Answer Key DNA Review - John Bowne High School
... Female mosquitoes spread diseases when they bite humans to obtain blood. It is only the females that do the biting. Research is being conducted to alter the DNA of male mosquitoes. These altered males could then mate with normal female mosquitoes. All of the resulting female offspring would ...
... Female mosquitoes spread diseases when they bite humans to obtain blood. It is only the females that do the biting. Research is being conducted to alter the DNA of male mosquitoes. These altered males could then mate with normal female mosquitoes. All of the resulting female offspring would ...
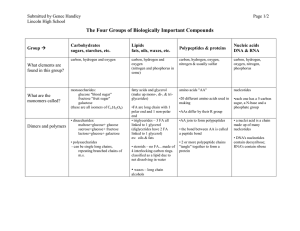
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... •FA are long chain with 1 polar end and 1 non-polar end • triglycerides – 3 FA all linked to 1 glycerol (diglycerides have 2 FA linked to 1 glycerol) ex: oils & fats • steroids – no FA…made of 4 interlocking carbon rings. classified as a lipid due to not dissolving in water ...
... •FA are long chain with 1 polar end and 1 non-polar end • triglycerides – 3 FA all linked to 1 glycerol (diglycerides have 2 FA linked to 1 glycerol) ex: oils & fats • steroids – no FA…made of 4 interlocking carbon rings. classified as a lipid due to not dissolving in water ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription and Translation
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
... Chain of aa called polypeptide Peptide bonds hold aa together 1 or more polypeptide chains can link and fold together to form a 3-dimensional protein • Proteins differ in number and sequence of aa • Protein structure determines their function ...
Protein Synthesis: Transcription
... insertion of a unique amino acid Language of the genetic code Multiple codons for the same amino acid Anticodon: on one end of tRNA complementary to a specific mRNA codon tRNA molecules carry different amino acids ...
... insertion of a unique amino acid Language of the genetic code Multiple codons for the same amino acid Anticodon: on one end of tRNA complementary to a specific mRNA codon tRNA molecules carry different amino acids ...
1. DNA (genetic info is passed down through DNA and RNA) A
... 2. “Spare” nucleotides are added bidirectionally to bond complementarily with use of DNA polymerases (DNA pol) 3. DNA pol only can add to the 3’ to 5’ side and new DNA is made in the 5’ to 3’direction 4. Replication bubbles open up and a replication fork is created because bubble is in half and it h ...
... 2. “Spare” nucleotides are added bidirectionally to bond complementarily with use of DNA polymerases (DNA pol) 3. DNA pol only can add to the 3’ to 5’ side and new DNA is made in the 5’ to 3’direction 4. Replication bubbles open up and a replication fork is created because bubble is in half and it h ...
Organic
... • The “code of life” • Specifically they code for proteins • Each NA’s role: DNA—stores the info (w/in chromosomes) for all of life’s processes (growth, metabolism, reproduction, etc.) RNA—messenger that carries the info out ...
... • The “code of life” • Specifically they code for proteins • Each NA’s role: DNA—stores the info (w/in chromosomes) for all of life’s processes (growth, metabolism, reproduction, etc.) RNA—messenger that carries the info out ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... exact genetic basis of a disorder, making it possible to develop more effective treatment for individuals affected by genetic disease. ...
... exact genetic basis of a disorder, making it possible to develop more effective treatment for individuals affected by genetic disease. ...
3rd of 7 Review Packets
... 2. “Spare” nucleotides are added bidirectionally to bond complementarily with use of DNA polymerases (DNA pol) 3. DNA pol only can add to the 3’ to 5’ side and new DNA is made in the 5’ to 3’direction 4. Replication bubbles open up and a replication fork is created because bubble is in half and it h ...
... 2. “Spare” nucleotides are added bidirectionally to bond complementarily with use of DNA polymerases (DNA pol) 3. DNA pol only can add to the 3’ to 5’ side and new DNA is made in the 5’ to 3’direction 4. Replication bubbles open up and a replication fork is created because bubble is in half and it h ...
Name: MACROMOLECULES Date: I. ELEMENTS AND
... 19. What is the effect of excess heat or a change in pH on an enzyme? _________________________________________________________________________________ V. LIPIDS: are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cutic ...
... 19. What is the effect of excess heat or a change in pH on an enzyme? _________________________________________________________________________________ V. LIPIDS: are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cutic ...
RNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon - set of three mRNA nucleotides that code for an ...
... RNA polymerase - the enzyme responsible for RNA transcription. Moves along gene and bonds appropriate RNA nucleotide to complimentary DNA nucleotide. Promoter - binding site on gene that RNA polymerase attaches to at the start of transcription. Codon - set of three mRNA nucleotides that code for an ...
dna
... part of the coding for a gene are referred to as INTRONS for intervening sequences More on this in the RNA transcription section ...
