federal circuit holds claims to isolated dna and to
... included most, or all, of the gene. The former ...
... included most, or all, of the gene. The former ...
Lambda Vectors and their replication
... • size of DNA to be introduced into the host cell • Problem: when making genomic libarary of large size (plants and mammals) only a portion of those fragments will be represented. If gene of interest is located in a large fragment, then you won’t be able to isolate that gene from the library. • Solu ...
... • size of DNA to be introduced into the host cell • Problem: when making genomic libarary of large size (plants and mammals) only a portion of those fragments will be represented. If gene of interest is located in a large fragment, then you won’t be able to isolate that gene from the library. • Solu ...
Reading Guide_08_EB_TandT
... While reading these chapters, constantly ask yourself, “How is this information helping me to understand how my cells respond to the environment and reproduce?” Chapter 1, pg 7-8 (Cells and Their DNA) 1. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes store their DNA? 2. What are genes? 3. Do bacteria and humans ...
... While reading these chapters, constantly ask yourself, “How is this information helping me to understand how my cells respond to the environment and reproduce?” Chapter 1, pg 7-8 (Cells and Their DNA) 1. How do prokaryotes and eukaryotes store their DNA? 2. What are genes? 3. Do bacteria and humans ...
Document
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP ...
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP ...
DNA Profiling: How many CATS
... one another. This means that each individual differs on average in 1 out of 1000 base pairs with any other individual. In addition, much of our DNA is considered “junk” DNA because it is not transcribed into RNA; thus, “junk” DNA does not influence protein expression and has no known function. These ...
... one another. This means that each individual differs on average in 1 out of 1000 base pairs with any other individual. In addition, much of our DNA is considered “junk” DNA because it is not transcribed into RNA; thus, “junk” DNA does not influence protein expression and has no known function. These ...
Amino acid Metabolism 2
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (P ...
... 2. A Roundup Ready plant is one that has been genetically modified so that an enzyme (EPSP synthase) can no longer bind to the active ingredient (glyphosphate) which is a competitive inhibitor of A) shikimate (in the aromatic amino acid pathway). B) tryptophan. C) lysine. D) phosphoenolpyruvate (P ...
Review Sheet - Science with Ms. Wang
... On the long chromosome is the gene for eye color (R/r) and this organism is heterozygous for eye color. On the short is the gene for hairiness (H/h) and the fly is also heterozygous for hair. Diagram two different options for how the homologous chromosomes could line up in metaphase I. For each ...
... On the long chromosome is the gene for eye color (R/r) and this organism is heterozygous for eye color. On the short is the gene for hairiness (H/h) and the fly is also heterozygous for hair. Diagram two different options for how the homologous chromosomes could line up in metaphase I. For each ...
Biological Molecules continued
... molecule, and also is likely to weaken the molecule’s bonds and therefore make it more reactive. Enzymes are unchanged after the reaction, therefore they can be used many times over, it are also what releases the products of the reaction. ...
... molecule, and also is likely to weaken the molecule’s bonds and therefore make it more reactive. Enzymes are unchanged after the reaction, therefore they can be used many times over, it are also what releases the products of the reaction. ...
CS "Autism and epilepsy"
... can be caused by a protein deficiency. Despite the recent progress achieved in biology and genetics, disorders caused by an insufficient production of a given protein are currently incurable. SINEUP represents a new therapeutic approach. By creating artificial non-coding RNA molecules that combine w ...
... can be caused by a protein deficiency. Despite the recent progress achieved in biology and genetics, disorders caused by an insufficient production of a given protein are currently incurable. SINEUP represents a new therapeutic approach. By creating artificial non-coding RNA molecules that combine w ...
1.2.3.A DNAAnalysisF - Clayton School District
... propel them through an agarose gel at different speeds. Scientists can use these RFLPs, Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms, a set of DNA puzzle pieces unique to the individual, to create a pattern called a DNA fingerprint. In order to avoid the confusion with actual fingerprinting, this techn ...
... propel them through an agarose gel at different speeds. Scientists can use these RFLPs, Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms, a set of DNA puzzle pieces unique to the individual, to create a pattern called a DNA fingerprint. In order to avoid the confusion with actual fingerprinting, this techn ...
