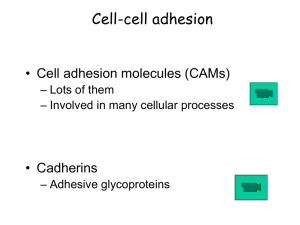
Document
... Cell-cell adhesion • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) – Lots of them – Involved in many cellular processes ...
... Cell-cell adhesion • Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) – Lots of them – Involved in many cellular processes ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... II State whether the following statements are True or False ...
... II State whether the following statements are True or False ...
Lecture 12/13 - Intracellular Transport + Cytoskeleton
... present within the AA sequence of an ER protein versus a nuclear protein? Include the modification to the ER protein that we discussed in class. 10.) What is glycosylation? What type of modification is this an example of? Be sure you can identify what the macromolecules are on this slide and any oth ...
... present within the AA sequence of an ER protein versus a nuclear protein? Include the modification to the ER protein that we discussed in class. 10.) What is glycosylation? What type of modification is this an example of? Be sure you can identify what the macromolecules are on this slide and any oth ...
File
... Initiator regions contain a purine-rich sequence called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence about 10 nucleotides 5’ of the initiator codon The Shine-Dalgarno sequence interacts with a complementary region on the 3’ end of 16S RNA ...
... Initiator regions contain a purine-rich sequence called the Shine-Dalgarno sequence about 10 nucleotides 5’ of the initiator codon The Shine-Dalgarno sequence interacts with a complementary region on the 3’ end of 16S RNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... acid to put into the polypeptide chain/protein. Click on the picture to see a video. ...
... acid to put into the polypeptide chain/protein. Click on the picture to see a video. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.