Lecture Outline
... hydrocarbons: found in smoke of all kinds) Deaminating agents affects cytosine and adenine nitrous acid Oxidative reactions reactive forms of oxygen produced by normal aerobic metabolism superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals Intercalating agents ethidium bromide agents insert bet ...
... hydrocarbons: found in smoke of all kinds) Deaminating agents affects cytosine and adenine nitrous acid Oxidative reactions reactive forms of oxygen produced by normal aerobic metabolism superoxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals Intercalating agents ethidium bromide agents insert bet ...
Chapter 9 – DNA-Based Information Technologies
... • After a cloning vector and insert DNA have been joined in vitro, recombinant DNA is introduced into a host cell such as E. coli (transformation) • Only a small percentage of cells take up the DNA • Selection -cells are grown under conditions in which only transformed cells survive • Screening - tr ...
... • After a cloning vector and insert DNA have been joined in vitro, recombinant DNA is introduced into a host cell such as E. coli (transformation) • Only a small percentage of cells take up the DNA • Selection -cells are grown under conditions in which only transformed cells survive • Screening - tr ...
Activation of S! nuclease at neutral pH fi
... Si nuclease is a single-strand-specific endonuclease that degrades DNA and RNA to nucleoside 5'-monophosphates. It has an acid pH optimum (4.0—4.5) and requires Zn 2+ or Co2"1" for maximal activity (1). This enzyme is widely used in DNA manipulation, mainly for the characterization of mRNAs (S r map ...
... Si nuclease is a single-strand-specific endonuclease that degrades DNA and RNA to nucleoside 5'-monophosphates. It has an acid pH optimum (4.0—4.5) and requires Zn 2+ or Co2"1" for maximal activity (1). This enzyme is widely used in DNA manipulation, mainly for the characterization of mRNAs (S r map ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... Nucleic Acids: Informational Macromolecules That Can Be Catalytic • Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. • A nucleotide consists of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base. • In DNA, the pentose sugar is deoxyribose; in RNA it is ribose. ...
... Nucleic Acids: Informational Macromolecules That Can Be Catalytic • Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides. • A nucleotide consists of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogen-containing base. • In DNA, the pentose sugar is deoxyribose; in RNA it is ribose. ...
DNA Extraction Lab - IISME Community Site
... The purpose of this lab is to extract DNA from a variety of cells and see DNA molecules. One way to purify a molecule is to get rid of everything but that molecule. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule that controls everything that happens in the cell. DNA contains the genetic code or comman ...
... The purpose of this lab is to extract DNA from a variety of cells and see DNA molecules. One way to purify a molecule is to get rid of everything but that molecule. Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA is the molecule that controls everything that happens in the cell. DNA contains the genetic code or comman ...
L2 Prokaryote vs Eukaryote Cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes
... Trace amounts: F, Si, V Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, Se, Mo, I Compounds composed of carbon backbones are said to be organic molecules. Backbone of the major macromolecules are made of carbon (valence of four), and offers many possibilities such as chains, branched chains, rings, double an ...
... Trace amounts: F, Si, V Cr, Mn, Fe, Ni, Co, Cu, Zn, Se, Mo, I Compounds composed of carbon backbones are said to be organic molecules. Backbone of the major macromolecules are made of carbon (valence of four), and offers many possibilities such as chains, branched chains, rings, double an ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... a) 3.7 map units; b) 7.8 map units; c) 11 map units; d) 15.4 map units; e) 22 map units. Consider the gel at the right, derived from a sequencing reaction based on the Sanger chain termination method. A ...
... a) 3.7 map units; b) 7.8 map units; c) 11 map units; d) 15.4 map units; e) 22 map units. Consider the gel at the right, derived from a sequencing reaction based on the Sanger chain termination method. A ...
Unit 2, Module 2 Biochemistry - rev 2012
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
... to occur. Enzymes regulate metabolism, allowing life to continue. Enzymes speed up reactions, making an enzyme a biological catalyst. Metabolism (each reaction) has a small range of temperature and pH at which it can proceed. Each reaction also needs some energy to begin. This is called activation e ...
Ch. 13 Genetic Engineering
... which takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms, to pass desired traits on to the next generation of organisms ...
... which takes advantage of naturally occurring genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms, to pass desired traits on to the next generation of organisms ...
Slide ()
... Two forms of muscular dystrophy are caused by deletion mutations in the dystrophin gene. (Adapted, with permission, from Hoffman and Kunkel 1989; photos, reproduced with permission, from Arthur P. Hays.) A. The relative position of the dystrophin gene within the Xp21 region of the X chromosome. An e ...
... Two forms of muscular dystrophy are caused by deletion mutations in the dystrophin gene. (Adapted, with permission, from Hoffman and Kunkel 1989; photos, reproduced with permission, from Arthur P. Hays.) A. The relative position of the dystrophin gene within the Xp21 region of the X chromosome. An e ...
Document
... Must make accurate copies. Otherwise the copy will not have the properties that made the original such as success ...
... Must make accurate copies. Otherwise the copy will not have the properties that made the original such as success ...
