Organic Molecule Cut-Outs
... 1. Cut out all the cut-outs that pertain to Proteins—including the equal sign, the oval, the rectangle, and the words “Proteins,” “polymer,” and “monomers.” 2. Arrange the cut-outs so that the Amino Acids form a protein (don't worry about the order of the amino acids). Include the equal sign; you wi ...
... 1. Cut out all the cut-outs that pertain to Proteins—including the equal sign, the oval, the rectangle, and the words “Proteins,” “polymer,” and “monomers.” 2. Arrange the cut-outs so that the Amino Acids form a protein (don't worry about the order of the amino acids). Include the equal sign; you wi ...
Document
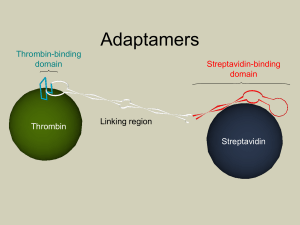
... • Binds strongly to biotin molecule • Used to bind biotinylated nucleic acids or peptides McDevitt, 1999 Big idea: Streptavidin protein expressed on the cell surface can be used to target any biotinylated DNA/protein to the cell surface. ...
... • Binds strongly to biotin molecule • Used to bind biotinylated nucleic acids or peptides McDevitt, 1999 Big idea: Streptavidin protein expressed on the cell surface can be used to target any biotinylated DNA/protein to the cell surface. ...
Macromolecule: Carbohydrates Polarity: Polar Functions: Store
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
... Amino acids (20) – monomers of proteins (C with amino group, carboxyl group, and R group/side chain) Essential amino acids (8) – not produced by the body and must be consumed in food Polypeptide – polymer composed of amino acid monomers joined by covalent bonds Denaturation – unfolding of a protein, ...
2. Propensity
... 8. Propensity to form MCI for two state proteins Pmc(i) = fmc(i) / ft(i) fmc(i) = frequency of occurrence of amino acids that form multiple contacts ft(i) = frequency of residues in the whole protein Ref: Gromiha, M.M. Protein bioinformatics: from sequence to function. Academic Press, 2010. 9. Prope ...
... 8. Propensity to form MCI for two state proteins Pmc(i) = fmc(i) / ft(i) fmc(i) = frequency of occurrence of amino acids that form multiple contacts ft(i) = frequency of residues in the whole protein Ref: Gromiha, M.M. Protein bioinformatics: from sequence to function. Academic Press, 2010. 9. Prope ...
File
... D. Purpose: store energy and provide barriers 1. Phospholipids form the cell membrane – we will come back to these E. Examples of those important to humans: Most steroids (esp. cholesterol) ...
... D. Purpose: store energy and provide barriers 1. Phospholipids form the cell membrane – we will come back to these E. Examples of those important to humans: Most steroids (esp. cholesterol) ...
Chapter 5 Guided Notes
... ○ Because it is misshapen, a denatured protein is biologically ____________________________________. ...
... ○ Because it is misshapen, a denatured protein is biologically ____________________________________. ...
Carbon Compounds
... Protein Conformation • Structure of a protein is directly related to its function • Protein conformation is determined when it is synthesized, and maintained by chemical interactions • Protein conformation also depends on environmental factors: pH, ...
... Protein Conformation • Structure of a protein is directly related to its function • Protein conformation is determined when it is synthesized, and maintained by chemical interactions • Protein conformation also depends on environmental factors: pH, ...
Proteins
... Most proteins contain all of the essential amino acids (EAAs)!! (except gelatin) Complete proteins supply all the EAAs needed to meet biologic requirements when consumed at recommended amounts ...
... Most proteins contain all of the essential amino acids (EAAs)!! (except gelatin) Complete proteins supply all the EAAs needed to meet biologic requirements when consumed at recommended amounts ...
Macromolecular Structures
... Membrane and cell surface proteins and peptides (11) Small proteins (54) Coiled coil proteins (5) Peptides (77) ...
... Membrane and cell surface proteins and peptides (11) Small proteins (54) Coiled coil proteins (5) Peptides (77) ...
SDS-PAGE of protein purified with the AllPrep RNA/Protein
... buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin column in step 5 of the protocol in the handbook (page 13). To avoid possible SDS precipitation in applications such as SDS-PAGE, protein purified using the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit should be cleaned up by acetone precipitation, as des ...
