Document
... Protein degradation rate varies 100x Most have motifs marking them for polyubiquitination: taken to proteosome & destroyed Other signals for selective degradation include PEST & KFERQ • PEST : found in many rapidly degraded proteins • Deletion increases t1/2 10x, adding PEST drops t1/2 10x • Sometim ...
... Protein degradation rate varies 100x Most have motifs marking them for polyubiquitination: taken to proteosome & destroyed Other signals for selective degradation include PEST & KFERQ • PEST : found in many rapidly degraded proteins • Deletion increases t1/2 10x, adding PEST drops t1/2 10x • Sometim ...
Prestained Protein Molecular Weight Marker
... 0.75mm – thick mini gels – 5µl 1.5mm – thick mini gels – 10µl 0.75mm – thick standard gels – 10µl 1.5mm – thick standard gels – 20µl Instruction for Use 1. Thaw the Marker at room temperature or heat at 37- 40°C for a few minutes to dissolve precipitated solids. Do not boil! 2. Vortex gently to ensu ...
... 0.75mm – thick mini gels – 5µl 1.5mm – thick mini gels – 10µl 0.75mm – thick standard gels – 10µl 1.5mm – thick standard gels – 20µl Instruction for Use 1. Thaw the Marker at room temperature or heat at 37- 40°C for a few minutes to dissolve precipitated solids. Do not boil! 2. Vortex gently to ensu ...
Class Notes 1 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... • Protein is grown from one end to another, by joining amino acids • Wikipedia: the correct tRNA, linked to a specific amino acid, is directed to the ribosome to be added to a growing (nascent) polypeptide – as the ribosome travels down the mRNA one codon at a time, another tRNA is attached to the m ...
... • Protein is grown from one end to another, by joining amino acids • Wikipedia: the correct tRNA, linked to a specific amino acid, is directed to the ribosome to be added to a growing (nascent) polypeptide – as the ribosome travels down the mRNA one codon at a time, another tRNA is attached to the m ...
30_General pathways of amino acids transformation
... Structural proteins – usually stable (lens protein crystallin lives during the whole life of the organism) Regulatory proteins - short lived (altering the amounts of these proteins can rapidly change the rate of metabolic processes) How can a cell distinguish proteins that are meant for degradation? ...
... Structural proteins – usually stable (lens protein crystallin lives during the whole life of the organism) Regulatory proteins - short lived (altering the amounts of these proteins can rapidly change the rate of metabolic processes) How can a cell distinguish proteins that are meant for degradation? ...
Solutions to 7.012 Problem Set 1
... a) What is the primary structure of a protein? What force or forces (covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, or van der Waals forces) are involved in primary structure? The primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of the amino acids. Covalent bonds link the individual amino acids b ...
... a) What is the primary structure of a protein? What force or forces (covalent bonds, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, or van der Waals forces) are involved in primary structure? The primary structure of a protein is the linear sequence of the amino acids. Covalent bonds link the individual amino acids b ...
or protein
... 1. Hydrolysis of proteins Proteins can be hydrolyzed by acid, alkali and proteases and broken down to peptides and mixture of amino acids. The resulting characteristic proportion of different amino acids, namely, the amino acid composition was used to distinguish different proteins before the days o ...
... 1. Hydrolysis of proteins Proteins can be hydrolyzed by acid, alkali and proteases and broken down to peptides and mixture of amino acids. The resulting characteristic proportion of different amino acids, namely, the amino acid composition was used to distinguish different proteins before the days o ...
6.1 Digestion and absorption assessment statements
... Pancreatic endopeptidase – proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze internal peptide bonds digesting proteins/polypeptides into shorter amino acid chains. Trypsin that works at pH 8 is an example. Explain the need for enzymes to digest most macromolecules in food into monomers in the small intestine. ...
... Pancreatic endopeptidase – proteolytic enzymes that hydrolyze internal peptide bonds digesting proteins/polypeptides into shorter amino acid chains. Trypsin that works at pH 8 is an example. Explain the need for enzymes to digest most macromolecules in food into monomers in the small intestine. ...