Recombination and Repair
... fragments of DNA from their environment. In conjugation, one cell directly transfers genes (e.g., plasmid) to another cell. In transduction, viruses transfer genes between prokaryotes. ...
... fragments of DNA from their environment. In conjugation, one cell directly transfers genes (e.g., plasmid) to another cell. In transduction, viruses transfer genes between prokaryotes. ...
Structures and Functions of Biomolecules (PDF Available)
... • The structural isomers are defined as isomers having some molecule formula but different structures. • The stereo isomers whereas have same molecular and structural formula but differ in configuration i.e. arrangement of atoms in space. • Stereo isomers are further sub grouped into optical isomers ...
... • The structural isomers are defined as isomers having some molecule formula but different structures. • The stereo isomers whereas have same molecular and structural formula but differ in configuration i.e. arrangement of atoms in space. • Stereo isomers are further sub grouped into optical isomers ...
DNA Extraction from Strawberries
... contain large amounts of DNA. Each cell in a strawberry contains 8 copies of its genetic information (octaploid), while human cells only contain 2 copies (diploid). The DNA being visualized in this lab is clumps of many copies of DNA from many different cells throughout the strawberries. Each materi ...
... contain large amounts of DNA. Each cell in a strawberry contains 8 copies of its genetic information (octaploid), while human cells only contain 2 copies (diploid). The DNA being visualized in this lab is clumps of many copies of DNA from many different cells throughout the strawberries. Each materi ...
Chapter 2 Human Genetics Overview The purpose of this chapter is
... DNA consists of two strands arranged in a helix joined together by chemical bases. o The DNA molecule resembles a ladder twisted in a helix shape. o Ladder rungs represent chemical units called bases (also called nitrogenous bases). ...
... DNA consists of two strands arranged in a helix joined together by chemical bases. o The DNA molecule resembles a ladder twisted in a helix shape. o Ladder rungs represent chemical units called bases (also called nitrogenous bases). ...
Lec. 2 - DNA replication 1
... Then, Pol I degrades the RNA part with its 5’-3’ exonuclease activity, and replaces it with DNA. Pol I is not highly processive, so stops before going far. ...
... Then, Pol I degrades the RNA part with its 5’-3’ exonuclease activity, and replaces it with DNA. Pol I is not highly processive, so stops before going far. ...
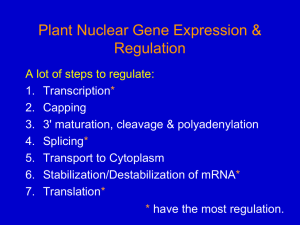
Nuclear gene expression 1
... condense into a solenoid; this inhibits factor binding to DNA targets. ...
... condense into a solenoid; this inhibits factor binding to DNA targets. ...
Structure of chicken calcitonin predicted by partial nucleotide
... Calcitonin, a 32 amino acid polypeptide produced in mammals by the C cells of the thyroid and m lower vertebrates by the ultrmobranchial gland, shows important differences in its amino acid sequence. Based on structure, three groups of calcitonins can be distinguished: (i) human and murine [1,2] (Pr ...
... Calcitonin, a 32 amino acid polypeptide produced in mammals by the C cells of the thyroid and m lower vertebrates by the ultrmobranchial gland, shows important differences in its amino acid sequence. Based on structure, three groups of calcitonins can be distinguished: (i) human and murine [1,2] (Pr ...
Notes - Haiku Learning
... 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): globular form that combines with proteins to make the ribosomes where proteins will be made RNA types ...
... 3. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): globular form that combines with proteins to make the ribosomes where proteins will be made RNA types ...
Catalogue Number CTK-611 Synonyms TFF
... The TFF2 protein was lyophilized from 0.4μm filtered solution at a concentration of 0.5mg/ml containing 20mM Tris pH-7.5, and 20mM NaCl. It is recommended to add deionized water to prepare a working stock solution of ...
... The TFF2 protein was lyophilized from 0.4μm filtered solution at a concentration of 0.5mg/ml containing 20mM Tris pH-7.5, and 20mM NaCl. It is recommended to add deionized water to prepare a working stock solution of ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... B. Carbohydrates C. Lipids D. Biotin and thiamine 63. Due to liver storage and enteropathic recycling sings of a deficiency of what vitamin may not be visible for five to six years? A. B-1 B. B-2 C. B-6 D. B-12 ...
... B. Carbohydrates C. Lipids D. Biotin and thiamine 63. Due to liver storage and enteropathic recycling sings of a deficiency of what vitamin may not be visible for five to six years? A. B-1 B. B-2 C. B-6 D. B-12 ...
Powerpoint
... Some R groups are reactive and will interact with other reactive R groups in the chain. These are the amino acids that are either charged or that have a sulphur atom. The interactions ( + and – attractions and S-S bridges) will fold the molecule over into a highly specific 3-dimensional shape. It is ...
... Some R groups are reactive and will interact with other reactive R groups in the chain. These are the amino acids that are either charged or that have a sulphur atom. The interactions ( + and – attractions and S-S bridges) will fold the molecule over into a highly specific 3-dimensional shape. It is ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.