Name
... 42. Browse the website until you get a good idea what the purpose of the site is. In your opinion, what is DNA.gov being used for? ...
... 42. Browse the website until you get a good idea what the purpose of the site is. In your opinion, what is DNA.gov being used for? ...
chapter 5 the structure and function of macromolecules
... Three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chain-like molecules called polymers. ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ...
... Three of the four classes of macromolecules—carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids—form chain-like molecules called polymers. ○ A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds. ○ The repeated units are small molecules called monomers. ...
Final Exam 2012 - Med Study Group
... They have double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. • They generally solidify at room temperature. • They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms. • They have fewer fatty acid molecules per fat molecule. 6. The structural level of a protein leas ...
... They have double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids. • They generally solidify at room temperature. • They contain more hydrogen than saturated fats having the same number of carbon atoms. • They have fewer fatty acid molecules per fat molecule. 6. The structural level of a protein leas ...
Red line lesson sketch
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
... First, use DNA subway to show how we can reveal features of a sequence. Create a project using a sample sequence. Once students have mastery, they can come back and create their own projects using real data. ...
Polymers and Amino Acids
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
... A peptide bond can be split by refluxing with hydrochloric acid. During hydrolysis, the water molecule adds across the peptide bond, forming a mixture of the two amino acids. ...
8th Grade Sixth Six Weeks Vocabulary
... an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an orga ...
... an organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells Teacher Information: Teach chains of a.a. = protein. any one of twenty different organic molecules that contain a carboxyl and an amino group and that combine to form proteins an orga ...
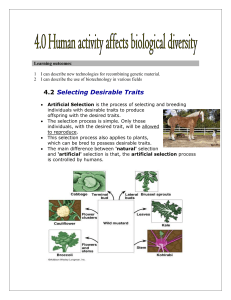
Sc9 - a 4.2 (teacher notes)
... Artificial Selection is the process of selecting and breeding individuals with desirable traits to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple. Only those individuals, with the desired trait, will be allowed to reproduce. This selection process also applies to plants, ...
... Artificial Selection is the process of selecting and breeding individuals with desirable traits to produce offspring with the desired traits. The selection process is simple. Only those individuals, with the desired trait, will be allowed to reproduce. This selection process also applies to plants, ...
Recombinant DNA Technology:
... commonly, restriction enzymes, that cut strands of DNA into smaller pieces (see figure -1). Bacteria use restriction enzymes to fight off attacking viruses, chopping up the viral DNA so that the virus can’t destroy the bacterial cell. Scientists use restriction enzymes in the lab to cut DNA into sma ...
... commonly, restriction enzymes, that cut strands of DNA into smaller pieces (see figure -1). Bacteria use restriction enzymes to fight off attacking viruses, chopping up the viral DNA so that the virus can’t destroy the bacterial cell. Scientists use restriction enzymes in the lab to cut DNA into sma ...
Exam Procedures: this isBMB 526 Exam #1 11/5/12 this is form A
... Questions 28 and 29 refer to two patients in a Case Study, designated as Case A. 28. A 2-day-old boy exhibits extreme lethargy and hyperventilation. Complete blood count (CBC) report documented megaloblastic anemia (low hematocrit, low RBC count, low plasma hemoglobin, and elevated mean corpuscular ...
... Questions 28 and 29 refer to two patients in a Case Study, designated as Case A. 28. A 2-day-old boy exhibits extreme lethargy and hyperventilation. Complete blood count (CBC) report documented megaloblastic anemia (low hematocrit, low RBC count, low plasma hemoglobin, and elevated mean corpuscular ...
Test I Study Guide
... 10- Why is water considered the “universal solvent?” 11- What are the major properties of water? 12- Define acids, bases, dissociation and explain the concepts of the pH scale. What is a buffer? 13- Explain the role of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis in the formation and breakdown of organic c ...
... 10- Why is water considered the “universal solvent?” 11- What are the major properties of water? 12- Define acids, bases, dissociation and explain the concepts of the pH scale. What is a buffer? 13- Explain the role of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis in the formation and breakdown of organic c ...
Chapter 2: Fundamentals of Chemistry The main subatomic particles
... •Some are isomers (same molecular formula but different structures) •e.g., glucose & fructose (C6H12O6) ...
... •Some are isomers (same molecular formula but different structures) •e.g., glucose & fructose (C6H12O6) ...
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... information for the synthesis of specific proteins. RNA (specifically, mRNA) carries this genetic information to the protein-synthesizing machinery. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides (p. 82, FIGURE 5.29) Each nucleotide monomer consists of a pentose covalently bonded to a phosphate ...
