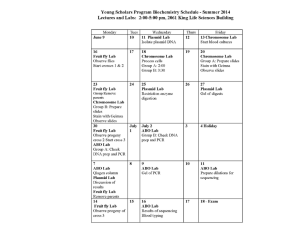
Document
... Endoplasmic (inside the cell); reticulum a network ER, a network inside the cell Disulfide bond formation occurs in the ER N-linked oligosaccharide synthesis is initiated in the ER; trimming and completion occurs in the Golgi Most O-glycosylation occurs in the Golgi Attachment of mannose 6-phosphate ...
... Endoplasmic (inside the cell); reticulum a network ER, a network inside the cell Disulfide bond formation occurs in the ER N-linked oligosaccharide synthesis is initiated in the ER; trimming and completion occurs in the Golgi Most O-glycosylation occurs in the Golgi Attachment of mannose 6-phosphate ...
Protein mteabolism
... proenzymes into duodenum. The release and activation of pancreatic zymogens is mediated by the secretion of cholecystokinine and secretin (GIT hormones). Activation of pancreatic zymogens: The pancreatic zymogens are: trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and pro-carboxypeptidases (A and B). Enteropeptidase ...
... proenzymes into duodenum. The release and activation of pancreatic zymogens is mediated by the secretion of cholecystokinine and secretin (GIT hormones). Activation of pancreatic zymogens: The pancreatic zymogens are: trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen and pro-carboxypeptidases (A and B). Enteropeptidase ...
Nucleic Acids
... Pepsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins in the stomach during digestion. It works at a pH of 2! Trypsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins as well. It works in the intestines with a pH of 8. Many snake venoms are enzymes that work when directly injected into blood or tissue (pH = ...
... Pepsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins in the stomach during digestion. It works at a pH of 2! Trypsin is an enzyme that helps break down proteins as well. It works in the intestines with a pH of 8. Many snake venoms are enzymes that work when directly injected into blood or tissue (pH = ...
Final Exam: Multiple Choice Portion Biochem Block Spring 2016
... D) electrons flow from NADH to oxygen, producing ATP 25. Which statement describes best what happens in the citric acid cycle? A) citrate condenses to form a protein B) glucose is cleaved into two molecules of pyruvate, releasing energy C) acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide, producing the elec ...
... D) electrons flow from NADH to oxygen, producing ATP 25. Which statement describes best what happens in the citric acid cycle? A) citrate condenses to form a protein B) glucose is cleaved into two molecules of pyruvate, releasing energy C) acetyl CoA is oxidized to carbon dioxide, producing the elec ...
Proteiinien rakenne ja laskostuminen
... τc = the correlation time for the electron-nuclear interaction ωh = the Larmor frequency of the nuclear spin R2sp = the paramagnetic relaxation enhancement R2sp = R2* - R2 R2* = the transverse relaxation rate constant for paramagnetic species R2 = the transverse relaxation rate constant for diamagne ...
... τc = the correlation time for the electron-nuclear interaction ωh = the Larmor frequency of the nuclear spin R2sp = the paramagnetic relaxation enhancement R2sp = R2* - R2 R2* = the transverse relaxation rate constant for paramagnetic species R2 = the transverse relaxation rate constant for diamagne ...
In-gel digestion of mouse membrane protein extract
... as calculated by GPMAW software for individual peptides which were identified only when using surfactant (red) or which were identified equally regardless of digest conditions (blue). ...
... as calculated by GPMAW software for individual peptides which were identified only when using surfactant (red) or which were identified equally regardless of digest conditions (blue). ...
Protein synthesis
... polypeptide chains Many polypeptide chains are covalently modified, either while they are still attached to the ribosome (cotranslational) or after their synthesis has been completed (posttranslational). These modifications may include removal of part of the translated sequence, or the covalent ...
... polypeptide chains Many polypeptide chains are covalently modified, either while they are still attached to the ribosome (cotranslational) or after their synthesis has been completed (posttranslational). These modifications may include removal of part of the translated sequence, or the covalent ...
Nutritional Requirements of Non
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
lecture 1
... Chain of nucleotides has alternating sugar and phosphate components, called the “sugarphosphate backbone.” Nitrogenous bases stick off backbone at regular intervals. ...
... Chain of nucleotides has alternating sugar and phosphate components, called the “sugarphosphate backbone.” Nitrogenous bases stick off backbone at regular intervals. ...
