Lecture 1 - Temple University
... Figure 3-4. Steric limitations on the bond angles in a polypeptide chain. (A) Each amino acid contributes three bonds (red) to the backbone of the chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Ca C bond, whose angle of rotati ...
... Figure 3-4. Steric limitations on the bond angles in a polypeptide chain. (A) Each amino acid contributes three bonds (red) to the backbone of the chain. The peptide bond is planar (gray shading) and does not permit rotation. By contrast, rotation can occur about the Ca C bond, whose angle of rotati ...
Nanodevices
... stepwise changes in conformation over micro- to millisec. Protein nanodevices include: (a) enzymes = protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions but are not destroyed in the process; (b) cell surface receptors acting as switches turning an extracellular chemical stimulus into a cell response; ...
... stepwise changes in conformation over micro- to millisec. Protein nanodevices include: (a) enzymes = protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions but are not destroyed in the process; (b) cell surface receptors acting as switches turning an extracellular chemical stimulus into a cell response; ...
Table of Contents
... the venom of the hornet Vespa basalis Further studies on the topography of the N-terminal region of human platelet glycoprotein Illa. Localization of monoclonal antibody epitopes and the putative fibrinogen-binding sites Comparative properties of three functionally different but structurally related ...
... the venom of the hornet Vespa basalis Further studies on the topography of the N-terminal region of human platelet glycoprotein Illa. Localization of monoclonal antibody epitopes and the putative fibrinogen-binding sites Comparative properties of three functionally different but structurally related ...
Lect 9: BioMacromolecular Visualization I: Principles - BIDD
... Specific disease proteins are targets for drug discovery Knowledge of their structure useful for drug design ...
... Specific disease proteins are targets for drug discovery Knowledge of their structure useful for drug design ...
From DNA to Protein
... • RNA polymerase binds to the promoter • The promoter is a specific sequence that tells the RNA polymerase where to bind and determines what DNA strand will serve as the template • In eukaryotes, specific proteins called transcription factors assist the RNA polymerase in binding and forming the ...
... • RNA polymerase binds to the promoter • The promoter is a specific sequence that tells the RNA polymerase where to bind and determines what DNA strand will serve as the template • In eukaryotes, specific proteins called transcription factors assist the RNA polymerase in binding and forming the ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2
... They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? Unsaturated fats have a double bond between at least two carbons in ...
... They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated and an unsaturated fat? Unsaturated fats have a double bond between at least two carbons in ...
Slide 1
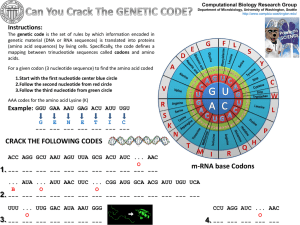
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
... The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences) is translated into proteins (amino acid sequences) by living cells. Specifically, the code defines a mapping between trinucleotide sequences called codons and amino acids. For a given codon ( ...
Aim 24: How does DNA code for the production of proteins through
... Step 4: Once the bases are all read, the attached amino acid chain is ________________________ o ...
... Step 4: Once the bases are all read, the attached amino acid chain is ________________________ o ...
Study Guide
... protein - a caloric nutrient that can be structural (materials) or functional (machines) and is made of amino acids. fat - a slippery molecule used for the body to store energy. carbohydrate - a carbon, hydrogen and oxygen molecule that includes sugar and starch. sugar - a ring-base molecule that ta ...
... protein - a caloric nutrient that can be structural (materials) or functional (machines) and is made of amino acids. fat - a slippery molecule used for the body to store energy. carbohydrate - a carbon, hydrogen and oxygen molecule that includes sugar and starch. sugar - a ring-base molecule that ta ...
Chapter 4 Cellular Metabolism
... aerobic respiration has two stages. What are they called? Kreb’s cycle and Electron transport chain Where do they occur? In the mitochondria What are the three end products of this process? Water, carbon dioxide, and energy Are any ATP’s formed in aerobic respiration? Yes If so, how many? Total of 3 ...
