lec-02-transcript
... together by means of a covalent bond known as the phosphodiester bond. This is formed between the 3' carbon of one sugar and 5' carbon of the next sugar via a phosphate group to give rise to a polynucleotide chain. DNA is composed of four different nitrogenous bases that are derivatives of the heter ...
... together by means of a covalent bond known as the phosphodiester bond. This is formed between the 3' carbon of one sugar and 5' carbon of the next sugar via a phosphate group to give rise to a polynucleotide chain. DNA is composed of four different nitrogenous bases that are derivatives of the heter ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 5: types of organic molecules
... pay attention to what makes an R group polar, nonpolar, or ionic (charged) and thus their hydrophobic or hydrophilic nature ...
... pay attention to what makes an R group polar, nonpolar, or ionic (charged) and thus their hydrophobic or hydrophilic nature ...
F 1
... 1900 Karl Correns- Discovered incomplete dominance 1900’s Reginald C. Punnett- Developed Punnett squares for determining probability of traits. 1900 Walter Sutton- Determined genes found on chromosomes. 1907 Thomas Hunt Morgan- Determined sex chromosome, determines sex of organism 1953 James Watson, ...
... 1900 Karl Correns- Discovered incomplete dominance 1900’s Reginald C. Punnett- Developed Punnett squares for determining probability of traits. 1900 Walter Sutton- Determined genes found on chromosomes. 1907 Thomas Hunt Morgan- Determined sex chromosome, determines sex of organism 1953 James Watson, ...
Biodegradable Polymers – From Delivery of Drugs to Tissue
... Abraham J. Domb Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
... Abraham J. Domb Institute of Drug Research, School of Pharmacy- Faculty of Medicine, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel ...
General Genetics General concepts Genetic information is
... neutral (i.e., no phenotypic or selective consequence) 3. such changes occur randomly in time (more or less), and so can be used to measure time in a relative sense 4. this “evolutionary clock” can be used to infer evolutionary histories and relationships 5. most useful molecular chronometers are mo ...
... neutral (i.e., no phenotypic or selective consequence) 3. such changes occur randomly in time (more or less), and so can be used to measure time in a relative sense 4. this “evolutionary clock” can be used to infer evolutionary histories and relationships 5. most useful molecular chronometers are mo ...
Genetics of bacteria
... Gene Expression Genetic information encoded in DNA is expressed by synthesis of specific RNAs and proteins, and information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. The DNA-directed synthesis of RNA is called transcription. Because the strands of double-helical DNA are antiparallel and complementary, only ...
... Gene Expression Genetic information encoded in DNA is expressed by synthesis of specific RNAs and proteins, and information flows from DNA to RNA to protein. The DNA-directed synthesis of RNA is called transcription. Because the strands of double-helical DNA are antiparallel and complementary, only ...
semester two final review key units 5 and 6 only
... 1. Definitions to know: monomer, polymer, biochemistry, hydrocarbon, carbohydrate, protein, lipids, and nucleic acids. Monomer: a molecule of any class of compounds, mostly organic that can react with other molecules that can form larger molecules Polymer: any of a class of natural or synthetic subs ...
... 1. Definitions to know: monomer, polymer, biochemistry, hydrocarbon, carbohydrate, protein, lipids, and nucleic acids. Monomer: a molecule of any class of compounds, mostly organic that can react with other molecules that can form larger molecules Polymer: any of a class of natural or synthetic subs ...
Changes in the genetic material (DNA)
... Point mutations usually affect no more than a single amino acid. The protein may be slightly affected or not affected at all. 2. Frameshift Mutation: a single gene or nitrogen base is deleted or added from the mRNA sequence causing a shift in the “reading frame” of the genetic message. Example: THE ...
... Point mutations usually affect no more than a single amino acid. The protein may be slightly affected or not affected at all. 2. Frameshift Mutation: a single gene or nitrogen base is deleted or added from the mRNA sequence causing a shift in the “reading frame” of the genetic message. Example: THE ...
Outlines_Ch16
... one plasmid per bacterial chromosome. • An F factor can integrate into the bacterial chromosome – Its own replication system is suppressed. ...
... one plasmid per bacterial chromosome. • An F factor can integrate into the bacterial chromosome – Its own replication system is suppressed. ...
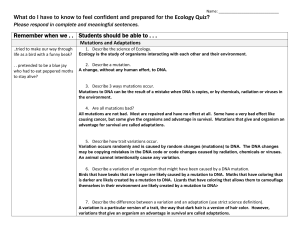
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... could result in fewer recessive genes. Any trait based on DNA could change over several generations if there is a DNA mutation. ...
... could result in fewer recessive genes. Any trait based on DNA could change over several generations if there is a DNA mutation. ...
Intracellular Distribution of Radioactivity in Nucleic Acid tration of
... of empirical factors, the specific activity the protein was calculated. ...
... of empirical factors, the specific activity the protein was calculated. ...
bio 30 ch 18 molecular genetics review
... b) More than 1 sequence is possible since some amino acids are coded for by more than 1 codon. c) Variability in mRNA due to mutation can still produce the same amino acid sequence since some amino acids are coded for by up to 6 different codons. 5. 1. DNA replication produces two double stranded mo ...
... b) More than 1 sequence is possible since some amino acids are coded for by more than 1 codon. c) Variability in mRNA due to mutation can still produce the same amino acid sequence since some amino acids are coded for by up to 6 different codons. 5. 1. DNA replication produces two double stranded mo ...
