Worksheet 1 - Ch. 2, 3 - Iowa State University
... b. Peptide bonds form between __________ and ___________ functional groups. 3. This is an image of an aquaporin protein; it lets water into the cell through a tunnel. a. What structure does it have? b. Determine whether polar and nonpolar amino acids would be located on the inside or outer layer of ...
... b. Peptide bonds form between __________ and ___________ functional groups. 3. This is an image of an aquaporin protein; it lets water into the cell through a tunnel. a. What structure does it have? b. Determine whether polar and nonpolar amino acids would be located on the inside or outer layer of ...
Chapter 5 - glenbrook s hs
... • Lipids with 4 fused carbon rings • Ex: cholesterol: cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
... • Lipids with 4 fused carbon rings • Ex: cholesterol: cell membranes; precursor for other steroids (sex hormones); atherosclerosis ...
The Chemistry of Life
... that refers to compounds containing carbon. All living things are organic. Organic compounds can be broken down within cells for energy or linked together to form long chains necessary for life. ...
... that refers to compounds containing carbon. All living things are organic. Organic compounds can be broken down within cells for energy or linked together to form long chains necessary for life. ...
Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]
... One molecule of -glucose joined to one molecule of fructose ...
... One molecule of -glucose joined to one molecule of fructose ...
biochem notes
... • Polymers- made of repeating monomers • Macromolecules- made up of large polymers ...
... • Polymers- made of repeating monomers • Macromolecules- made up of large polymers ...
Macromolecules Worksheet #2
... Short Answer questions 1. What is the relationship between glucose, fructose, and galactose? They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated ...
... Short Answer questions 1. What is the relationship between glucose, fructose, and galactose? They are isomers of one another – They have the same chemical formula but differ in how those elements are bonded to each other within the molecule. 2. What are the structural differences between a saturated ...
Chem for Bio 9, part 2- Biological Macromolecules
... Atoms in bonds are free to rotate around the bonds ...
... Atoms in bonds are free to rotate around the bonds ...
Unit 1: Biology Review
... - There are 4 types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. - Carbohydrates function primarily for short term and intermediate energy use. However carbohydrates can also provide structure. - There are 3 classes of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysac ...
... - There are 4 types of biomolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. - Carbohydrates function primarily for short term and intermediate energy use. However carbohydrates can also provide structure. - There are 3 classes of carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysac ...
The Biochemistry of Life
... in the hundreds of thousands • Both are polymers (hence "polysaccharides"); that is, each is built from repeating units, monomers, much as a chain is built from its links ...
... in the hundreds of thousands • Both are polymers (hence "polysaccharides"); that is, each is built from repeating units, monomers, much as a chain is built from its links ...
Chap 2-3 Notes - WordPress.com
... Chap 2 Section 3 Carbon Compounds: The Chemistry of Carbon Organic Chemistry : the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Macromolecules: formed by a process known as polymerization. Monomers: small units that can join together with other small units to form Polymers larg ...
... Chap 2 Section 3 Carbon Compounds: The Chemistry of Carbon Organic Chemistry : the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Macromolecules: formed by a process known as polymerization. Monomers: small units that can join together with other small units to form Polymers larg ...
Chapter-4 part-2 Energy Metabolism
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
... • “Isozymes” may look different but catalyze the same reaction ...
answers to study guide
... carbs have a CHO ratio of 1:2:1, can tell molecular structure by numerous –OH lipids have a CH ratio of 1:2, and only 2 oxygens, molecular structure has numerous C-H bonds protein molecular structure – look for amino and carboxyl functional groups monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide number ...
... carbs have a CHO ratio of 1:2:1, can tell molecular structure by numerous –OH lipids have a CH ratio of 1:2, and only 2 oxygens, molecular structure has numerous C-H bonds protein molecular structure – look for amino and carboxyl functional groups monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide number ...
Chemistry of Life
... Chemical mechanism by which cells make and break polymers is the same even though monomers may be different for different macromolecules Enzymes: special class of proteins which catalyze (speed up) reactions between specific substances ...
... Chemical mechanism by which cells make and break polymers is the same even though monomers may be different for different macromolecules Enzymes: special class of proteins which catalyze (speed up) reactions between specific substances ...
Exam 1 Review KEY
... 10.) A molecule that is a mirror image of another, having a key functional group oriented in a different direction, is called a ___stereoisomer________ of the other. 11.) What forms do humans and plants store glucose as? Humans – glycogen Plants – starch 12.) Sketch the structure of the following ty ...
... 10.) A molecule that is a mirror image of another, having a key functional group oriented in a different direction, is called a ___stereoisomer________ of the other. 11.) What forms do humans and plants store glucose as? Humans – glycogen Plants – starch 12.) Sketch the structure of the following ty ...