... part of the coding for a gene are referred to as INTRONS for intervening sequences More on this in the RNA transcription section ...
Genetics Learning Goals
... exhibits the nature of science. C4) Explain how diversity of all life on Earth can be coded by DNA, even it only uses four bases. D4) Apply Messelson & Stahl’s experiment to support that DNA replication is semi-conservative. E4) Explain how one gene can code for more than one protein. F4) Explain wh ...
... exhibits the nature of science. C4) Explain how diversity of all life on Earth can be coded by DNA, even it only uses four bases. D4) Apply Messelson & Stahl’s experiment to support that DNA replication is semi-conservative. E4) Explain how one gene can code for more than one protein. F4) Explain wh ...
Unti 8-9 - DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... exhibits the nature of science. C4) Explain how diversity of all life on Earth can be coded by DNA, even it only uses four bases. D4) Apply Messelson & Stahl’s experiment to support that DNA replication is semi-conservative. E4) Explain how one gene can code for more than one protein. F4) Explain wh ...
... exhibits the nature of science. C4) Explain how diversity of all life on Earth can be coded by DNA, even it only uses four bases. D4) Apply Messelson & Stahl’s experiment to support that DNA replication is semi-conservative. E4) Explain how one gene can code for more than one protein. F4) Explain wh ...
The Genetic Code The nucleotide bases of the DNA strand
... Once the tRNA has found it’s position along the mRNA it locks into a distinct place. The tRNA also carries – as a specific correlation to its nucleotide sequence - one distinct amino acid. A tRNA is therefore distinct for its three nucleotides at one end, and its proper amino acid at the other end o ...
... Once the tRNA has found it’s position along the mRNA it locks into a distinct place. The tRNA also carries – as a specific correlation to its nucleotide sequence - one distinct amino acid. A tRNA is therefore distinct for its three nucleotides at one end, and its proper amino acid at the other end o ...
PCR-Presentation
... Introduction • PCR, polymerase chain reaction, is an invitro technique for amplification of a region of DNA whose sequence is known or which lies between two regions of known sequence • Before PCR, DNA of interest could only be amplified by over-expression in cells and this with limited yield ...
... Introduction • PCR, polymerase chain reaction, is an invitro technique for amplification of a region of DNA whose sequence is known or which lies between two regions of known sequence • Before PCR, DNA of interest could only be amplified by over-expression in cells and this with limited yield ...
Make a DNA Model - Flinn Scientific
... DNA is the common acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is considered the molecular “blueprint” which the body uses for creating new proteins. The DNA structure is universal. All organisms from bacteria to plants to animals have DNA. The DNA molecule is made up of several components—phosphate group ...
... DNA is the common acronym for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is considered the molecular “blueprint” which the body uses for creating new proteins. The DNA structure is universal. All organisms from bacteria to plants to animals have DNA. The DNA molecule is made up of several components—phosphate group ...
DNA→ RNA
... means that when it makes a copy, one half of the old strand is always kept in the new strand. This helps reduce the number of copy errors ...
... means that when it makes a copy, one half of the old strand is always kept in the new strand. This helps reduce the number of copy errors ...
Answer all the questions Time allowed : 49 minutes 1. State two
... Each DNA molecule is formed from two complementary polynucleotide chains running anti-parallel to each other. In a polynucleotide chain, adjacent nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester bridges . A phosphate gro up, a deoxyribose and a nitrogenous base join together to form a nucleotide. P ...
... Each DNA molecule is formed from two complementary polynucleotide chains running anti-parallel to each other. In a polynucleotide chain, adjacent nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester bridges . A phosphate gro up, a deoxyribose and a nitrogenous base join together to form a nucleotide. P ...
SBI4U Molecular genetics UNIT_AK
... c. RNA primase as a high affinity for the lagging strand, and primes it often d. There is only enough free energy to synthesize one strand continuously ___ 12.Which of the following post-transcriptional modifications is carried out in a prokaryotic cell? a. 5’ cap of 7-methyl guanosine and 3’ poly-A ...
... c. RNA primase as a high affinity for the lagging strand, and primes it often d. There is only enough free energy to synthesize one strand continuously ___ 12.Which of the following post-transcriptional modifications is carried out in a prokaryotic cell? a. 5’ cap of 7-methyl guanosine and 3’ poly-A ...
Mutations - KingsfieldBiology
... Any change to the quantity or structure of DNA of an organism is known as a mutation. Mutations can occur in either somatic cells (body cell) and germ cells (those that produce the gametes (these can be passed on!)). Changes in the structure or number of a whole chromosome is know as a chromos ...
... Any change to the quantity or structure of DNA of an organism is known as a mutation. Mutations can occur in either somatic cells (body cell) and germ cells (those that produce the gametes (these can be passed on!)). Changes in the structure or number of a whole chromosome is know as a chromos ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.