DISCUSSION QUESTIONS KEY Exercise 16: DNA Fingerprinting
... How long are each of our simulated viruses in base pair (bp) units? Show your calculations. (By the way, real viruses are typically much longer.) From the drawing in the Results section students can read from their labeled standard DNA fragments the approximate length of the fragments that make up e ...
... How long are each of our simulated viruses in base pair (bp) units? Show your calculations. (By the way, real viruses are typically much longer.) From the drawing in the Results section students can read from their labeled standard DNA fragments the approximate length of the fragments that make up e ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Recombinant DNA: Any DNA molecule that has been manipulated so that it contains DNA from two or more sources. 2. Explain how using one restriction enzyme to cut both a plasmid and a gene of interest will allow the gene to be inserted into the plasmid. Answer: The restriction enzyme cuts the plasmid ...
... Recombinant DNA: Any DNA molecule that has been manipulated so that it contains DNA from two or more sources. 2. Explain how using one restriction enzyme to cut both a plasmid and a gene of interest will allow the gene to be inserted into the plasmid. Answer: The restriction enzyme cuts the plasmid ...
Welcome to DNA Replication 101
... Welcome to DNA Replication 101 If one cell is going to divide to produce two new cells, the first cell must copy all of its parts before it can split in half. The cell grows, makes more organelles, and copies its genetic information (the DNA) so that the new cells each have a copy of everything they ...
... Welcome to DNA Replication 101 If one cell is going to divide to produce two new cells, the first cell must copy all of its parts before it can split in half. The cell grows, makes more organelles, and copies its genetic information (the DNA) so that the new cells each have a copy of everything they ...
Document
... RESULTS Phage proteins remained outside the bacterial cells during infection, while phage DNA entered the cells. When cultured, bacterial cells with radioactive phage DNA released new phages with some radioactive phosphorus. CONCLUSION Hershey and Chase concluded that DNA, not protein, functions as ...
... RESULTS Phage proteins remained outside the bacterial cells during infection, while phage DNA entered the cells. When cultured, bacterial cells with radioactive phage DNA released new phages with some radioactive phosphorus. CONCLUSION Hershey and Chase concluded that DNA, not protein, functions as ...
File - Ms. Poole`s Biology
... • 1. Write down 6 letters of DNA (label 5’ and 3’ ends) • 2. Write the corresponding mRNA sequence (label 5’ and 3’ ends) • 3. Write the amino acid chain ...
... • 1. Write down 6 letters of DNA (label 5’ and 3’ ends) • 2. Write the corresponding mRNA sequence (label 5’ and 3’ ends) • 3. Write the amino acid chain ...
Chapter 2
... folded chains. Eg. Disulfide bond is a covalent bond between sulfur atoms in two cysteine amino acids that are near each other. Quaternary structure describes proteins with more than one polypeptide chain. Hemoglobin has four subunits. ...
... folded chains. Eg. Disulfide bond is a covalent bond between sulfur atoms in two cysteine amino acids that are near each other. Quaternary structure describes proteins with more than one polypeptide chain. Hemoglobin has four subunits. ...
Lecture 2 - Cell assembly
... • Vacuoles or vesicles – spaces in the cytoplasm that can store solids or gases • Mesosomes/Organelles –a membrane system internal to the cell which facilitates protein function; there are these structures specifically for photosynthesis ...
... • Vacuoles or vesicles – spaces in the cytoplasm that can store solids or gases • Mesosomes/Organelles –a membrane system internal to the cell which facilitates protein function; there are these structures specifically for photosynthesis ...
carbonyl group
... This group is always on a terminal C – so no need to specify location by number Condensed it is symbolized by a -CHO group at the end of the formula Aldehydes have characteristic scents and tastes – Cinnamon, bannana, apple, raspberry flavors are ...
... This group is always on a terminal C – so no need to specify location by number Condensed it is symbolized by a -CHO group at the end of the formula Aldehydes have characteristic scents and tastes – Cinnamon, bannana, apple, raspberry flavors are ...
Packet 2 - Organic Chemistry
... Nucleotides are monomers that consist of pentose (the pentagon shape in the diagram) attached to a phosphate group and nitrogenous base Pentose can be deoxyribose (as in DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid) or ribose (as in RNA or ___________nucleic acid) DNA and RNA are central to heredity/genetics and ...
... Nucleotides are monomers that consist of pentose (the pentagon shape in the diagram) attached to a phosphate group and nitrogenous base Pentose can be deoxyribose (as in DNA or deoxyribose nucleic acid) or ribose (as in RNA or ___________nucleic acid) DNA and RNA are central to heredity/genetics and ...
Biology Test Chapters 13 Name and Honor Code: 1. The insertion of
... b. autosomes c. vectors d. transgenic organisms 6. The process by which desired traits of certain plants & animals are selected and passed on to their future generations: a. karyotype b. selective breeding c. human genome d. gene therapy 7. Bacterial proteins that have the ability to cut both strand ...
... b. autosomes c. vectors d. transgenic organisms 6. The process by which desired traits of certain plants & animals are selected and passed on to their future generations: a. karyotype b. selective breeding c. human genome d. gene therapy 7. Bacterial proteins that have the ability to cut both strand ...
File
... Elements of Life- Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are hydrates of Carbon. This means they have the general formula (CH2O)n • Consist only of C,H, and O. Lack the other elements except in rare cases • Exist as monomers (single sugars) or polymers of sugars (disaccharides and polysaccharides) ...
... Elements of Life- Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates are hydrates of Carbon. This means they have the general formula (CH2O)n • Consist only of C,H, and O. Lack the other elements except in rare cases • Exist as monomers (single sugars) or polymers of sugars (disaccharides and polysaccharides) ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.