Protein Synthesis Study Questions
... 21. Which RNA determines the amino acid sequence? 22. Which RNA makes the A, P, and E sites? 23. Which RNA carries amino acids to be assembled into a protein? 24. Which RNA is broken down after the protein is made? 25. Draw a charged tRNA with the anticodon CCA. 26. List all mRNA codons that do not ...
... 21. Which RNA determines the amino acid sequence? 22. Which RNA makes the A, P, and E sites? 23. Which RNA carries amino acids to be assembled into a protein? 24. Which RNA is broken down after the protein is made? 25. Draw a charged tRNA with the anticodon CCA. 26. List all mRNA codons that do not ...
ADP: adenine diphosphate. The low-energy form of ATP. Contains
... Because DNA polymerase will bind only to double-stranded nucleic acid it is necessary to produce a hybrid DNA-RNA strand on the single-stranded template strand of DNA before replication of that sequence can begin. The RNA is referred to as primer RNA Procaryotes: ...
... Because DNA polymerase will bind only to double-stranded nucleic acid it is necessary to produce a hybrid DNA-RNA strand on the single-stranded template strand of DNA before replication of that sequence can begin. The RNA is referred to as primer RNA Procaryotes: ...
Exam 1
... 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate binding causes an induced fit. ...
... 28. The _________________________ model of enzyme/substrate binding is inadequate because the molecules are not static; substrate binding causes an induced fit. ...
Heredity Picture Vocabulary
... the genetic information needed to make new cells and carry out cell functions. ...
... the genetic information needed to make new cells and carry out cell functions. ...
Sample Prep for Denaturing PAGE of DNA
... DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing (Taq Polymerase) Protocol for a formula ...
... DNA samples for denaturing gel electrophoresis must be denatured prior to loading, to avoid time dependent denaturation artifacts on the gel. This is usually carried out by diluting the sample into 95% formamide and heating to 95°C, see the Dideoxy Sequencing (Taq Polymerase) Protocol for a formula ...
DNA-Based Mutations
... 1. Gene Mutations -- error during one of the processes that involves basepairing of nucleic acids (eg. DNA replication, transcription, translation), or, error perpetuated by base-pairing process. *focus of Bio 12 2. Chromosomal Mutations -- where an entire chromosome is affected. eg. Trisomy 21 (3 c ...
... 1. Gene Mutations -- error during one of the processes that involves basepairing of nucleic acids (eg. DNA replication, transcription, translation), or, error perpetuated by base-pairing process. *focus of Bio 12 2. Chromosomal Mutations -- where an entire chromosome is affected. eg. Trisomy 21 (3 c ...
NAME: :__________PERIOD:____ Cell Structure, DNA Structure
... 11. Although some is found in the nucleus, the majority of DNA is located in the ___________ of the cell. a.) vacuole ...
... 11. Although some is found in the nucleus, the majority of DNA is located in the ___________ of the cell. a.) vacuole ...
Studying the Human Genome
... DNA is a HUGE molecule that is difficult to manipulate In the 1970s, scientists discovered they could use natural enzymes to analyze DNA Today, scientists read DNA base sequences by using enzymes to cut, separate, and replicate DNA base by base ...
... DNA is a HUGE molecule that is difficult to manipulate In the 1970s, scientists discovered they could use natural enzymes to analyze DNA Today, scientists read DNA base sequences by using enzymes to cut, separate, and replicate DNA base by base ...
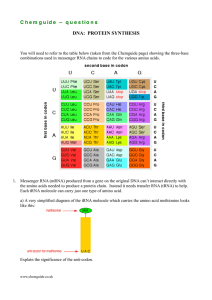
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... The various controls when clicked highlight parts of the DNA molecule or move it into different positions. The students can also use the mouse to grab the DNA to move it to see its structure. The color legend is given when you “click for explanation” under C H O N P. For example, clicking “Backbone ...
... The various controls when clicked highlight parts of the DNA molecule or move it into different positions. The students can also use the mouse to grab the DNA to move it to see its structure. The color legend is given when you “click for explanation” under C H O N P. For example, clicking “Backbone ...