... aerobic respiration has two stages. What are they called? Kreb’s cycle and Electron transport chain Where do they occur? In the mitochondria What are the three end products of this process? Water, carbon dioxide, and energy Are any ATP’s formed in aerobic respiration? Yes If so, how many? Total of 3 ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
... We will also study the process where RNA is used to make proteins. Specifically, we will study each part (transcription and translation), the steps involved and the enzymes involved. We will also look more specifically at mutations; how they can occur and what effects they might have. Pages in the b ...
Basic Biochemistry Powerpoint
... other lipids and in organic solvents (alcohol, ether) or detergents • Most of the structure of lipids is non-polar • Formed almost exclusively of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Contain C, H, and O, but the proportion of oxygen in lipids is less than in carbohydrates ...
... other lipids and in organic solvents (alcohol, ether) or detergents • Most of the structure of lipids is non-polar • Formed almost exclusively of carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Contain C, H, and O, but the proportion of oxygen in lipids is less than in carbohydrates ...
lec---10
... 1. A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence 2. A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation ...
... 1. A polypeptide is a polymer of amino acids connected in a specific sequence 2. A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation ...
I. Cell Components
... Rough ER: site of protein synthesis (ribosomes attach to rough ER) Smooth ER: site of lipid synthesis ...
... Rough ER: site of protein synthesis (ribosomes attach to rough ER) Smooth ER: site of lipid synthesis ...
#24926 HAAO A Antibod
... N is an exccitotoxin who ose toxicity is mediated d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has been n suggested to play a role in disorde ers pathogenesis of neurological and ...
... N is an exccitotoxin who ose toxicity is mediated d by its ability to activa ate glutamate N-methyl-D-asspartate recceptors. Inccreased cerebral levelss of QUIN may partic cipate in th he ammatory dissorders. HAA AO has been n suggested to play a role in disorde ers pathogenesis of neurological and ...
Chap1 Overview of Biological Systems
... Rough ER: site of protein synthesis (ribosomes attach to rough ER) Smooth ER: site of lipid synthesis ...
... Rough ER: site of protein synthesis (ribosomes attach to rough ER) Smooth ER: site of lipid synthesis ...
Chemical Approaches for Quantitative and Functional Proteomics
... – Small molecules – Other proteins ...
... – Small molecules – Other proteins ...
Examination in Gene Technology, TFKE38 2011-10-18
... 4) You want to study the ribosomal proteins and has therefore chosen to clone protein L21. The figure below (figure 2) shows the DNA sequence and protein sequence of L21. NOTE: This question provides a total of 20 points a) Construct primers to find the gene in a cDNA library (2p) b) In order to qu ...
... 4) You want to study the ribosomal proteins and has therefore chosen to clone protein L21. The figure below (figure 2) shows the DNA sequence and protein sequence of L21. NOTE: This question provides a total of 20 points a) Construct primers to find the gene in a cDNA library (2p) b) In order to qu ...
DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen?
... are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
... are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
of the protein - Duplin County Schools
... With a single nucleotide, there are only 4 possible codes (41). For two nucleotides, there are only 16 possible codes (42). However, for three nucleotides there are 64 possible codes (43), and that is enough to code for the 20 amino acids. ...
... With a single nucleotide, there are only 4 possible codes (41). For two nucleotides, there are only 16 possible codes (42). However, for three nucleotides there are 64 possible codes (43), and that is enough to code for the 20 amino acids. ...
Design of Novel Organocatalytic Click Chemistry: Biological and Medicinal Application.
... fluorescence tags has become a major tool in modern biotechnology and cell biology. Encoding fusion proteins with comparatively large fluorescent proteins (FPs) as originally developed by the Chalfie and Tsien groups is currently the most widely applied technique. As synthetic dyes typically offer b ...
... fluorescence tags has become a major tool in modern biotechnology and cell biology. Encoding fusion proteins with comparatively large fluorescent proteins (FPs) as originally developed by the Chalfie and Tsien groups is currently the most widely applied technique. As synthetic dyes typically offer b ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.