2 Molecular - bloodhounds Incorporated
... B. Will normally form anions C. Will normally form cations D. Frequently form hydrogen bonds ...
... B. Will normally form anions C. Will normally form cations D. Frequently form hydrogen bonds ...
Summer 2011 Proposal for UNCA Undergraduate Research
... pathways. Due to the nature of its function, G12 has the potential to promote malignant, uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis, classifying it as a proto-oncoprotein. Indeed, analysis of cDNA libraries collected from sarcoma tissue samples has implicated G12 as a strong transforming oncoprotein ...
... pathways. Due to the nature of its function, G12 has the potential to promote malignant, uncontrolled cell growth and metastasis, classifying it as a proto-oncoprotein. Indeed, analysis of cDNA libraries collected from sarcoma tissue samples has implicated G12 as a strong transforming oncoprotein ...
A2 Module 2814: Chains, Rings and Spectroscopy
... (called the L-series). The mirror-image molecules would not fit into the correct three-dimensional shape. Therefore if organisms are fed on a mixture of enantiomers, they can only absorb the ones from the correct series. It follows that chiral molecules synthesised in cells (proteins, carbohydrates ...
... (called the L-series). The mirror-image molecules would not fit into the correct three-dimensional shape. Therefore if organisms are fed on a mixture of enantiomers, they can only absorb the ones from the correct series. It follows that chiral molecules synthesised in cells (proteins, carbohydrates ...
Bioinformatics Take Home Test #1 –Due 9/19/16
... B. There are multiple unrelated solutions for the same functionality, exemplified by the fact that there are non-homologous enzymes inhabiting completely different regions of protein space with the same function. C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can tak ...
... B. There are multiple unrelated solutions for the same functionality, exemplified by the fact that there are non-homologous enzymes inhabiting completely different regions of protein space with the same function. C. An exact function does not need to be hit upon, because natural selection can tak ...
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid
... The arginine is hydrolyzed to produce the urea and to reform the ornithine. The ornithine reenters the mitochondrial matrix. ...
... The arginine is hydrolyzed to produce the urea and to reform the ornithine. The ornithine reenters the mitochondrial matrix. ...
video slide
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they self-assemble into a bilayer o The phospholipids form the outer part that is in contact with the water. o The fatty acids form the inner part that is away from water. ...
... • When phospholipids are added to water, they self-assemble into a bilayer o The phospholipids form the outer part that is in contact with the water. o The fatty acids form the inner part that is away from water. ...
Helthy diet * myths and reality - Visegrad University Association
... Gastric irritation that occurs when the stomach contains more than 10% sugar. Constipation. ...
... Gastric irritation that occurs when the stomach contains more than 10% sugar. Constipation. ...
On the Importance of Amino Acid Sequence and Spatial Proximity of
... fit this to simple sigmoids. The fits show no clear residue dependence at the range of interaction distances typically known to be relevant to protein structure and folding (0–10 Å). This is not surprising since the fits are dominated by the data at long distances and would look very similar for scr ...
... fit this to simple sigmoids. The fits show no clear residue dependence at the range of interaction distances typically known to be relevant to protein structure and folding (0–10 Å). This is not surprising since the fits are dominated by the data at long distances and would look very similar for scr ...
5. Nucleotides are covalently linked to form nucleic acids by the
... Some procaryotic cells (e.g. archaebacteria) contain a nucleus. All procaryotic cells lack lysosomes. All procaryotic cells lack mitochondria. ...
... Some procaryotic cells (e.g. archaebacteria) contain a nucleus. All procaryotic cells lack lysosomes. All procaryotic cells lack mitochondria. ...
Protein Structure
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
... state depends strongly on its local environment. This feature is often exploited and histidine is used as a molecular switch. ...
Lecture 10 - Columbus Labs
... MCAT Question Enterokinase is a protease that cleaves after lysine residues. It will sometimes cleave at other basic residues. Which of the following amino acids can also serve as a target for enterokinase? A. Proline B. Arginine C. Tryptophan D. Alanine ...