Genetics Study Guide
... How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
... How many people in the above example are carriers of albinism, but are not albino? ___ ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
Title
... a.Blocking the formation of mediator proteins b. Suppression of transcription by binding to the TATA box c. Initiate transcription by forming an initiation complex d. Allosteric inhibition of RNA polymerase e. None of the above When an effector molecule binds to a transcription repressor protein, t ...
... a.Blocking the formation of mediator proteins b. Suppression of transcription by binding to the TATA box c. Initiate transcription by forming an initiation complex d. Allosteric inhibition of RNA polymerase e. None of the above When an effector molecule binds to a transcription repressor protein, t ...
DNA_LAdders_files/StoS 100bp DNA Ladder flyer new
... 11 fragments suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-1,500 bp. The 500 and 1,500 bp bands have increased intensity to serve as referce points. The approximate mass of DNA in each band is provided (0,5ug a load) for a ...
... 11 fragments suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophoresis. The DNA includes fragments ranging from 100-1,500 bp. The 500 and 1,500 bp bands have increased intensity to serve as referce points. The approximate mass of DNA in each band is provided (0,5ug a load) for a ...
Classical and Modern Genetics
... • Fidelity in copying information • Specificity in information • Expression of gene via manufacturing of polypeptide leading to protein (e.g., enzyme) • Genetic Code is conserved in evolution – all organisms use the exact same coding process • Example of Genetic Code: laboratory exercise ...
... • Fidelity in copying information • Specificity in information • Expression of gene via manufacturing of polypeptide leading to protein (e.g., enzyme) • Genetic Code is conserved in evolution – all organisms use the exact same coding process • Example of Genetic Code: laboratory exercise ...
DNA
... form hydrogen bonds, connecting the two strands. – Based on details of their structure, adenine would form two hydrogen bonds only with thymine and guanine would form three hydrogen bonds only with cytosine. – This finding explained Chargaff’s rules. ...
... form hydrogen bonds, connecting the two strands. – Based on details of their structure, adenine would form two hydrogen bonds only with thymine and guanine would form three hydrogen bonds only with cytosine. – This finding explained Chargaff’s rules. ...
lecture notes
... Residues form peptide bonds (C atom of amino acid Ai bonds with N atom of amino acid Ai+1 Proteins are peptide bonds and form a polypeptide chain Nucleic Acids RNA : ribonucleic acid DNA : deoxyribonucleic acid. Has a sugar backbone attached to a phosphate residue. Is a double helix structur ...
... Residues form peptide bonds (C atom of amino acid Ai bonds with N atom of amino acid Ai+1 Proteins are peptide bonds and form a polypeptide chain Nucleic Acids RNA : ribonucleic acid DNA : deoxyribonucleic acid. Has a sugar backbone attached to a phosphate residue. Is a double helix structur ...
HOW ARE PROTEINS MADE?
... What is the maximum number of amino acids that could be coded for by this section of mRNA? ...
... What is the maximum number of amino acids that could be coded for by this section of mRNA? ...
5 questions per round and 9 rounds with 10 team tourney
... Genetics tournament: 12 questions per round and 6 rounds with 16 team tourney. 1. What is the complimentary mRNA for the DNA strand AGGAC? (UCCUG) 2. What is the specific site where a tRNA with the currently synthesized strand of amino acids would be located on the ribosome? (p site) 3. What can be ...
... Genetics tournament: 12 questions per round and 6 rounds with 16 team tourney. 1. What is the complimentary mRNA for the DNA strand AGGAC? (UCCUG) 2. What is the specific site where a tRNA with the currently synthesized strand of amino acids would be located on the ribosome? (p site) 3. What can be ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... nonsense mutations (which change an amino acid-encoding codon into a stop codon). Mutations that involve insertion or deletion of nucleotides are called frameshift mutations. Expanding repeat mutations increase the number of copies of three-or four-nucleotide sequences over several generations. This ...
... nonsense mutations (which change an amino acid-encoding codon into a stop codon). Mutations that involve insertion or deletion of nucleotides are called frameshift mutations. Expanding repeat mutations increase the number of copies of three-or four-nucleotide sequences over several generations. This ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.