Managing people in sport organisations: A strategic human resource
... (S-D sequence) on the mRNA. Next, the initiator tRNA that reads AUG is charged with fMet. The charged initiator tRNA associates with the small ribosome subunit and finds the start codon. Assembly is helped by initiation factors (IF1, IF2, and IF3)—not shown. (B) During elongation peptide bonds are f ...
... (S-D sequence) on the mRNA. Next, the initiator tRNA that reads AUG is charged with fMet. The charged initiator tRNA associates with the small ribosome subunit and finds the start codon. Assembly is helped by initiation factors (IF1, IF2, and IF3)—not shown. (B) During elongation peptide bonds are f ...
DNA Technologies
... • Upon cell lysis, DNA (and cellular proteins) stick to the paper • Specific probes can be used to detect the presence of specific macromolecules • To detect specific DNA, a radiolabeled DNA probe, complementary to the target sequence, is used. • How would you detect specific proteins? ...
... • Upon cell lysis, DNA (and cellular proteins) stick to the paper • Specific probes can be used to detect the presence of specific macromolecules • To detect specific DNA, a radiolabeled DNA probe, complementary to the target sequence, is used. • How would you detect specific proteins? ...
Operons
... (or vice versa), or from one plasmid to another Sometimes transposable elements are called “jumping genes” ...
... (or vice versa), or from one plasmid to another Sometimes transposable elements are called “jumping genes” ...
MS Word - VCU Secrets of the Sequence
... DNA separate and each acts as a template for the synthesis (or replication) of a new strand. New bases are paired with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form a new strand of DNA. DNA regulates cellular function by directing the creation of certain proteins. It acts as a m ...
... DNA separate and each acts as a template for the synthesis (or replication) of a new strand. New bases are paired with the template strand, and are then connected to one another to form a new strand of DNA. DNA regulates cellular function by directing the creation of certain proteins. It acts as a m ...
Manipulating DNA - Biology R: 4(A,C)
... Reading the DNA sequence: Obtain a single stranded piece of an organism’s DNA. As it replicates with bases labeled with color coded fluorescent dyes, the replication stops forming a fragment. After all of the DNA has replicated, tiny labeled fragments are left. The fragments are separated b ...
... Reading the DNA sequence: Obtain a single stranded piece of an organism’s DNA. As it replicates with bases labeled with color coded fluorescent dyes, the replication stops forming a fragment. After all of the DNA has replicated, tiny labeled fragments are left. The fragments are separated b ...
Chapter 16 - Molecular Basis of Inheritance DNA as the Genetic
... Helicase - Unwinds parental double helix at replication forks ssb proteins- bind to and stabilize ssDNA Topoisomerase - Corrects “overwinding” ahead of replication forks; breaks, swivels, and rejoins DNA strands Primase - synthesizes single primer for leading strand; synthesizes RNA primer for each ...
... Helicase - Unwinds parental double helix at replication forks ssb proteins- bind to and stabilize ssDNA Topoisomerase - Corrects “overwinding” ahead of replication forks; breaks, swivels, and rejoins DNA strands Primase - synthesizes single primer for leading strand; synthesizes RNA primer for each ...
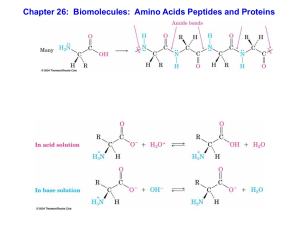
Chapter 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids Peptides and Proteins
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
... Contains an imidazole ring that is partially protonated in neutral solution Only the pyridine-like, doubly bonded nitrogen in histidine is basic. The pyrrole-like singly bonded nitrogen is nonbasic because its lone pair of electrons is part of the 6 electron aromatic imidazole ring (see Section 24 ...
Electrical induction hypothesis to explain enhancer-promoter
... processes, including the regulation of gene expression, DNA replication, and chromatin structure (Cremer and Cremer 2001). The technique of chromosome conformation capture (3C) evaluates long‐range interactions between specific pairs of loci by using spatially constrained ligation followed by locus‐ ...
... processes, including the regulation of gene expression, DNA replication, and chromatin structure (Cremer and Cremer 2001). The technique of chromosome conformation capture (3C) evaluates long‐range interactions between specific pairs of loci by using spatially constrained ligation followed by locus‐ ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.