IB Chemistry Brakke ECA - Topic B TBD09
... When many 2-amino acid molecules react together a protein is formed. These proteins have primary, secondary and tertiary structures. (a) State the type of intermolecular force responsible for maintaining the secondary structure. ...
... When many 2-amino acid molecules react together a protein is formed. These proteins have primary, secondary and tertiary structures. (a) State the type of intermolecular force responsible for maintaining the secondary structure. ...
2.3: Carbon-Based Molecules
... • Muscle cells have enzymes that are triggered in response to the neurotransmitters ...
... • Muscle cells have enzymes that are triggered in response to the neurotransmitters ...
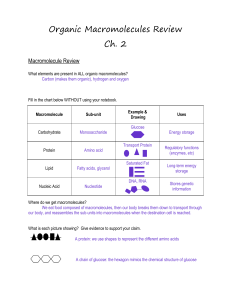
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
LAB 7
... Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids are the four major groups of organic molecules found in living organisms. This lab deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle ...
... Carbohydrates, fats, proteins and nucleic acids are the four major groups of organic molecules found in living organisms. This lab deals with the important class of organic molecules known as proteins. They are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle ...
msc mlt-1st sem(1563)
... What are the important no covalent interactions within proteins? How do weak interactions result in a stable structure? ...
... What are the important no covalent interactions within proteins? How do weak interactions result in a stable structure? ...
Document
... most enzymes have a globular tertiary structure. • Fibrous structure: Water IN-soluble polypeptide chains that extend along one axis. These proteins are most often involved in protection and maintaining cell/tissue structure and include collagen, keratin, and elastin. 4. Quaternary: Multiple polypep ...
... most enzymes have a globular tertiary structure. • Fibrous structure: Water IN-soluble polypeptide chains that extend along one axis. These proteins are most often involved in protection and maintaining cell/tissue structure and include collagen, keratin, and elastin. 4. Quaternary: Multiple polypep ...
0c5168dab2ecd61778b5bb175973dab5 UNPDF
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
... 10. The significance of “directionality” of the monomers in a polymer is that when you put the monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have ______________________ a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process ? c. What kind of bond is formed ge ...
Bioinformatics how to predict protein structure using comparative
... Result (protein A is Similar to protein B) ...
... Result (protein A is Similar to protein B) ...
Inverse mapping
... 2130 identical protein units, each with 158 amino acid residues, that form the viral protein coat around a single stretch of RNA that comprises 6400 nucleotides. ...
... 2130 identical protein units, each with 158 amino acid residues, that form the viral protein coat around a single stretch of RNA that comprises 6400 nucleotides. ...
keystone apr 2011 - module 1 answers
... Part C: Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells both contain ribosomes to make proteins, a plasma membrane to control what enters and leaves the cell, genetic material, and a cytoplasm. 9. Part A: A protein is a polymer consisting of many subunits called amino acids. Amino acids are joined together b ...
... Part C: Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells both contain ribosomes to make proteins, a plasma membrane to control what enters and leaves the cell, genetic material, and a cytoplasm. 9. Part A: A protein is a polymer consisting of many subunits called amino acids. Amino acids are joined together b ...
Effect of protein aggregation and protein structure on magnetite
... forming the magnetosome organelle. Being also biocompatible, magnetosomes could be used in many biomedical applications as in cell separation, etc. MamC from Magnetococcus marinus MC-1 has been shown to control the size of magnetite crystals in in vitro experiments, thereby demonstrating its potenti ...
... forming the magnetosome organelle. Being also biocompatible, magnetosomes could be used in many biomedical applications as in cell separation, etc. MamC from Magnetococcus marinus MC-1 has been shown to control the size of magnetite crystals in in vitro experiments, thereby demonstrating its potenti ...
pH - Bio-Link
... equilibrium by adding a compound that can dissociate in water to change the concentration of either H+ or OH- ions. An acid is a compound that can release H+ ions in solution. Bases are compounds that can accept H+ ions. In practical terms, a lower pH means a higher H+ concentration, or greater aci ...
... equilibrium by adding a compound that can dissociate in water to change the concentration of either H+ or OH- ions. An acid is a compound that can release H+ ions in solution. Bases are compounds that can accept H+ ions. In practical terms, a lower pH means a higher H+ concentration, or greater aci ...
ORGANELLES AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Worksheet #3
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
... A. Organelle Functions and Protein Synthesis 1) Organelle Functions: a. Define the function of the following items and indicate if it is an organelle or not CELLULAR STRUCTURES: Plasma Membrane ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... the organisms from part (b). Briefly describe how this additional energy is generated. Some of this additional energy comes directly from further oxidation of pyruvate into CO2. The electrons from NADH are used to generate further energy. These electrons are donated to a series of membrane proteins, ...
... the organisms from part (b). Briefly describe how this additional energy is generated. Some of this additional energy comes directly from further oxidation of pyruvate into CO2. The electrons from NADH are used to generate further energy. These electrons are donated to a series of membrane proteins, ...
Brief overview of Bio backgound
... Restricts the flow of ions into certain lung cells Lung is less able to expel fluids ...
... Restricts the flow of ions into certain lung cells Lung is less able to expel fluids ...
... i) Estimate the pI of the peptide that you viewed for problem 5 on Pset 2 (sequence is Ala-Glu-Leu). You can do this by calculating the charge at a number of different pH values, or use excel to do these calculations for you (5 pts) ii) Assume you want to purify this peptide for a mixture of other p ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. Circle the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did b ...
... (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. Circle the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. Color the fatty acid chains the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did b ...
Lecture PPT
... proteins to be analysed are isolated from cell lysate or tissues by biochemical fractionation or affinity selection. This often includes a final step of onedimensional gel electrophoresis, and defines the 'sub-proteome' to be analysed. MS of whole proteins is less sensitive than peptide MS and the m ...
... proteins to be analysed are isolated from cell lysate or tissues by biochemical fractionation or affinity selection. This often includes a final step of onedimensional gel electrophoresis, and defines the 'sub-proteome' to be analysed. MS of whole proteins is less sensitive than peptide MS and the m ...
Sample Exam 1
... b. Different enzymes recognize different substrates. c. Different enzymes have different tertiary structures. d. Different enzymes have different primary structures. e. All of the above. 24. The ________ is the part of an enzyme that recognizes a specific substrate. a. active site b. alpha helix c. ...
... b. Different enzymes recognize different substrates. c. Different enzymes have different tertiary structures. d. Different enzymes have different primary structures. e. All of the above. 24. The ________ is the part of an enzyme that recognizes a specific substrate. a. active site b. alpha helix c. ...
AP test2
... b. ___________________are the location of cellular respiration. c. _______________ and _______________ are microfilaments located on the outside of the cell and are used for cell movement. d. Damaged proteins or organelles are recycled in __________________. 5. What is the function of the nucleus. 6 ...
... b. ___________________are the location of cellular respiration. c. _______________ and _______________ are microfilaments located on the outside of the cell and are used for cell movement. d. Damaged proteins or organelles are recycled in __________________. 5. What is the function of the nucleus. 6 ...
The Four major Groups of
... dehydrated to form polypeptides or proteins. • Humans have about 20 different amino acids from which proteins are synthesized. The difference between one protein and another has to do with the number of amino acids that a protein contains and the unique sequences in which the amino acids are arrange ...
... dehydrated to form polypeptides or proteins. • Humans have about 20 different amino acids from which proteins are synthesized. The difference between one protein and another has to do with the number of amino acids that a protein contains and the unique sequences in which the amino acids are arrange ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.