Name:
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
... 11. What is a codon and what does each one stand for on an mRNA strand? 12. What amino acid does the CAG codon code for? 13. What is the first codon in all mRNA sequences? 14. What transports the amino acids to the ribosome during translation? ...
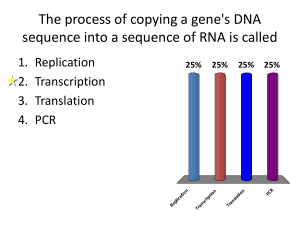
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... A DNA strand with the sequence AACGTAACG is transcribed. What is the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized? 1. AACGTAACG ...
... A DNA strand with the sequence AACGTAACG is transcribed. What is the sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized? 1. AACGTAACG ...
All Living things pass on their genetic heritage by common processes.
... George Beadle and Edward Tatum (late 40’s to early 50’s) used X-rays to induce mutations in Neurospora crassa, which were unable to synthesize amino acid and vitamins. They traced the defect to the enzymes involved in their synthesis. 2 Hershey-Chase (1952) experiment extended Avery, Macleod and McC ...
... George Beadle and Edward Tatum (late 40’s to early 50’s) used X-rays to induce mutations in Neurospora crassa, which were unable to synthesize amino acid and vitamins. They traced the defect to the enzymes involved in their synthesis. 2 Hershey-Chase (1952) experiment extended Avery, Macleod and McC ...
SB2a Build DNA using the Nucleotides Then Print
... 2. Arrange the DNA nucleotides so that it is unzipped or pulled apart without the DNA helicase molecules (scissors) present. 3. Leave enough room in between the top and bottom DNA strand to place the RNA nucleotides. 4. Copy and paste the RNA nucleotides next to the bottom DNA strand on this slide t ...
... 2. Arrange the DNA nucleotides so that it is unzipped or pulled apart without the DNA helicase molecules (scissors) present. 3. Leave enough room in between the top and bottom DNA strand to place the RNA nucleotides. 4. Copy and paste the RNA nucleotides next to the bottom DNA strand on this slide t ...
The DNA connection - Somerset Academy North Las Vegas
... DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, G guanine, C cytosine) ...
... DNA has four different nitrogen basis (A adenine, T thymine, G guanine, C cytosine) ...
Topics covered on this exam include: cellular respiration
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. How do they differ structurally? How are their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? W ...
... 1. Compare and contrast DNA with RNA. How do they differ structurally? How are their functions different? 2. What are the components of a single nucleotide? Dow we find nucleotides in both RNA and DNA? 3. Be able to go between DNA DNA, DNA RNA and RNA RNA. 4. What are the three types of RNA? W ...
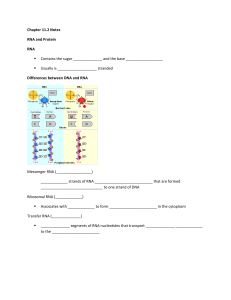
DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis 1. Define: Nucleotide
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
... Nucleotide – Nucleotides are small, organic molecules made up of a pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group and one nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil). Nucleotides are used as the "building blocks" of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They are also used to fo ...
I. DNA A. WHAT IS IT?
... • DNA has the “message” that is replicated for all new cells. • The message is sent out into the cells by transcription. • Proteins are assembled by translating the message. ...
... • DNA has the “message” that is replicated for all new cells. • The message is sent out into the cells by transcription. • Proteins are assembled by translating the message. ...
common to all organisms
... 1. Fill out the COMPLIMENTARY DNA strands on each strip! 2. Cut all the pictures and gene segments apart from one another. 3. The human DNA strand is: ATG-TAC-AAC-GGA-CAG. Glue this one at the top of your notebook page! 4. Put the images in order from most to least related to human in your ...
... 1. Fill out the COMPLIMENTARY DNA strands on each strip! 2. Cut all the pictures and gene segments apart from one another. 3. The human DNA strand is: ATG-TAC-AAC-GGA-CAG. Glue this one at the top of your notebook page! 4. Put the images in order from most to least related to human in your ...
DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation STUDY GUIDE
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
... What are the main functions of DNA polymerase? The main function of tRNA is to: What is the term for a three-nucleotide sequence that codes for an amino acid? How many amino acids are used to make up the all of the proteins in the human body? A tRNA that carries the amino acid methionine pairs with ...