... MCAT Question Enterokinase is a protease that cleaves after lysine residues. It will sometimes cleave at other basic residues. Which of the following amino acids can also serve as a target for enterokinase? A. Proline B. Arginine C. Tryptophan D. Alanine ...
proteins - Technische Universität München - Physik
... – Structure formation or folding process • The folded three-dimensional structure of a biomolecule is directly related to its function. ...
... – Structure formation or folding process • The folded three-dimensional structure of a biomolecule is directly related to its function. ...
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) Recombinant Human Cardiotrophin-1
... Reconstitution: Centrifuge the vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, pH 8.0 to a concentration of ≤ 1.0 mg/ml. Do not vortex. This solution can be stored at 2-8°C for up to 1 week. For extended storage, it is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein (example ...
... Reconstitution: Centrifuge the vial prior to opening. Reconstitute in 20mM Tris, pH 8.0 to a concentration of ≤ 1.0 mg/ml. Do not vortex. This solution can be stored at 2-8°C for up to 1 week. For extended storage, it is recommended to further dilute in a buffer containing a carrier protein (example ...
amino acid
... Once it is completely and correctly folded, it is considered a protein. (other small changes or modifications may also occur before the protein is completely functional) The structure of each protein in unique; Structure leads to function! Protein Folding ...
... Once it is completely and correctly folded, it is considered a protein. (other small changes or modifications may also occur before the protein is completely functional) The structure of each protein in unique; Structure leads to function! Protein Folding ...
Zoology – The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... Zoology – The Chemical Basis of Animal Life I. Attributes of Living Organisms A. It would seem a simple thing to define life, but it actually isn’t. Many of the characteristics of life can be found in nonliving things. 1. It is easier to describe the characteristics of life. B. Composition and Struc ...
... Zoology – The Chemical Basis of Animal Life I. Attributes of Living Organisms A. It would seem a simple thing to define life, but it actually isn’t. Many of the characteristics of life can be found in nonliving things. 1. It is easier to describe the characteristics of life. B. Composition and Struc ...
Chemical Organization of Life
... forming a double helix the two backbones run in opposite 5´ to 3´ directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel The nitrogenous bases in DNA form hydrogen bonds in a ...
... forming a double helix the two backbones run in opposite 5´ to 3´ directions from each other, an arrangement referred to as antiparallel The nitrogenous bases in DNA form hydrogen bonds in a ...
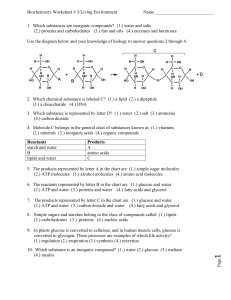
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... 12. The reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
... 12. The reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
Section 1 Workbook Unit 1 ANSWERS File
... Oxygen is larger and can therefore, pull electrons towards it (away from the hydrogen). This creates 2 areas of different charge. The H+ of one water molecule will bond with the O of another w ...
... Oxygen is larger and can therefore, pull electrons towards it (away from the hydrogen). This creates 2 areas of different charge. The H+ of one water molecule will bond with the O of another w ...
x - Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics
... NMR structure determinations [1-4]. In the first stage, cloned DNA molecules coding for proteins of interest are transcribed and translated on a small scale (25 microL) to determine levels of protein expression and solubility. The amount of protein produced (typically 2-10 micrograms) is sufficient ...
... NMR structure determinations [1-4]. In the first stage, cloned DNA molecules coding for proteins of interest are transcribed and translated on a small scale (25 microL) to determine levels of protein expression and solubility. The amount of protein produced (typically 2-10 micrograms) is sufficient ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... 4. DNA continues to have errors due to carcinogens and simple errors. II. ...
... 4. DNA continues to have errors due to carcinogens and simple errors. II. ...
Chapter 14 Nutrition Nutrients A nutrient is a component of food that
... Trans-fatty acids are made by hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids for commercial products and may reduce the ability of cells to clear cholesterol from the bloodstream ...
... Trans-fatty acids are made by hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acids for commercial products and may reduce the ability of cells to clear cholesterol from the bloodstream ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.