... information for the synthesis of specific proteins. RNA (specifically, mRNA) carries this genetic information to the protein-synthesizing machinery. A nucleic acid strand is a polymer of nucleotides (p. 82, FIGURE 5.29) Each nucleotide monomer consists of a pentose covalently bonded to a phosphate ...
Hwa Chong Institution Chemical bonding (Worksheet 5) Covalent
... only one lone pair of electrons on N, hence it can only form at most 2 H-bonds. Similarly for hydrogen fluoride, it has 3 lone pairs on F, but only one H atom. Hence it can only form 2 H-bonds. The greater the number of H-bonds, the higher the energy required to break them, and the higher the boilin ...
... only one lone pair of electrons on N, hence it can only form at most 2 H-bonds. Similarly for hydrogen fluoride, it has 3 lone pairs on F, but only one H atom. Hence it can only form 2 H-bonds. The greater the number of H-bonds, the higher the energy required to break them, and the higher the boilin ...
See DNA Essay possibilities
... #3. Many biological structures are composed of smaller units assembled into more complex structures having functions based on their structural organization. For THREE of the following complex structures, describe the smaller units, their assembly into the larger structures, and one major function of ...
... #3. Many biological structures are composed of smaller units assembled into more complex structures having functions based on their structural organization. For THREE of the following complex structures, describe the smaller units, their assembly into the larger structures, and one major function of ...
Table Minimal Crystallographic and refinement statistics
... Average pairwise r.m.s.d.** (Å) All RNA heavy RNA binding site All nucleotides (Special parts??) apical, tetraloop, symmetric bulge **[AUTHOR: Please indicate number of structures used in r.m.s.d. calculations] Pairwise r.m.s.d. was calculated among ## refined structures. [AUTHOR: Ramachandran stati ...
... Average pairwise r.m.s.d.** (Å) All RNA heavy RNA binding site All nucleotides (Special parts??) apical, tetraloop, symmetric bulge **[AUTHOR: Please indicate number of structures used in r.m.s.d. calculations] Pairwise r.m.s.d. was calculated among ## refined structures. [AUTHOR: Ramachandran stati ...
notes - Southington Public Schools
... important) this discovery led to a Nobel Prize in medicine (Shimomura, Chalfie, Tsien 2008) since the gene is tacked on to other GM attempts, allowing visual proof that cells in a sample or organism got the new gene being studied. The Human Genome Genome = the complete set of genes for an organism. ...
... important) this discovery led to a Nobel Prize in medicine (Shimomura, Chalfie, Tsien 2008) since the gene is tacked on to other GM attempts, allowing visual proof that cells in a sample or organism got the new gene being studied. The Human Genome Genome = the complete set of genes for an organism. ...
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
... time for pairing with RNA nucleotides. In the wake of the advancing RNA synthesis, the double helix re-forms and the RNA molecule just synthesized peels away from the DNA template strand. The RNA polymerase II uses nucleotides with three phosphate groups as substrates. They remove two phosphates as ...
... time for pairing with RNA nucleotides. In the wake of the advancing RNA synthesis, the double helix re-forms and the RNA molecule just synthesized peels away from the DNA template strand. The RNA polymerase II uses nucleotides with three phosphate groups as substrates. They remove two phosphates as ...
Ch. 13 - Genetic Engineering
... the cell, the external DNA gets incorporated into the bacterium’s own DNA. Recombinant DNA has been made. The cell has been transformed. It will make a new protein(s). ...
... the cell, the external DNA gets incorporated into the bacterium’s own DNA. Recombinant DNA has been made. The cell has been transformed. It will make a new protein(s). ...
DNA as the Genetic Material
... 1. Remember, DNA consists of a nitrogenous base (which can be adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C)), a pentose sugar called deoxyribose, and a phosphate group 2. Chargaff also discovered that the amount of A is always close to T, and G = C. 3. Hence, Chargaff’s rule: A pairs with T ...
... 1. Remember, DNA consists of a nitrogenous base (which can be adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C)), a pentose sugar called deoxyribose, and a phosphate group 2. Chargaff also discovered that the amount of A is always close to T, and G = C. 3. Hence, Chargaff’s rule: A pairs with T ...
Wiki - DNA Fingerprinting, Individual Identification and Ancestry
... A typical genetic fingerprint, which looks on average at ten different microsatellites, does not reveal anything about your personality, your mental capabilities, your ethnicity or possible predispositions to disease. However, exhaustive studies on human populations from all over the world have show ...
... A typical genetic fingerprint, which looks on average at ten different microsatellites, does not reveal anything about your personality, your mental capabilities, your ethnicity or possible predispositions to disease. However, exhaustive studies on human populations from all over the world have show ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.