Nutritional Requirements of Non
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
... Other plant and animal proteins are often used in combination with SBM. • Fishmeal (60-70% CP) (Crude Protein) • Milk products, such as dried skimmed milk (33% CP) and dried whey (13.3% CP) • Meat and bone meal (50% CP) • Spray dried plasma protein and bloodmeal (86% CP) ...
Protein catabolism in metabolic acidosis: inhibition of glycolysis by
... 6. England, B.K., Chast-ain, J.L. & Mitch, ...
... 6. England, B.K., Chast-ain, J.L. & Mitch, ...
Protein stability
... ionic…………………….. can be attractive or repulsive surface residues………. major contribution to protein stability internal residues………. major contribution to protein stability compactness………….. can affect stability or flexibility loops…………………….short loops increases stability at higher temperatur ...
... ionic…………………….. can be attractive or repulsive surface residues………. major contribution to protein stability internal residues………. major contribution to protein stability compactness………….. can affect stability or flexibility loops…………………….short loops increases stability at higher temperatur ...
L5 Food proteins - e
... proportions similar to those required for synthesis of human tissue proteins [Note: Gelatin prepared from animal collagen is an exception; it has a low biological value as a result of deficiencies in several essential amino acids.] ...
... proportions similar to those required for synthesis of human tissue proteins [Note: Gelatin prepared from animal collagen is an exception; it has a low biological value as a result of deficiencies in several essential amino acids.] ...
Chapter 21
... exist on the same molecule • AA are ionic compounds • They are internal salts • In solution their form changes depending on the pH AA’s ...
... exist on the same molecule • AA are ionic compounds • They are internal salts • In solution their form changes depending on the pH AA’s ...
organic molecules webquest
... 1. Lipids are soluble/insoluble in water. Circle one. 2. What happens during Dehydration Synthesis (hint: it involves chains & a molecule) 3. Saturated fatty acids originate from where? 4. Unsaturated fatty acids originate from where? 5. Why are phospholipids so important to cells? 6. List 3 positiv ...
... 1. Lipids are soluble/insoluble in water. Circle one. 2. What happens during Dehydration Synthesis (hint: it involves chains & a molecule) 3. Saturated fatty acids originate from where? 4. Unsaturated fatty acids originate from where? 5. Why are phospholipids so important to cells? 6. List 3 positiv ...
STUDY GUIDE
... Sugars and starches are __________________________, which always have a carbon to hydrogen ratio of 2:1. They are composed of building blocks called _________________________. Two of these units can be attached to each other through a process called ________________________, which results in a _____ ...
... Sugars and starches are __________________________, which always have a carbon to hydrogen ratio of 2:1. They are composed of building blocks called _________________________. Two of these units can be attached to each other through a process called ________________________, which results in a _____ ...
Which macromolecule stores genetic information? A. proteins B
... provides instructions for the assembly of proteins. DNA categorized as which type of macromolecule? A.lipid B.carbohydrate C.protein D.nucleic acid ...
... provides instructions for the assembly of proteins. DNA categorized as which type of macromolecule? A.lipid B.carbohydrate C.protein D.nucleic acid ...
Example Problem Set for CHEM106 Section 002 Test 2
... 2) You are mutating amino acids in a protein to test predictions about which residues are important for a protein’s function. Which of each pair of amino acid substitutions listed below would you expect to disrupt protein structure the most? Explain. a) b) c) d) ...
... 2) You are mutating amino acids in a protein to test predictions about which residues are important for a protein’s function. Which of each pair of amino acid substitutions listed below would you expect to disrupt protein structure the most? Explain. a) b) c) d) ...
100% ISO Protein
... • Free from Bovine Growth Hormone or BSE • Suitable for all body types and ages • Convenient to use, shakes up easily with no blending required • Available in three tasty flavours: Chocolate (made with Cocoa Camino),Vanilla, and Unflavoured (perfect for making fresh fruit smoothies) • Easy to digest ...
... • Free from Bovine Growth Hormone or BSE • Suitable for all body types and ages • Convenient to use, shakes up easily with no blending required • Available in three tasty flavours: Chocolate (made with Cocoa Camino),Vanilla, and Unflavoured (perfect for making fresh fruit smoothies) • Easy to digest ...
Document
... All the polypeptides are denatured and behave as random coils All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS do ...
... All the polypeptides are denatured and behave as random coils All the polypeptides have the same charge per unit length All are subject to the same electromotive force in the electric field Separation based on the sieving effect of the polyacrylamide gel Separation is by molecular weight only SDS do ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.