Chapter 17 Powerpoint
... More Modification • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
... More Modification • RNA splicing – Initial RNA sequence is approximately 8,000 nucleotides – Generally, only approx. 1,200 are needed, though. – Noncoding areas are found in between coding areas ...
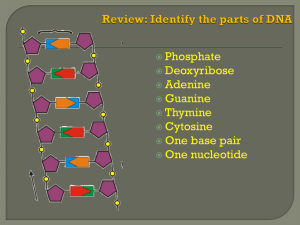
DNA is an abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic acid
... much broader, encompassing a wide range of procedures designed to alter genetic material, not only copying genes, but in some cases, making completely new proteins. ...
... much broader, encompassing a wide range of procedures designed to alter genetic material, not only copying genes, but in some cases, making completely new proteins. ...
DNA RNA Protein Hwk KEY
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
... GTP (like ATP) Provides energy to charge tRNA's, catalyze peptide bonding, and move ribosomes… mRNA Its sequence of codons determines order of a.a.'s in protein ribosome Holds mRNA; takes in tRNA-a.a.'s; rbs enzymes make peptide bonds between a.a.'s tRNA Adapter molecules that carry a.a.'s to the rb ...
E1-3 NotesProtein Synth
... 1. DNA stores and transmits genetic information 2. DNA tells cells which proteins to make 3. DNA tells cells when to make proteins 4. Proteins form structural units of cells 5. Proteins control chemical reactions in cells B. DNA Structure 1. Made of repeating subunits called nucleotides 2. Each DNA ...
... 1. DNA stores and transmits genetic information 2. DNA tells cells which proteins to make 3. DNA tells cells when to make proteins 4. Proteins form structural units of cells 5. Proteins control chemical reactions in cells B. DNA Structure 1. Made of repeating subunits called nucleotides 2. Each DNA ...
CELL CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS 1. - Queensland Science Teachers
... 1. (a) Define the term “autotrophic”. (b) What types of organisms are autotrophic? 2. Differentiate between several types of heterotrophic nutrition, and give an example of each. 3. Distinguish between an element and a compound. 4. What is the exact meaning of each of the following terms: (a) atom ( ...
... 1. (a) Define the term “autotrophic”. (b) What types of organisms are autotrophic? 2. Differentiate between several types of heterotrophic nutrition, and give an example of each. 3. Distinguish between an element and a compound. 4. What is the exact meaning of each of the following terms: (a) atom ( ...
RNA
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – formed during transcription of DNA in the nucleus and is the template for protein synthesis at the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – carries specific amino acids to the ribosomes for translation of the genetic code • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – binds to proteins to form ribosomes ...
Chemical Compounds Overview
... i. Saturated- All carbon bonds are single bonds ii. Unsaturated- Carbon has one or more double bonds with another atom. 3. Proteins a. Functions vary; construction (structural proteins), cell function (functional proteins), etc. b. Monomers- amino acid c. Polymers- polypeptide d. Example: Enzymes- b ...
... i. Saturated- All carbon bonds are single bonds ii. Unsaturated- Carbon has one or more double bonds with another atom. 3. Proteins a. Functions vary; construction (structural proteins), cell function (functional proteins), etc. b. Monomers- amino acid c. Polymers- polypeptide d. Example: Enzymes- b ...
Modern Genetics Outline
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
... (join) together in a certain way known as _________ pairing. __________ (A) and _________ (T) bond together. __________ (G) and _________ (C) bond together. No other combinations are __________. DNA Replication During reproduction, _____ makes exact _______ of itself (__________). The proc ...
Genetics
... This helix is referred to as chromatin during interphase of the cell cyce & as chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. In the double helix, complemetary strands match-up in a specific way. Think of it as a latter that got sawed down the middle. When you put it together again, each step conne ...
... This helix is referred to as chromatin during interphase of the cell cyce & as chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. In the double helix, complemetary strands match-up in a specific way. Think of it as a latter that got sawed down the middle. When you put it together again, each step conne ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
... 9. Messenger RNA: carries hereditary information from DNA and delivers it to the site of translation 10. Transfer RNA: acts as an interpreter molecule, translating mRNA sequences into amino acid sequences 11. Ribosomal RNA: help build proteins; they function at the sites of translation 12. Codons: t ...