Chemistry 464 Biochemistry First Hour Exam
... Actually the COO- is close to its pKa so it is only about ½ protonated at pH2 ...
... Actually the COO- is close to its pKa so it is only about ½ protonated at pH2 ...
AP Biology Review – Unit 1
... and aligned. Many proteins contain both types of secondary structure. ...
... and aligned. Many proteins contain both types of secondary structure. ...
TRANSLASI - alanindra
... mRNAs code for only a single gene. (Although there are a few exceptions, mainly among the eukaryotic viruses). • Note that translation does not start at the first base of the mRNA. There is an untranslated region at the beginning of the mRNA, the 5’ untranslated region (5’ UTR). ...
... mRNAs code for only a single gene. (Although there are a few exceptions, mainly among the eukaryotic viruses). • Note that translation does not start at the first base of the mRNA. There is an untranslated region at the beginning of the mRNA, the 5’ untranslated region (5’ UTR). ...
Proteins Introduction Aspects of a protein`s structure Primary
... eukaryotes i.e. one of the structurally complex cell types) and cell nucleus ...
... eukaryotes i.e. one of the structurally complex cell types) and cell nucleus ...
Prokaryotes
... Thermophiles and hyperthermophiles branch closest to the root of the universal tree ii. Euryarchaeota collection of the major archaeal phenotypes dominated by methanogens and extreme halophiles ...
... Thermophiles and hyperthermophiles branch closest to the root of the universal tree ii. Euryarchaeota collection of the major archaeal phenotypes dominated by methanogens and extreme halophiles ...
Protein - HCC Learning Web
... and transport amino acids to cells protein is made (i.e. synthesized) inside cells according to DNA ...
... and transport amino acids to cells protein is made (i.e. synthesized) inside cells according to DNA ...
TRANSLATION NOTES - Randolph High School
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
... Definition of Translation The decoding of mRNA’s message into a protein Happens in the ribosome Also known as Protein Synthesis, which is when proteins are made by stringing amino acids together to form long chains (20+ types of amino acids in humans) ...
Chemistry of Proteins Model Making
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
... Proteins are the main structural and growth components of cells in tissues such as skin, hair, muscle and blood. Other proteins serve in regulatory capacity as enzymes and hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in m ...
投影片 1
... Profound Influence on Protein Folding (Left) Wild-type GroEL/GroES with a folding substrate (green) is shown. (Middle) Changing the cavity size by deleting or replicating the motifs at the C terminus of each GroEL subunit affects substrate folding. (Right) Alteration of the surface charge of the cav ...
... Profound Influence on Protein Folding (Left) Wild-type GroEL/GroES with a folding substrate (green) is shown. (Middle) Changing the cavity size by deleting or replicating the motifs at the C terminus of each GroEL subunit affects substrate folding. (Right) Alteration of the surface charge of the cav ...
Bio Chap 2 Biomolecules
... • They exist as rings with an integral Oxygen and many H and OH groups. • The simplest are monosaccharides, such as glucose, fructose, or ...
... • They exist as rings with an integral Oxygen and many H and OH groups. • The simplest are monosaccharides, such as glucose, fructose, or ...
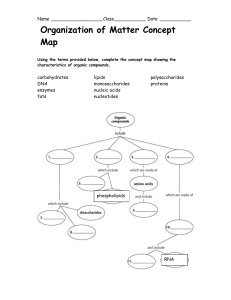
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... Nucleic Acids 19. You notice a thin layer of a substance that is slimy and doesn’t mix with water. It is also liquid at room temperature, and was found in the kitchen. You may infer that it is EXACTLY what type of macromolecule? (The macromolecule AND the kind of macromolecule. Look in your notes!) ...
... Nucleic Acids 19. You notice a thin layer of a substance that is slimy and doesn’t mix with water. It is also liquid at room temperature, and was found in the kitchen. You may infer that it is EXACTLY what type of macromolecule? (The macromolecule AND the kind of macromolecule. Look in your notes!) ...
PPT File
... occur in a vast range of sizes Many small peptides exert effects at very low concentrations: ...
... occur in a vast range of sizes Many small peptides exert effects at very low concentrations: ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.