Last Name - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Test Prep Sections: These questions were taken from New York and Texas State Tests. Can you compete with the brightest around the nation? ...
... Test Prep Sections: These questions were taken from New York and Texas State Tests. Can you compete with the brightest around the nation? ...
Review for Molecular Genetics Quest
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
... 5. Where does this happen? Make sure to label location and type of cell. There are two answers for this!! ...
05E-NucleicAcids
... • The nitrogen bases, rings of carbon and nitrogen, come in two types: purines and pyrimidines. • Pyrimidines have a single six-membered ring. • The three different pyrimidines, cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) differ in atoms attached to the ring. • Purine have a six-membered ring joined ...
... • The nitrogen bases, rings of carbon and nitrogen, come in two types: purines and pyrimidines. • Pyrimidines have a single six-membered ring. • The three different pyrimidines, cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) differ in atoms attached to the ring. • Purine have a six-membered ring joined ...
Genetics
... In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic acid. How is DNA organized to serve as the genetic material? DNA, although single-stranded in a few viruses, is usually a double-stranded molecule ...
... In eukaryotes & prokaryotes it is DNA, in viruses it can be either DNA or RNA. What do DNA & RNA stand for? DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid / RNA: ribonucleic acid. How is DNA organized to serve as the genetic material? DNA, although single-stranded in a few viruses, is usually a double-stranded molecule ...
(DNA and RNA).
... ALLELE: Any one of the possible variations of a specific gene. For example, of the gene that determines hair color, there’s one allele for brown hair, another allele for black hair, etc. CHROMOSOME: A threadlike body composed of genes, located in the nucleus of a cell. Human cells contain 46 chromos ...
... ALLELE: Any one of the possible variations of a specific gene. For example, of the gene that determines hair color, there’s one allele for brown hair, another allele for black hair, etc. CHROMOSOME: A threadlike body composed of genes, located in the nucleus of a cell. Human cells contain 46 chromos ...
(1) End labelling
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
... Primer extension • * This labelling technique uses random oligonucleotides (usually hexadeoxyribonucleotide moleculessequences of six deoxynucleotides) to primer synthesis of a DNA strand by DNA polymerase. • * The DNA to be labelled is denaturated by heating, and the oligonucleotide primer annealed ...
Introduction to Psychology
... strands of DNA spiral about one other. The double helix looks something like an immensely long ladder twisted into a helix, or coil. The sides of the "ladder" are formed by a backbone of sugar and phosphate molecules, and the "rungs" consist of nucleotide bases joined weakly in the middle by the h ...
... strands of DNA spiral about one other. The double helix looks something like an immensely long ladder twisted into a helix, or coil. The sides of the "ladder" are formed by a backbone of sugar and phosphate molecules, and the "rungs" consist of nucleotide bases joined weakly in the middle by the h ...
Greatest Discoveries with Bill Nye: Genetics
... 15. Watson & Crick used the X-Ray of a DNA molecule taken by _________________ __________________. 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? ...
... 15. Watson & Crick used the X-Ray of a DNA molecule taken by _________________ __________________. 16. What did Rosalyn Franklin die of? ...
MCDB 1030 – Spring 2003
... A nucleotide is one building block of a polynucleotide that is polymer form. DNA strands are polynucleotides, constructed from DNA nucleotides (monomers). b) What are three important structural differences between DNA and RNA? The ribose sugar in ribonucleotides (the building blocks for RNA) has an ...
... A nucleotide is one building block of a polynucleotide that is polymer form. DNA strands are polynucleotides, constructed from DNA nucleotides (monomers). b) What are three important structural differences between DNA and RNA? The ribose sugar in ribonucleotides (the building blocks for RNA) has an ...
verbal quiz genetics 2017
... 20. DNA can’t leave the nucleus so / mRNA copies the genetic code and brings it to ribosome 21. 3 ways RNA is different then DNA / 1. RNA is single stranded, 2. The sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose, 3. U instead of T 22. Every 3 base sequence in of mRNA is called a codon and codes for / One am ...
... 20. DNA can’t leave the nucleus so / mRNA copies the genetic code and brings it to ribosome 21. 3 ways RNA is different then DNA / 1. RNA is single stranded, 2. The sugar is ribose instead of deoxyribose, 3. U instead of T 22. Every 3 base sequence in of mRNA is called a codon and codes for / One am ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.