Unit 9 Completed Vocabulary - WAHS
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
... transformation – process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria. bacteriophage – a virus that infects bacteria. nucleotide – monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. base pairing – principl ...
259071_DNAStructureStudyGuide
... to the back of this sheet. You can find all of the answers by clicking on the link labeled “DNA – Structure basics” 1. Write a simplified version of the idea that is known as “The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology”. (What I’m looking for here is the three word ...
... to the back of this sheet. You can find all of the answers by clicking on the link labeled “DNA – Structure basics” 1. Write a simplified version of the idea that is known as “The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology”. (What I’m looking for here is the three word ...
Genetics - Liberty Public Schools
... • Allele- an alternative form of a gene at a specific locus. • Eukaryotes have pairs of identical chromosomes- diploid. May have two alleles of a gene. • Prokaryotes are not diploid. ...
... • Allele- an alternative form of a gene at a specific locus. • Eukaryotes have pairs of identical chromosomes- diploid. May have two alleles of a gene. • Prokaryotes are not diploid. ...
Lab 1 Introduction to nucleic acids Structural Properties
... INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEIC ACIDS • In biological systems, they serve as information-carrying molecules. • As DNA and RNA are the major molecules of molecular biology, understanding their structure is critical to understand the mechanisms of gene replication and protein synthesis. • What are DNA and RN ...
... INTRODUCTION TO NUCLEIC ACIDS • In biological systems, they serve as information-carrying molecules. • As DNA and RNA are the major molecules of molecular biology, understanding their structure is critical to understand the mechanisms of gene replication and protein synthesis. • What are DNA and RN ...
1: Making new DNA 2: Making RNA from DNA 3: Making Protein
... 3: Making Protein from RNA a) How many DNA or RNA base pairs code for each amino acid? b) Write an example of DNA RNA Amino Acid c) Suppose there was a change in the base sequence in DNA. What would happen to the RNA or Protein? ...
... 3: Making Protein from RNA a) How many DNA or RNA base pairs code for each amino acid? b) Write an example of DNA RNA Amino Acid c) Suppose there was a change in the base sequence in DNA. What would happen to the RNA or Protein? ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis Notes Organizer
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
... 2. RNA, like DNA, is a nucleic acid made of nucleotides. What are the four differences between DNA and RNA? a. ...
Reading Study Guide B
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
Protein Synthesis - Manhasset Public Schools
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
... Protein Synthesis Involves two processes: 1. Transcription: the copying of the genetic message (DNA) into a molecule of mRNA 2. Translation: mRNA is used to assemble an amino acid sequence into a polypeptide ...
DNA Notes Day 2 PowerPoint
... 1. DNA helicase unzips the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds holding the bases together 2. The two strands unwind creating a replication fork. 3. Each strand serves as a template so the correct pair can come in and bind to the strands 4. DNA polymerase joins the nucleotides together and proofreads ...
... 1. DNA helicase unzips the DNA by breaking the hydrogen bonds holding the bases together 2. The two strands unwind creating a replication fork. 3. Each strand serves as a template so the correct pair can come in and bind to the strands 4. DNA polymerase joins the nucleotides together and proofreads ...
M220 Lecture 13 DNA is replicated by a process known as semi
... codons in the form of mRNA in the transcription process. The 64 different code words only code for 20 different amino acids. Since more than one 3 letter code word codes for the same amino acid, the code is said to be redundant (degenerate). For example, you will notice that there are 6 different co ...
... codons in the form of mRNA in the transcription process. The 64 different code words only code for 20 different amino acids. Since more than one 3 letter code word codes for the same amino acid, the code is said to be redundant (degenerate). For example, you will notice that there are 6 different co ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... 45 a 2-subunit, subcellular, globular structure composed of rRNA and proteins on which proteins are translated 46 nucleic acid composed of ribose, phosphate groups, and nucleotide bases 47 enzyme which makes the RNA copy of DNA 48 type of replication in which each new DNA molecule has 1 of the 2 ori ...
... 45 a 2-subunit, subcellular, globular structure composed of rRNA and proteins on which proteins are translated 46 nucleic acid composed of ribose, phosphate groups, and nucleotide bases 47 enzyme which makes the RNA copy of DNA 48 type of replication in which each new DNA molecule has 1 of the 2 ori ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.