Chapter 5: Biological Molecules Molecules of Life • All life made up
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
... Side Chain (R group) – accounts for different properties Structure & Function o Functional protein consists of 1 or more polypeptides coiled, twisted, & folded into a unique shape o Amino acid order determines protein’s 3-D structure, which determines function 4 Levels of Protein Folding o Pri ...
Cell Metabolism Review
... completely oxidized to CO2) by Cellular Respiration. In cellular respiration, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is completely oxidized to CO2 by going through two more steps: Acetyl Coenzyme A (AcCoA) formation (also known as oxidative decarboxylation), then the Citric Acid Cycle (also known ...
... completely oxidized to CO2) by Cellular Respiration. In cellular respiration, pyruvate enters the mitochondria where it is completely oxidized to CO2 by going through two more steps: Acetyl Coenzyme A (AcCoA) formation (also known as oxidative decarboxylation), then the Citric Acid Cycle (also known ...
Notes Chemical Basis for Life BIO.A.2
... • Different types of fatty acids: – Saturated - all single, covalent bonds in between carbons in chain – Unsaturated - one double bond between carbons in chain – Polyunsaturated - many double bonds between carbons in chain ...
... • Different types of fatty acids: – Saturated - all single, covalent bonds in between carbons in chain – Unsaturated - one double bond between carbons in chain – Polyunsaturated - many double bonds between carbons in chain ...
Biochemistry - ScienceGeek.net
... When 2 amino acids bond together, water is released as the carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the amine end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond, as illustrated at the left. Because water is lost, the process is called: Condensation synthesis, or… ...
... When 2 amino acids bond together, water is released as the carboxyl end of one amino acid bonds to the amine end of the adjacent one forming a peptide bond, as illustrated at the left. Because water is lost, the process is called: Condensation synthesis, or… ...
Examples
... energy and structures for cell membranes – include fats(solids from animals), oils(liquids from plants), and waxes – the ratio of hydrogens to oxygens is greater than 2 : 1 and varies from one lipid to another – made from one glycerol molecule and three fatty acids by ...
... energy and structures for cell membranes – include fats(solids from animals), oils(liquids from plants), and waxes – the ratio of hydrogens to oxygens is greater than 2 : 1 and varies from one lipid to another – made from one glycerol molecule and three fatty acids by ...
4 Types Biological Molecules in plants and animals
... being eaten. Glucose is smallest sugar and is dissolved directly into the bloodstream. Starches are long chains of simple sugars joined together to make natural polymers. ...
... being eaten. Glucose is smallest sugar and is dissolved directly into the bloodstream. Starches are long chains of simple sugars joined together to make natural polymers. ...
Chapter 11
... dissolve in water. Cholesterol is a fat that is needed by cells, but high cholesterol may lead to heart disease. Nucleic Acids – Biological molecules such as DNA that have the ability to store the genetic code. DNA is a huge molecule with millions of individual atoms. P224: Carbohydrates Plant cells ...
... dissolve in water. Cholesterol is a fat that is needed by cells, but high cholesterol may lead to heart disease. Nucleic Acids – Biological molecules such as DNA that have the ability to store the genetic code. DNA is a huge molecule with millions of individual atoms. P224: Carbohydrates Plant cells ...
Chapter 2 ppt
... Acidosis:Blood pH below 7.35 Alkalosis: Blood pH above 7.45 A person usually cannot survive if the pH drops to 6.9 or rises to 7.8 for more than a few hours. ...
... Acidosis:Blood pH below 7.35 Alkalosis: Blood pH above 7.45 A person usually cannot survive if the pH drops to 6.9 or rises to 7.8 for more than a few hours. ...
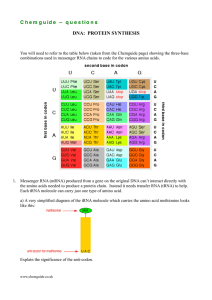
C h e m g u id e –... DNA: PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
... C h e m g u id e – q u e s t i o n s b) Give the two possible anti-codons for the amino acid tyrosine (Tyr). c) Give the anti-codon for the amino acid tryptophan (Trp). d) Protein synthesis is controlled by a ribosome which comes in two parts – a smaller part and a bigger part. The smaller part is ...
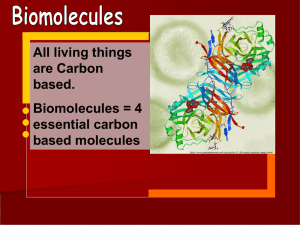
Biomolecules
... All living things are Carbon based. Biomolecules = 4 essential carbon based molecules http://www.genomenewsnetwork.org/articles/11_00/crystal_structure_image.shtml ...
... All living things are Carbon based. Biomolecules = 4 essential carbon based molecules http://www.genomenewsnetwork.org/articles/11_00/crystal_structure_image.shtml ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.


![Biochemistry_and_Digestion_2010[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008289894_1-a2dae968af20e40d29d6bcd9c3fab727-300x300.png)