MGB_LNA_Substitutes
... The above melting curves of a molecular beacon (FAM-BHQ) show that the incorporation of 3 propynyl-dC bases into its hairpin region increase its melting temperature by 4.5°C. It is important to note that the effective increase of melting temperature per single nucleotide exchange is subject to varia ...
... The above melting curves of a molecular beacon (FAM-BHQ) show that the incorporation of 3 propynyl-dC bases into its hairpin region increase its melting temperature by 4.5°C. It is important to note that the effective increase of melting temperature per single nucleotide exchange is subject to varia ...
(A) Cytosine (C)
... of the DNA double helix • An RNA molecule is single polynucleotide chain (single strand). • DNA molecules have two polynucleotide strands (double strand) that spiral around تدور حلزونياto form a double helix حلزون مزدوج. ...
... of the DNA double helix • An RNA molecule is single polynucleotide chain (single strand). • DNA molecules have two polynucleotide strands (double strand) that spiral around تدور حلزونياto form a double helix حلزون مزدوج. ...
Fall 08 Chapter 3 Worksheet
... 3. True/False: Fats have lots of double bonds in their fatty acid chains ...
... 3. True/False: Fats have lots of double bonds in their fatty acid chains ...
SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... The scissors below represent the enzyme called DNA helicase. It is responsible for cutting the DNA molecule in half by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases so that transcription can occur. Copy and paste the nucleotides from a previous slide to show how transcription occurs. RNA nucleotide ...
... The scissors below represent the enzyme called DNA helicase. It is responsible for cutting the DNA molecule in half by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the bases so that transcription can occur. Copy and paste the nucleotides from a previous slide to show how transcription occurs. RNA nucleotide ...
mr._a_powerpoint---organic_for_assignments
... • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds ...
... • Saturated fats have long chains with no double-bonds • Unsaturated fats have double bonds • Polyunsaturated fats have many double bonds ...
BIO 101 Exam 2 Practice Quiz Name
... You will be able to use a periodic table for your exam. Multiple Choice 1. What is the weakest type of chemical bond? a. Covalent b. Ionic ...
... You will be able to use a periodic table for your exam. Multiple Choice 1. What is the weakest type of chemical bond? a. Covalent b. Ionic ...
Study Guide for LS
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
... - Rosalind Franklin was able to create images of DNA molecules and discover that DNA was spiral shaped. ...
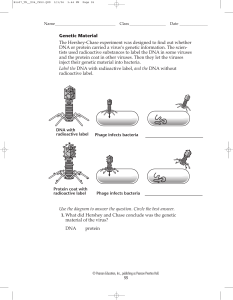
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
... DNA or protein carried a virus’s genetic information. The scientists used radioactive substances to label the DNA in some viruses and the protein coat in other viruses. Then they let the viruses inject their genetic material into bacteria. Label the DNA with radioactive label, and the DNA without ra ...
Small-Molecule Detection and Enantiopurity Measurement using
... properties for applications in biosensing and bioimaging. One area of our research involves using DNA aptamers as recognition elements for the development of new small-molecule detection and characterization assays. A central goal in these experiments is to pursue novel analysis techniques that are ...
... properties for applications in biosensing and bioimaging. One area of our research involves using DNA aptamers as recognition elements for the development of new small-molecule detection and characterization assays. A central goal in these experiments is to pursue novel analysis techniques that are ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... Polysaccharides release more energy, over a longer period of time because there are simply more bonds to break. You can form complex carbs through dehydration synthesis/reactions, removing water, and binding simpler mono/disaccharides. To break down the carbs, your body uses hydrolysis reactions to ...
... Polysaccharides release more energy, over a longer period of time because there are simply more bonds to break. You can form complex carbs through dehydration synthesis/reactions, removing water, and binding simpler mono/disaccharides. To break down the carbs, your body uses hydrolysis reactions to ...
1-2 Biomolecules
... 1. Like complex carbohydrates, proteins are biomolecules that serve many functions and can be chemically broken down and restructured. Both proteins and complex carbohydrates have which of the following? a. polymers of smaller subunits b. sequence of sugars c. lipids of large molecules d. nucleotide ...
... 1. Like complex carbohydrates, proteins are biomolecules that serve many functions and can be chemically broken down and restructured. Both proteins and complex carbohydrates have which of the following? a. polymers of smaller subunits b. sequence of sugars c. lipids of large molecules d. nucleotide ...
BIOMOLECULES
... NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium A ____________________ is made up of a sugar, a ...
... NO other kind of atom can form the number and variety of molecules that ___________________ can because it can bond to 4 other atoms at the same time to make carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. A. hydrogen B. oxygen C. carbon D. sodium A ____________________ is made up of a sugar, a ...
Document
... 12. How many amino acids are coded for by the following sequence of DNA? _______ ATCGACTTAGGC 13. Explain why many different proteins can be created from only 23 amino acids. ...
... 12. How many amino acids are coded for by the following sequence of DNA? _______ ATCGACTTAGGC 13. Explain why many different proteins can be created from only 23 amino acids. ...
Slide 1
... rather like a string of beads. Each of these small units is called a GENE. There may be many thousands of GENES on each chromosome. ...
... rather like a string of beads. Each of these small units is called a GENE. There may be many thousands of GENES on each chromosome. ...
DNA Workshop - Lapeer High School
... Go the following website: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/ Click on the link that says “DNA Workshop Activity” A new window should open. Follow the directions and answer the questions as you go along. First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and ...
... Go the following website: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/aso/tryit/dna/ Click on the link that says “DNA Workshop Activity” A new window should open. Follow the directions and answer the questions as you go along. First click the button in the upper left that says “DNA Replication.” Follow the prompts and ...
Discussion Guide Chapter 15
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
Vocabulary DNA Structure
... molecules that consist of a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) with a nitrogenous base attached to their 1’ carbon and a phosphate group attached to their 5’ carbon ...
... molecules that consist of a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) with a nitrogenous base attached to their 1’ carbon and a phosphate group attached to their 5’ carbon ...
DNA and RNA
... facts to get you started: Nucleic acids are the molecules that code the genetic information of organisms. The ...
... facts to get you started: Nucleic acids are the molecules that code the genetic information of organisms. The ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that provides the instructions for making proteins? ...
... 1. DNA codes for what macromolecule? Provide three examples of proteins necessary in our bodies a. b. c. 2. Where is the code within the DNA molecule that provides the instructions for making proteins? ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
... DNA is used to make a single strand of RNA that is ...
Document
... A twisted ladder with two long chains of alternating phosphates and sugars. The nitrogen bases act as the “rungs” joining the two strands. ...
... A twisted ladder with two long chains of alternating phosphates and sugars. The nitrogen bases act as the “rungs” joining the two strands. ...
DNA to Proteins
... * A gene is a string or group of nucleotides that give the cell information on how to make a protein. * Humans have over 30,000 genes ...
... * A gene is a string or group of nucleotides that give the cell information on how to make a protein. * Humans have over 30,000 genes ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.