... buffer should not be used to equilibrate the Protein Cleanup spin column in step 5 of the protocol in the handbook (page 13). To avoid possible SDS precipitation in applications such as SDS-PAGE, protein purified using the AllPrep RNA/Protein Kit should be cleaned up by acetone precipitation, as des ...
Organelle Riddles I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I brea
... I’ve been called a storage tank by those with little taste. I’m a sac filled with water, food, enzymes, or waste. ...
... I’ve been called a storage tank by those with little taste. I’m a sac filled with water, food, enzymes, or waste. ...
Lecture 4: Amino Acids
... • Sequence comparisons among analogous proteins are important in comparing how proteins function and have indicated evolutionary relationships among proteins • Amino acid sequence analyses have important clinical applications because many diseases are caused by mutations that lead to an amino acid c ...
... • Sequence comparisons among analogous proteins are important in comparing how proteins function and have indicated evolutionary relationships among proteins • Amino acid sequence analyses have important clinical applications because many diseases are caused by mutations that lead to an amino acid c ...
L6 Proteins of cereals and legumes - e
... group of basic amino acids, for example, arginine, histidine and lysine, may form insoluble phytateprotein complexes. At a pH above the isoelectric point of proteins, the charge of proteins as well as that of the phytic acid is negative – direct interaction would be impossible, however, interaction ...
... group of basic amino acids, for example, arginine, histidine and lysine, may form insoluble phytateprotein complexes. At a pH above the isoelectric point of proteins, the charge of proteins as well as that of the phytic acid is negative – direct interaction would be impossible, however, interaction ...
UNIT 1 review PPT
... • Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide in animals • Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells ...
... • Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide in animals • Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells ...
What are macromolecules? Cells are built primarily from the largest
... organic macromolecules are. This list is really important to understanding cells, so really memorize it well. It will pop up again and again throughout the semester. Carbohydrates are the "sugars." Both the simple sugars (like glucose and table sugar) and complex sugars (like starch). The complex su ...
... organic macromolecules are. This list is really important to understanding cells, so really memorize it well. It will pop up again and again throughout the semester. Carbohydrates are the "sugars." Both the simple sugars (like glucose and table sugar) and complex sugars (like starch). The complex su ...
Study Guide Responses
... Water-accounts for over 60% of the body weight, and provides the basis for various body fluids. Appropriate body temperature-when too high or too low, physiological activities cease, primarily because molecules are destroyed or become nonfunctional. Appropriate atmospheric pressure�the force exerted ...
... Water-accounts for over 60% of the body weight, and provides the basis for various body fluids. Appropriate body temperature-when too high or too low, physiological activities cease, primarily because molecules are destroyed or become nonfunctional. Appropriate atmospheric pressure�the force exerted ...
3.2 and 3.3
... Monomer of Nucleic acids are….. Name the three groups in one monomer… Nucleic acids primary function is to …… What process puts these monomers together to form long chains…. • What process breaks down ATP for energy….. ...
... Monomer of Nucleic acids are….. Name the three groups in one monomer… Nucleic acids primary function is to …… What process puts these monomers together to form long chains…. • What process breaks down ATP for energy….. ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... (methionine) to the ribosome. • Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. • The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must complement codon for amino acid to be added to protein chain ...
... (methionine) to the ribosome. • Each tRNA carries one type of amino acid. • The anticodon (three nitrogen bases on tRNA) must complement codon for amino acid to be added to protein chain ...
Laura Bassi Centres of Expertise - PlantBioP Plant
... Glycosylation, the addition of sugar residues, is an important protein modification. Serum proteins carry a heterobereous and complex N-glycosylation pattern. Although the biological impact of specific N-glycan profiles is largely unknown, many studies have demonstrated that certain N-glycan residue ...
... Glycosylation, the addition of sugar residues, is an important protein modification. Serum proteins carry a heterobereous and complex N-glycosylation pattern. Although the biological impact of specific N-glycan profiles is largely unknown, many studies have demonstrated that certain N-glycan residue ...
Unit 1 Page 1 Unit Vocabulary Terms Carbohydrate
... ● Carbohydrate - A group that includes sugar and starch that is used for energy or structure; can be small molecules (monosaccharides or disaccharides) or large molecules (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.) ● Proteins - A three-dimensional biological macromolecule constructed from a set ...
... ● Carbohydrate - A group that includes sugar and starch that is used for energy or structure; can be small molecules (monosaccharides or disaccharides) or large molecules (polysaccharides such as starch and cellulose.) ● Proteins - A three-dimensional biological macromolecule constructed from a set ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.